MCQ and Extra Questions - Exploring Forces | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1:
Which of the following best defines a force in scientific terms?
Option A: The ability to see an object clearly
Option B: A push or pull resulting from interaction between objects
Option C: The weight of an object
Option D: The speed of a moving object
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Force is defined as a push or pull on an object arising due to interaction with another object.
- This interaction can cause changes in speed, direction, or shape.
- Why others are incorrect: A is unrelated to mechanics; C is a specific type of force due to gravity; D is a possible effect but not the definition.
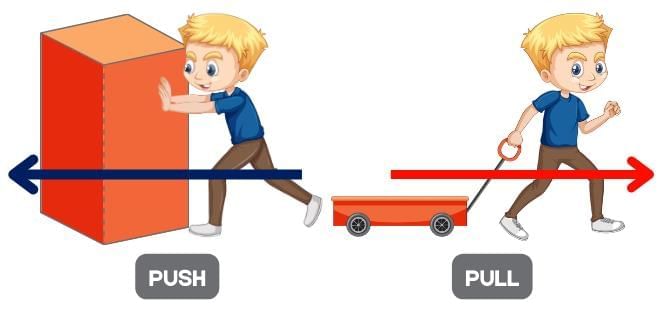
Question 2:
When you push a wall and it doesn’t move, which of the following is true?
Option A: No force is applied
Option B: A force is applied but no motion is produced
Option C: The wall exerts no force back
Option D: The wall becomes weightless
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Even if there is no visible motion, a force exists — you are pushing against the wall and the wall pushes back with equal magnitude (Newton’s third law).
- No movement can occur when forces are balanced.
- Why others are incorrect: A is false — force exists without visible displacement. C ignores reaction forces. D is irrelevant to the situation.

Question 3:
Which unit is used internationally (SI) to measure force?
Option A: Joule
Option B: Kilogram
Option C: Newton
Option D: Watt
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- The SI unit of force is the newton (N), named after Sir Isaac Newton.
- 1 N is the force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass by 1 m/s².
- Why others are incorrect: Joule is for energy, kilogram for mass, and watt for power.
Question 4:
Which force opposes the motion of objects and always acts in the opposite direction of movement?
Option A: Magnetic force
Option B: Electrostatic force
Option C: Gravitational force
Option D: Frictional force
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
- Friction is a contact force resisting motion between surfaces in contact, acting opposite to movement.
- It arises due to surface irregularities and interlocking at a microscopic level.
- Why others are incorrect: A and B are non-contact forces acting by attraction/repulsion, C pulls objects toward Earth but doesn’t oppose horizontal sliding directly.
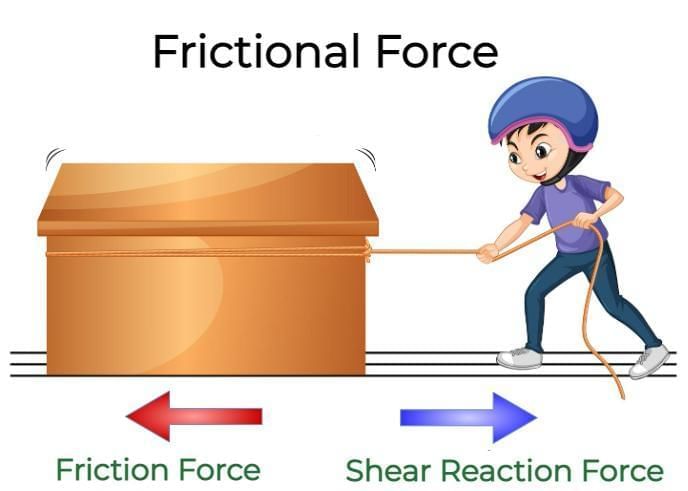
Question 5:
Which of these is a non-contact force?
Option A: Muscular force
Option B: Frictional force
Option C: Gravitational force
Option D: Spring force
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Gravitational force acts from a distance without physical contact — pulling all masses toward each other (notably toward Earth).
- Why others are incorrect: A, B, and D require direct/physical contact to act.
Question 6:
When two like magnetic poles are brought near each other, they:
Option A: Attract each other
Option B: Repel each other
Option C: Lose their magnetism
Option D: Neither attract nor repel
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Like poles (North–North or South–South) repel; unlike poles attract — a property of magnetic force.
- Why others are incorrect: A reverses correct rule; C is false unless magnet overheated/damaged; D ignores clear evidence of magnetic interaction.
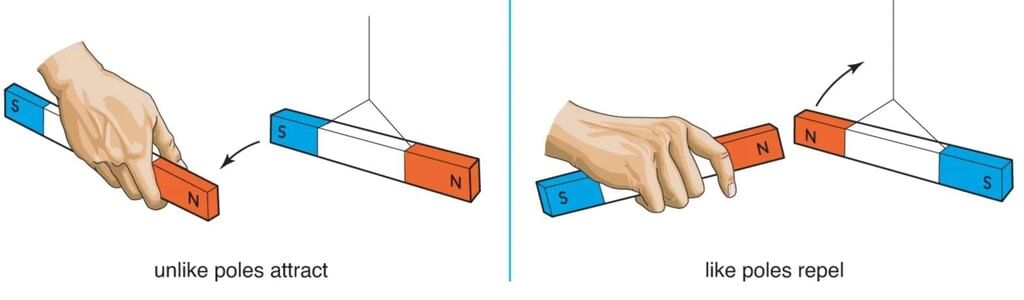
Question 7:
What type of charges repel each other in electrostatic interactions?
Option A: Positive and positive
Option B: Positive and negative
Option C: Neutral and positive
Option D: Neutral and neutral
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Like charges repel, unlike charges attract; so positive–positive or negative–negative both repel.
- Why others are incorrect: B are unlike charges, so they attract; C and D have at least one neutral object and do not repel in electrostatics.
Question 8:
An object has a mass of 10 kg on Earth. Which statement about its weight is correct?
Option A: It weighs the same everywhere in the universe
Option B: It will weigh less on the Moon due to lower gravity
Option C: Its mass will change on the Moon
Option D: Its weight becomes zero on Earth
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Weight depends on gravitational force; on the Moon (about 1/6th Earth’s gravity), the same mass has less weight.
- Mass remains constant regardless of location.
- Why others are incorrect: A ignores variable gravity; C confuses weight with mass; D is impossible unless in freefall/orbit (apparent weightlessness).
Question 9:
What is the upward force exerted by a fluid on an immersed object called?
Option A: Thrust
Option B: Pressure
Option C: Upthrust or buoyant force
Option D: Surface tension
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Buoyant force is the upward push a liquid (or gas) exerts on objects; if equal to object’s weight, it floats.
- Why others are incorrect: A is general push; B is force per unit area; D relates to liquid surfaces resisting deformation.
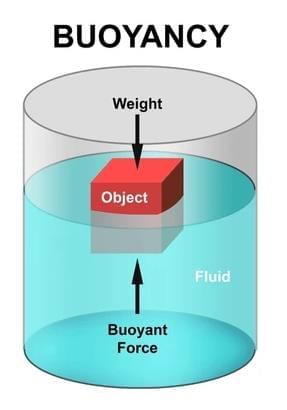
Question 10:
If two surfaces in contact are made rougher, the friction between them generally:
Option A: Decreases
Option B: Increases
Option C: Becomes zero
Option D: Changes direction
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Rougher surfaces have more microscopic interlocking points, increasing resistance to motion and thus increasing friction.
- Why others are incorrect: A is opposite of reality; C requires perfectly smooth & no contact friction; D friction already opposes relative motion.
Question 11:
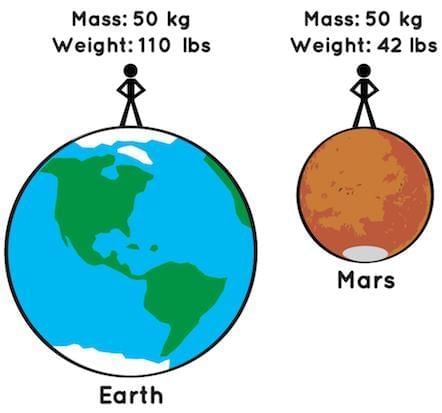
Which statement correctly distinguishes mass from weight?
Option A: Mass changes with location; weight does not
Option B: Weight is the amount of matter, mass is the pull of gravity
Option C: Mass is constant; weight varies with gravity
Option D: Mass and weight are identical physical quantities
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Mass measures quantity of matter in kg/g and is independent of location; weight is gravitational force (in N) on that mass and changes with gravity.
- Why others are incorrect: A reverses truth; B swaps definitions; D is inaccurate — they’re related but not the same.
Short Answer Questions
Q12. Why do ships made of steel float on water even though steel is denser than water?
Answer:
- Ships are designed with a hollow and broad structure that allows them to displace a large volume of water.
- According to Archimedes’ principle, the buoyant force acting on an object is equal to the weight of the water displaced by it.
- Even though steel itself is dense, the overall average density of the ship (including the hollow space filled with air) becomes less than that of water.
- As a result, the buoyant force balances or exceeds the ship’s weight, allowing it to float.
Q13. Why do small paper pieces get attracted to a balloon rubbed on wool?
Answer:
- When a balloon is rubbed on wool, friction transfers electrons, giving the balloon a negative charge.
- This charged balloon produces an electrostatic force.
- Neutral objects like small paper pieces experience a temporary separation of charges (induced charges). The side of the paper closer to the balloon becomes slightly positive, so it gets attracted.
- Thus, the papers jump towards the balloon due to electrostatic attraction, not magnetism or heat.
Q14. Which factor does not affect the buoyant force on an object in a liquid?
Answer:
The buoyant force on an object is determined by Archimedes’ principle, which states it depends on:
Density of the liquid – denser liquids exert a greater upward force.
Volume of liquid displaced – larger displacement produces greater buoyant force.
Acceleration due to gravity (g) – stronger gravity increases buoyant force.
The shape of the container has no effect because buoyancy depends only on the interaction between the object and the liquid, not the container holding it.
Q15. Why is it difficult to walk on ice compared to a rough road?
Answer:
- Walking requires friction between the feet (or footwear) and the ground for grip and forward movement.
- On ice, the surface is smooth and has very low friction, so the feet cannot get enough grip.
- This lack of traction causes slipping, making it hard to walk.
- On rough roads, friction is higher, which provides better grip and stability.
- Therefore, it is harder to walk on ice due to reduced friction, not because of gravity or lack of friction on rough roads.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ and Extra Questions - Exploring Forces - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the different types of forces discussed in the study of forces in Class 8? |  |
| 2. How does friction affect motion in everyday life? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between mass and weight? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of balanced and unbalanced forces? |  |
| 5. What role did Isaac Newton play in the understanding of forces? |  |





















