MCQ and Extra Questions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1:
Which statement best explains why broad backpack straps feel more comfortable than narrow straps when carrying the same load?
Option A: Broad straps reduce the force of gravity
Option B: Broad straps increase area and reduce pressure on shoulders
Option C: Narrow straps increase mass of the bag
Option D: Broad straps increase friction with clothes
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Pressure equals force per unit area; the same weight spread over a larger area creates less pressure on the shoulders, improving comfort.
- This is why cloth pads under head loads or broad bucket handles also reduce discomfort.
- Why others are incorrect: Gravity and mass do not change (A, C), and friction with clothes (D) is not the reason for reduced pressure.
Question 2:
Which is the correct SI unit of pressure and its equivalent name?
Option A: N/m — newton
Option B: N/m² — pascal
Option C: kg/m² — joule
Option D: N·m — watt
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
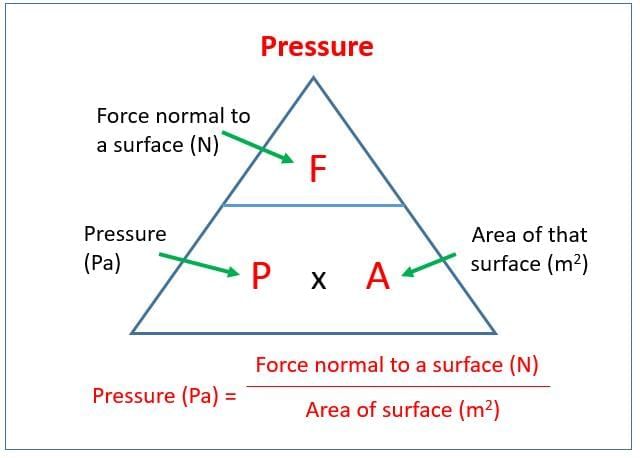
- Pressure is force per unit area; its SI unit is N/m², called the pascal (Pa).
- Millibar (mb) and hectopascal (hPa) are common for atmospheric pressure, both equal to 100Pa.
- Why others are incorrect: N/m (A) is not pressure; kg/m² (C) is not an SI unit for pressure; N·m (D) is work/energy (joule).
Question 3:
If the height of a water column increases in a vertical pipe, what happens to the pressure at the bottom?
Option A: Decreases because area stays constant
Option B: Increases because pressure depends on column height
Option C: Remains the same because volume is unchanged
Option D: Becomes zero because water is incompressible
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Liquid pressure at a depth depends primarily on the height of the liquid column above that point; greater height means greater pressure.
- This explains why overhead tanks at higher levels give stronger tap flow below.
- Why others are incorrect: Area or volume (A, C) are not the determining factors here; pressure never becomes zero in a filled column (D).
Question 4:
Liquids in a container exert pressure:
Option A: Only at the bottom
Option B: Only on the sides
Option C: Only upward
Option D: In all directions on the container walls and bottom
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
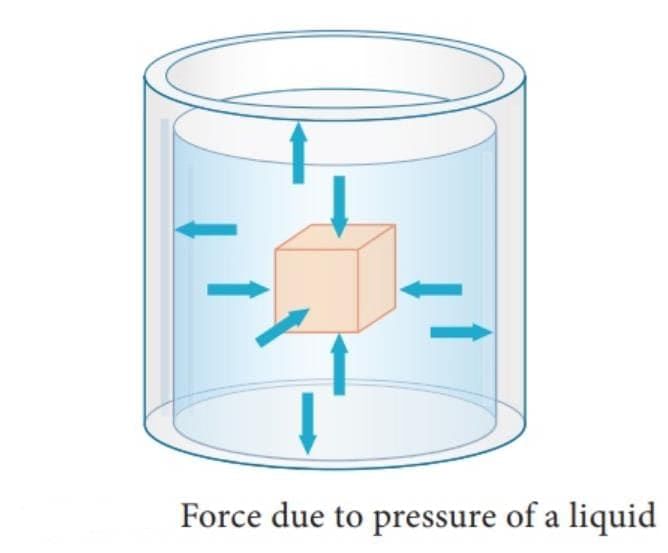
- Liquid pressure acts in all directions—downward, sideways, and even upward—on container surfaces at a given depth.
- Equal-height side holes spurt water with similar streams, demonstrating side pressure.
- Why others are incorrect: A, B, C are incomplete and ignore directional nature of fluid pressure.
Question 5:
Why are the bases of dams built broader than the top?
Option A: To store more water above
Option B: Because water pressure is least at the bottom
Option C: To withstand higher horizontal water pressure at greater depths
Option D: To reduce the weight of the dam
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Water pressure increases with depth, so the base experiences the greatest lateral pressure and must be thicker to resist it.
- Structural stability also benefits from a wider base.
- Why others are incorrect: A is unrelated; B is false (pressure is greatest at bottom); D contradicts the need for strength.
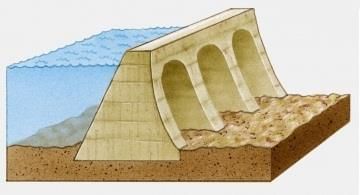 Dams build broader at base
Dams build broader at base
Question 6:
Which statement about atmospheric pressure is correct?
Option A: It is too small to have measurable effects
Option B: It acts only downward
Option C: It acts in all directions and is balanced by internal body pressure
Option D: It can crush us unless we breathe deeply
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Atmospheric pressure acts omnidirectionally; we are not crushed because internal fluids and gases exert an equal counterpressure.
- This also explains why suction cups stick when internal air is expelled, creating a pressure difference.
- Why others are incorrect: A underestimates its magnitude; B is incorrect—pressure is not only downward; D is unscientific.
Question 7:
Air flows from:
Option A: Low pressure to high pressure regions
Option B: High pressure to low pressure regions
Option C: Cold regions to hot regions regardless of pressure
Option D: Higher altitudes to lower altitudes only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
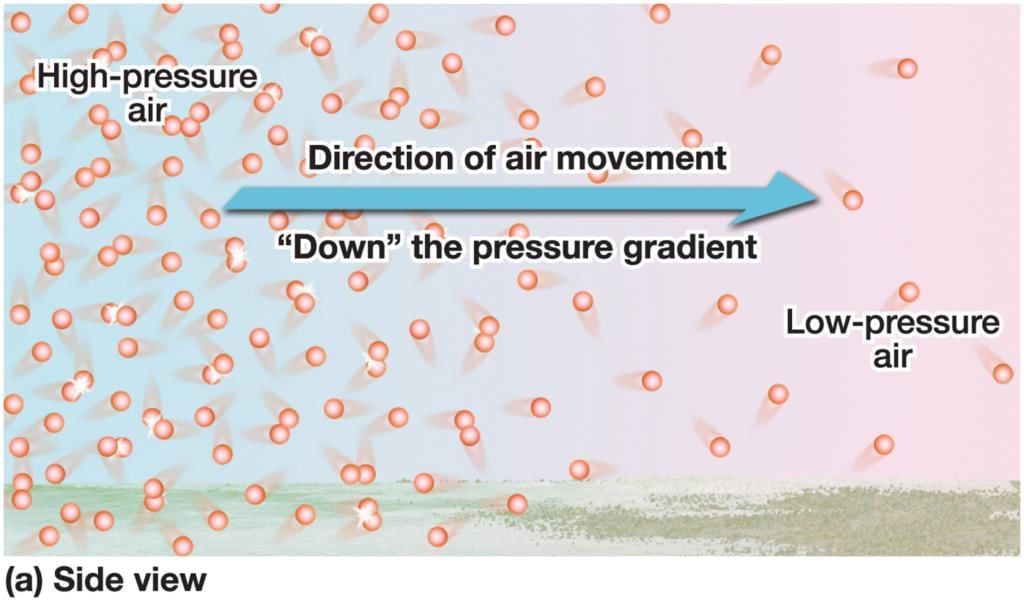
- Winds are driven by pressure gradients: air moves from high to low pressure, which explains sea breezes (day) and land breezes (night).
- Temperature differences often create these pressure differences.
- Why others are incorrect: A reverses the direction; C ignores pressure’s role; D is not a universal rule.
Question 8:
What happens to pressure in a region where wind speed becomes very high?
Option A: Pressure increases
Option B: Pressure decreases
Option C: Pressure remains constant
Option D: Wind speed and pressure are unrelated
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- High-speed winds are associated with lower pressure regions, which can create roof-lifting effects due to pressure differences.
- Blowing between two balloons makes them move closer for the same reason—reduced pressure in the fast airflow region.
- Why others are incorrect: A and C contradict observed phenomena; D ignores the fundamental wind–pressure link.
Question 9:
Why is it generally safer to keep doors and windows open during very strong windstorms?
Option A: To let rain in and wash floors
Option B: To equalize pressure inside and outside, reducing uplift on roofs
Option C: To increase indoor air pressure further
Option D: To stop wind from entering the house
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Fast winds over roofs lower outside pressure; opening passages reduces pressure differences, lowering the risk of roofs being blown off.
- This minimizes damaging uplift forces on structures.
- Why others are incorrect: A is irrelevant; C can worsen differential; D is not feasible in strong storms.
Question 10:
Which process directly supplies energy that intensifies a developing cyclone?
Option A: Freezing of seawater
Option B: Condensation of water vapor releasing latent heat
Option C: Cooling of upper atmosphere by snow
Option D: Evaporation removing heat from air permanently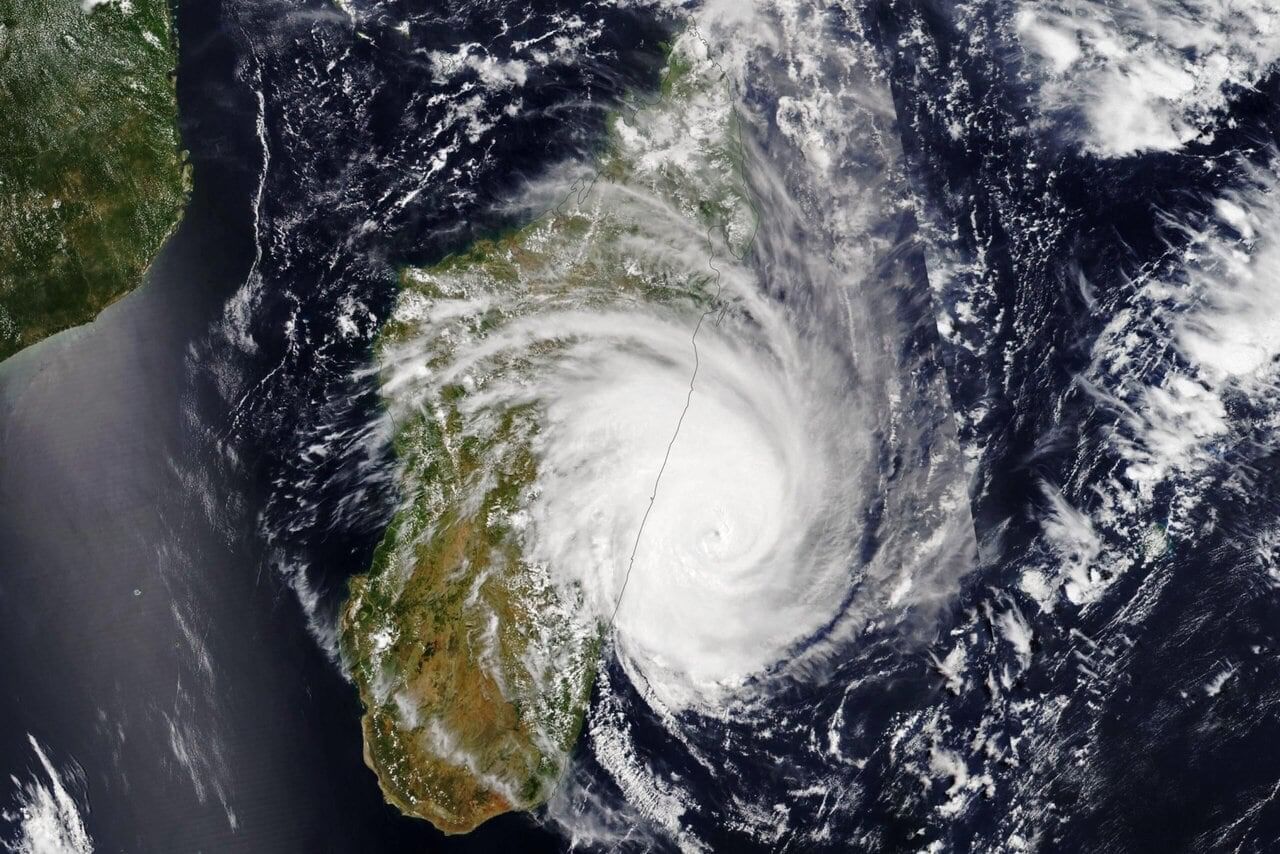
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- When moist air rises and water vapor condenses into droplets, latent heat is released, warming and accelerating the ascending air, deepening low pressure.
- This positive feedback powers cyclones over warm oceans.
- Why others are incorrect: A and C are not cyclone drivers; D removes heat locally but the key intensification comes from heat release during condensation.
Short Answer Questions
Q1. What is true about the “eye” of a mature cyclone?
Answer:
- The eye is the central region of a cyclone where the air pressure is the lowest.
- Winds inside the eye are calm, and the weather can be clear compared to the surrounding storm.
- The most destructive winds and heaviest rainfall actually occur in the eyewall, which surrounds the eye.
- As cyclones move over land, they weaken because the supply of warm, moist air is cut off.
Q2. Which sequence best describes how thunderstorms form?
Answer:
- Thunderstorms begin when warm, moist air rises rapidly.
- As it rises, the air cools and condenses, forming clouds and releasing heat.
- This process leads to the growth of towering cumulonimbus clouds with heavy rain and strong winds.
- Collisions of water droplets and ice particles inside the clouds cause charge separation, leading to lightning and thunder.
- Thus, the correct sequence is: warm moist air rises → cools and condenses → storm clouds and precipitation with winds.
Q3. Why does a suction cup (rubber sucker) stick firmly to a smooth surface?
Answer:
- When pressed against a smooth surface, most of the air under the suction cup is forced out.
- This creates a region of low pressure inside the cup.
- The higher atmospheric pressure outside then pushes the suction cup tightly against the surface.
- To remove it, one must break the seal and allow air to enter, reducing the pressure difference.
- It works due to atmospheric pressure, not magnetism or gravity.
Q4. What is the safest practice outdoors during lightning?
Answer:
- The best safety measure is to avoid open water, metal objects, and tall isolated structures.
- In an open area, crouch low with minimal contact with the ground to reduce the risk of a direct strike or ground current.
- Vehicles with metal bodies provide relative safety, and buildings can be protected with lightning conductors.
- Standing under trees or holding umbrellas with metal tips increases the risk of being struck.
Q5. What change most reliably increases water pressure at ground-level taps connected to a rooftop tank?
Answer:
- Water pressure in taps depends mainly on the vertical height (head) of water above the outlet.
- Raising the tank to a greater height increases this hydrostatic pressure, improving water flow at ground level.
- The tank’s diameter, amount of water, or color do not affect the pressure if the height remains the same.
- Therefore, the most effective solution is to place the tank at a greater height above the taps.
|
54 videos|263 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ and Extra Questions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the relationship between pressure and wind patterns? |  |
| 2. How do storms and cyclones form? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of winds and their characteristics? |  |
| 4. What are the effects of cyclones on the environment and human life? |  |
| 5. How can we prepare for storms and cyclones? |  |





















