MCQ (Solution) - The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Question 1:
In a solution of sugar in water, which terms correctly identify the roles of sugar and water?
Option A: Sugar is the solvent; water is the solute
Option B: Both are solutes
Option C: Sugar is the solute; water is the solvent
Option D: Both are solvents
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
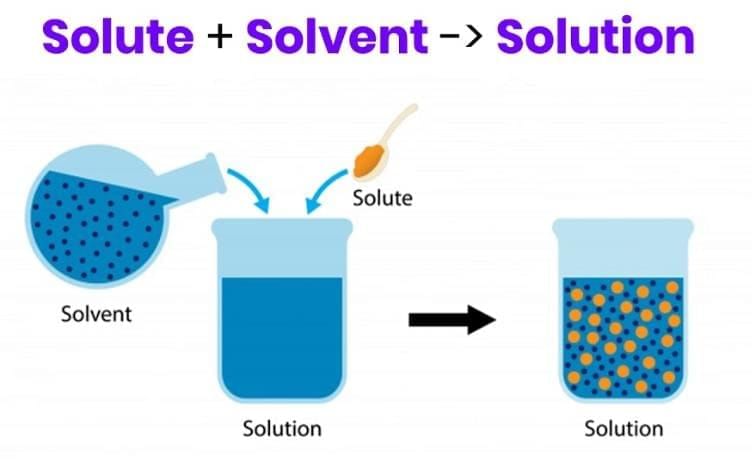
- A uniform mixture like sugar in water is a solution; the substance present in smaller amount that dissolves (sugar) is the solute, while the medium (water) is the solvent.
- Even when sugar is large in amount (as in chashni), water remains the solvent by definition in a solid–liquid solution.
- Why others are incorrect: A reverses roles; B and D misuse solution terminology.
Question 2:
Air is considered a gaseous solution because:
Option A: Nitrogen chemically binds to oxygen
Option B: Gases are evenly mixed; nitrogen is the solvent and other gases are solutes
Option C: Air contains dust
Option D: Air is a pure compound
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
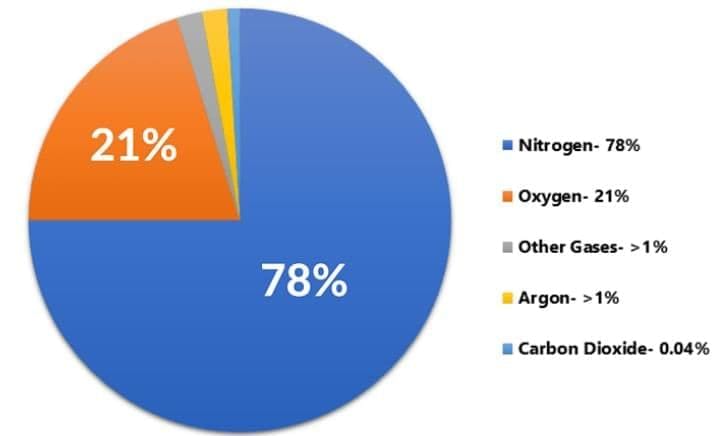
- Air is a uniform mixture of gases; the major component (nitrogen) is treated as the solvent and minor components (oxygen, argon, CO₂, etc.) as solutes.
- Why others are incorrect: A implies chemical bonding (not true here); C refers to pollutants not defining uniformity; D misclassifies air.
Question 3:
A solution in which no more solute dissolves at a given temperature is called:
Option A: Dilute solution
Option B: Unsaturated solution
Option C: Saturated solution
Option D: Colloid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- A saturated solution holds the maximum solute at that temperature; additional solute remains undissolved at the bottom.
- An unsaturated solution can still dissolve more solute at that temperature.
- Why others are incorrect: A relates to concentration level; B is the opposite case; D is a different dispersion type.
Question 4:
What is the most direct way to make a saturated sugar solution start dissolving more sugar again?
Option A: Cool the solution
Option B: Heat the solution
Option C: Stop stirring
Option D: Add sand first
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- For most solids in liquids, solubility increases with temperature; heating converts a saturated solution at lower temperature into an unsaturated one at higher temperature.
- Why others are incorrect: A reduces solubility; C does not increase the solubility limit; D is irrelevant and insoluble.
Question 5:
Which statement correctly compares concentrated and dilute solutions?
Option A: Concentrated has more solute per fixed amount of solution than dilute
Option B: Dilute has more solute per fixed amount of solution than concentrated
Option C: Both have the same amount of solute
Option D: Dilute and concentrated are absolute, not relative
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
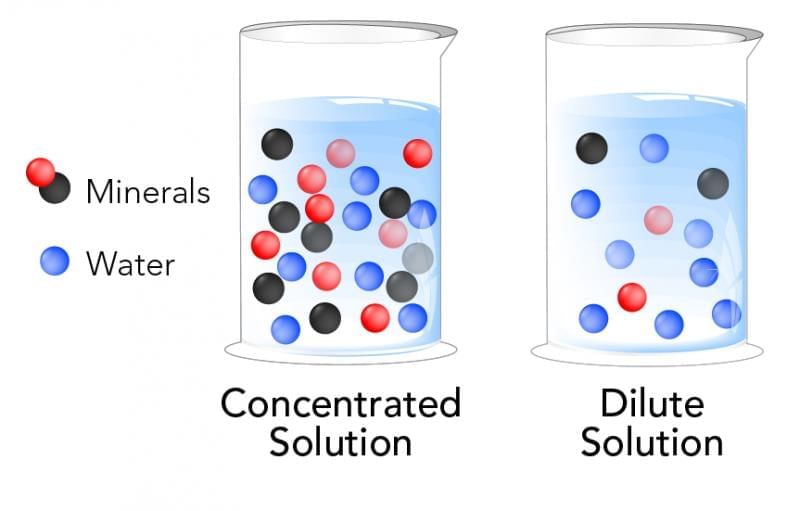
- Concentration refers to amount of solute per fixed amount of solution/solvent; “concentrated” means higher proportion than “dilute.”
- These are relative terms depending on the comparison basis.
- Why others are incorrect: B reverses; C ignores differences; D contradicts their relative nature.
Question 6:
Which change in temperature generally increases the solubility of a gas in water?
Option A: Increasing temperature
Option B: Decreasing temperature
Option C: Holding temperature constant
Option D: Heating and cooling alternately
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Gas solubility in liquids typically decreases with higher temperature and increases as temperature falls; cold water holds more dissolved oxygen, sustaining aquatic life.
- Why others are incorrect: A lowers gas solubility; C and D don’t target the correct trend.
Question 7:
Which best explains why oil floats on water in a glass?
Option A: Oil has higher density than water
Option B: Oil and water chemically react
Option C: Oil has lower density and is immiscible with water
Option D: Oil is the solvent for water
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
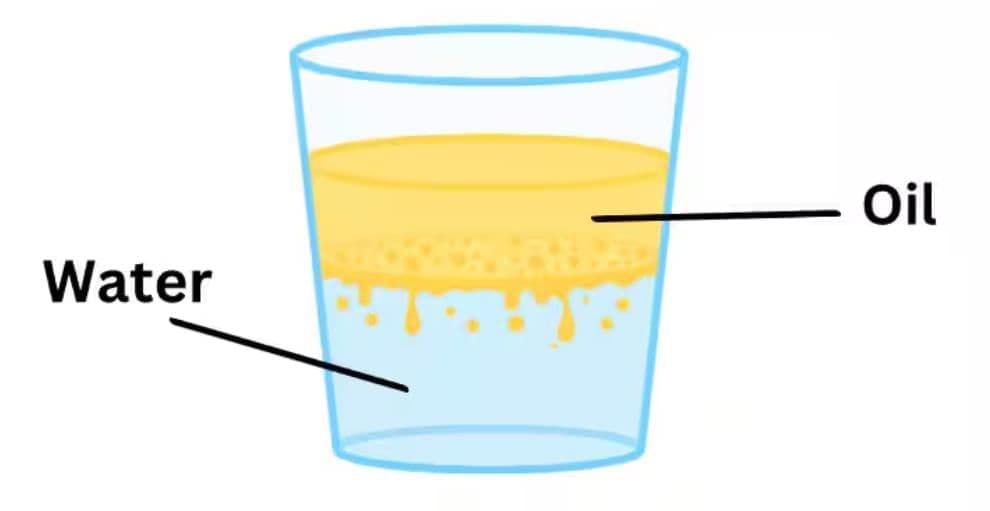
- Floating indicates oil’s density is lower than water’s; oil is also immiscible, so layers form with oil on top.
- Why others are incorrect: A predicts sinking; B does not occur; D misassigns solvent roles.
Question 8:
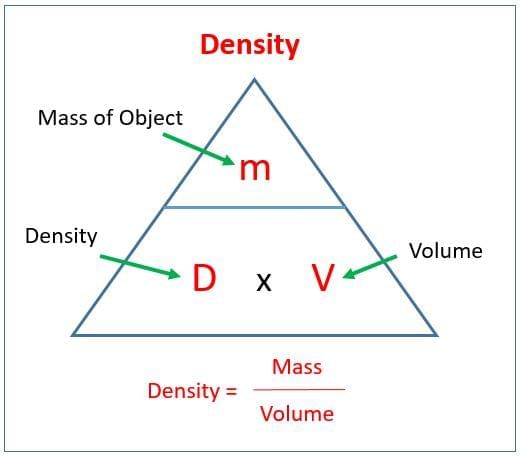
Which formula and SI unit pair for density is correct?
Option A: Density = Volume/Mass; unit m³/kg
Option B: Density = Mass/Volume; unit kg/m³
Option C: Density = Mass × Volume; unit kg·m³
Option D: Density = Mass/Area; unit kg/m²
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Density is mass per unit volume; SI unit is kg/m³; for liquids and small samples, g/mL or g/cm³ is common (1 mL = 1 cm³).
- Why others are incorrect: A inverts; C multiplies; D uses wrong denominator.
Question 9:
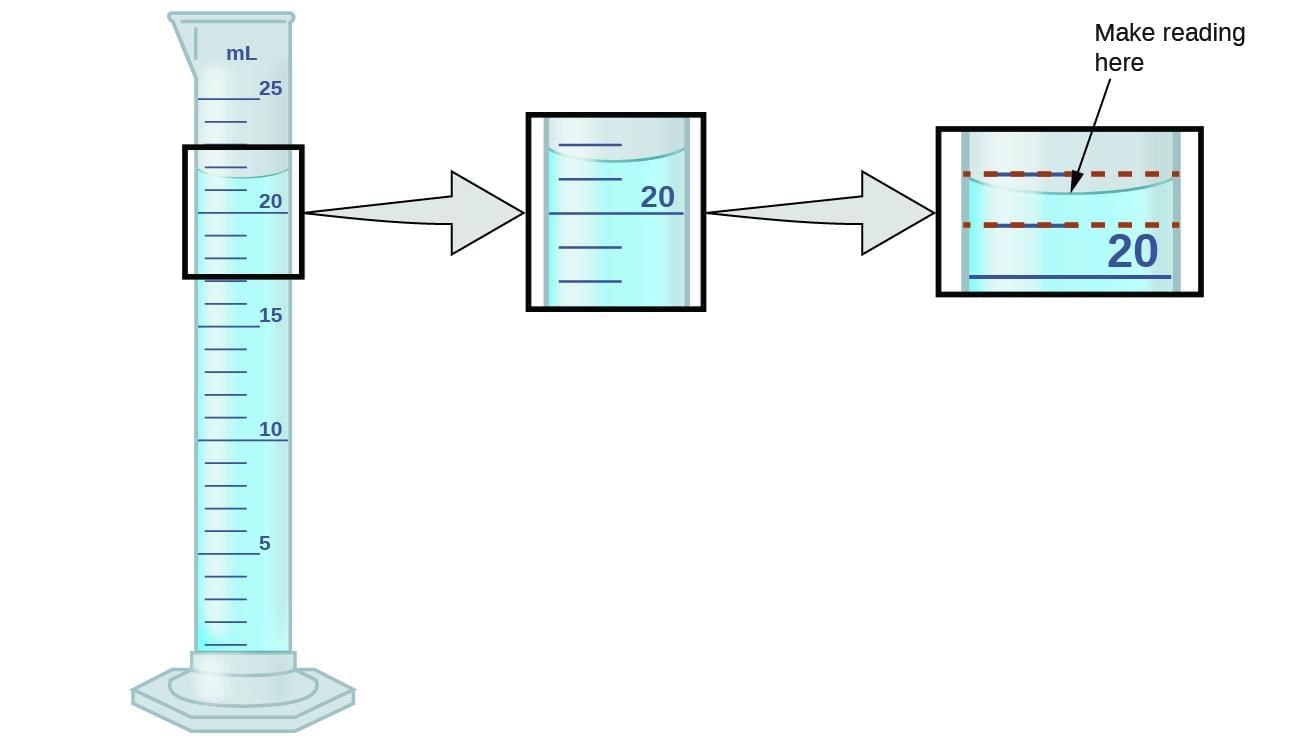
Why are measuring cylinders tall and narrow rather than short and wide for the same capacity?
Option A: To get a higher, clearer meniscus and finer scale divisions for better accuracy
Option B: To reduce glass usage only
Option C: To prevent liquids from evaporating
Option D: To make pouring impossible
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
A tall, narrow column produces more noticeable level changes per small volume, enabling finer graduations and accurate meniscus reading at eye level.
Question 10:
Which reading rule for a colourless liquid in a measuring cylinder is correct?
Option A: Read at the top of the meniscus, from above eye level
Option B: Read at the bottom of the meniscus, with eyes level to it
Option C: Read any visible line, eye position doesn’t matter
Option D: Always add 1 mL for meniscus
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- For most colourless liquids (like water), read the bottom of the meniscus with eyes level to avoid parallax error; for opaque/coloured liquids, read the top edge.
- Why others are incorrect: A inverts the rule; C causes parallax error; D is arbitrary.
Question 11:
An object has mass 16.400 g and displaces water from 50 mL to 55 mL in a cylinder. Its density is:
Option A: 0.30 g/cm³
Option B: 0.91 g/cm³
Option C: 16.40 g/cm³
Option D: 3.28 g/cm³
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
- Displacement gives volume = 55−50 = 5 mL = 5 cm³; density = 16.400 g / 5 cm³ = 3.28 g/cm³.
- Since water is ~1 g/cm³, this object is denser than water and would sink.
Question 12:
Which statement about temperature’s effect on density is generally true?
Option A: Heating increases density of all substances
Option B: Heating decreases density because volume expands while mass stays same
Option C: Temperature has no effect on density
Option D: Cooling always decreases density
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- As temperature rises, particles move apart; volume increases, mass constant ⇒ density (mass/volume) decreases; hot air rises for this reason.
- Water has special behavior near 4°C, but the general trend holds.
- Why others are incorrect: A and D contradict typical behavior; C overlooks thermal expansion.
Question 13:
Why does ice float on liquid water?
Option A: Ice is denser because it is colder
Option B: Ice has a structure that occupies more volume for the same mass, making it less dense than water
Option C: Water loses mass on cooling
Option D: Floating objects must be heavier
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Water’s structure expands on freezing, decreasing density; water is densest near 4°C, so ice (0°C) is less dense and floats, insulating water below.
- Why others are incorrect: A gets trend wrong; C mass doesn’t vanish; D is physically wrong.
Question 14:
Which change increases a gas’s density most directly?
Option A: Increase pressure at constant temperature
Option B: Decrease pressure at constant temperature
Option C: Heat the gas at constant pressure
Option D: Remove mass but keep volume same
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Gases are compressible; higher pressure reduces volume at constant mass (and often constant temperature), thereby increasing density.
- Why others are incorrect: B expands gas; C expands volume at constant pressure; D lowers density.
Question 15:
Two objects have these mass–volume pairs: A(200 g, 40 cm³), B(240 g, 60 cm³). Which is denser and what does that imply about floating in water?
Option A: A is denser (5.0 g/cm³) and sinks; B is 4.0 g/cm³ and sinks
Option B: A is less dense than B and floats
Option C: Both are 1.0 g/cm³ and float
Option D: B is denser (6.0 g/cm³) and floats
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- A: 200/40 = 5.0 g/cm³; B: 240/60 = 4.0 g/cm³; both densities exceed ~1 g/cm³, so both would sink; A is denser than B.
- Why others are incorrect: B reverses; C miscalculates; D miscomputes density and floating behavior.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ (Solution) - The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the difference between a solute and a solvent? |  |
| 2. How does temperature affect the solubility of a substance? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of solutions in everyday life? |  |
| 4. What is the process of dissolution, and what factors influence it? |  |
| 5. Can solutions be separated back into their components? If so, how? |  |





















