MCQ (Solution) - Light: Mirrors and Lenses | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Question 1:
Which statement correctly distinguishes concave and convex spherical mirrors?
Option A: Concave mirrors curve outward; convex mirrors curve inward
Option B: Concave mirrors curve inward; convex mirrors curve outward
Option C: Both concave and convex mirrors are flat
Option D: Concave mirrors never form inverted images
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
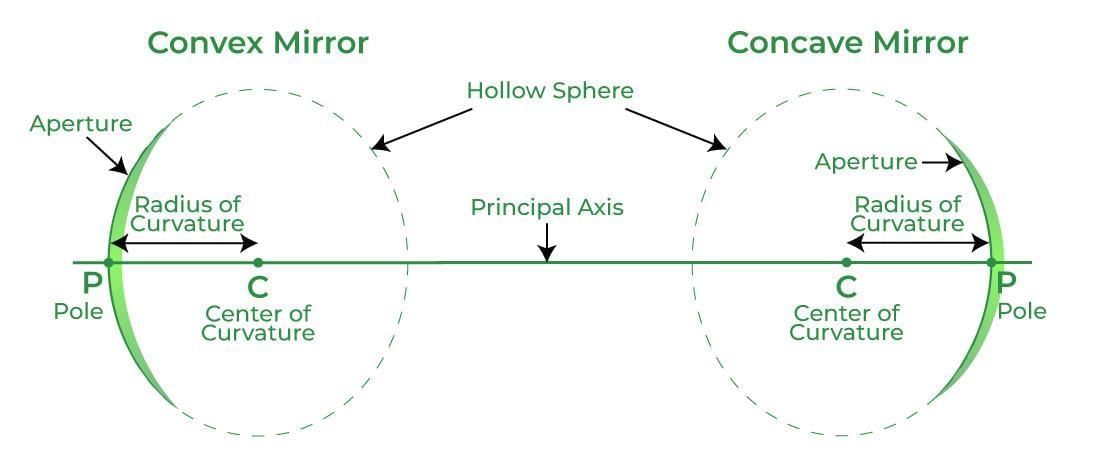
- A concave mirror has an inward-curving reflecting surface; a convex mirror has an outward-curving reflecting surface.
- Concave mirrors can produce inverted images when the object is sufficiently far; convex mirrors never produce inverted images for real objects.
- Why others are incorrect: A swaps definitions; C confuses spherical with plane mirrors; D is false—concave mirrors do invert for larger object distances.
Question 2:
A convex mirror used as a vehicle’s side-view mirror shows:
Option A: Always erect and diminished images with a wider field of view
Option B: Sometimes inverted, sometimes erect images with same size
Option C: Always inverted and enlarged images
Option D: Erect and same-sized images with narrow field of view
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Convex mirrors always give erect, diminished images and cover a larger area, hence the safety warning “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear.”
- Why others are incorrect: B and C contradict convex mirror image nature; D confuses with plane mirrors and ignores wide field of view.

Question 3:
When an object is placed close to a concave mirror, the image seen is typically:
Option A: Erect and enlarged
Option B: Erect and diminished
Option C: Inverted and diminished for all distances
Option D: Inverted and same-sized
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Near a concave mirror, the image is erect and magnified; farther away, the image becomes inverted (initially enlarged, then diminishing with distance).
- Why others are incorrect: B describes convex mirror behavior; C and D ignore distance-dependent image changes for concave mirrors.
Question 4:
Which pair correctly matches device and the mirror type used?
Option A: Dentist’s mouth mirror — convex mirror
Option B: Road intersection safety mirror — concave mirror
Option C: Torch reflector — concave mirror
Option D: Side-view mirror of a car — concave mirror
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Concave reflectors converge light into a beam (torch/headlights); convex mirrors are used for wide-angle viewing (side-view mirrors, intersection mirrors).
- Dentists use concave mirrors to get enlarged, close-up views.
- Why others are incorrect: A: dentist needs concave; B: safety mirror is convex; D: vehicles use convex, not concave.
 Uses of Concave Mirrors
Uses of Concave Mirrors
Question 5:
The first law of reflection states that:
Option A: Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection
Option B: Incident ray equals reflected ray
Option C: Incident and reflected rays are perpendicular
Option D: Reflection occurs only on plane mirrors
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
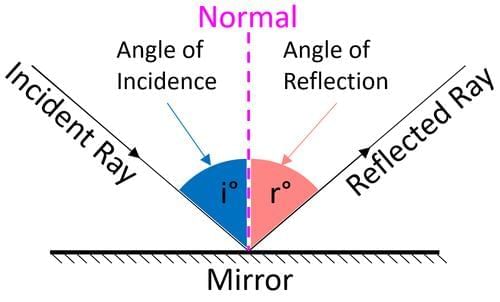
- Law 1: ∠i = ∠r for any reflecting surface (plane or spherical), measured from the normal at the point of incidence.
- Why others are incorrect: B is meaningless; C is not general; D is false—laws hold for all mirrors.
Question 6:
The second law of reflection states that the incident ray, normal, and reflected ray:
Option A: Lie in different planes
Option B: Lie in the same plane
Option C: Are all parallel
Option D: Coincide for any angle
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Law 2: The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
- Why others are incorrect: A contradicts the law; C and D are special/impossible cases, not the general rule.
Question 7:
Multiple parallel light rays fall on a concave mirror. After reflection, the rays:
Option A: Remain parallel
Option B: Converge
Option C: Diverge
Option D: Disappear
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Concave mirrors converge parallel incident rays; convex mirrors cause divergence; plane mirrors keep them parallel.
- Why others are incorrect: A applies to plane mirrors; C applies to convex; D is unphysical.
Question 8:
A convex lens is placed in front of text at a small distance. The text appears:
Option A: Erect and enlarged
Option B: Inverted and enlarged
Option C: Erect and diminished
Option D: Inverted and same-sized
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
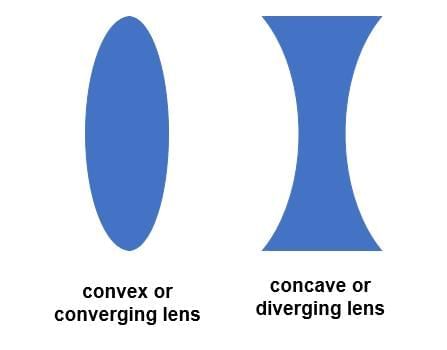
- For close objects, a convex lens acts as a magnifier producing an erect, enlarged image (basis of magnifying glasses and reading lenses).
- Farther objects may produce inverted images whose size varies with distance.
- Why others are incorrect: B and D occur for certain object distances but inverted is not for close viewing; C describes concave lens behavior.
Question 9:
Which statement about a concave lens is always true for real objects?
Option A: It always forms an erect and diminished image
Option B: It always forms an inverted and enlarged image
Option C: It can form an erect enlarged image
Option D: It produces no image
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Concave lenses are diverging; they always produce virtual, erect, and diminished images of real objects.
- Why others are incorrect: B and C contradict the diverging nature; D is false—images exist (virtual).
Question 10:
Why can a concave mirror or a convex lens burn paper when used with sunlight in the right setup?
Option A: They absorb light and convert it to electricity
Option B: They converge sunlight to a small bright spot, concentrating energy and heating the paper
Option C: They block infrared rays
Option D: They create light from darkness
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Concave mirrors and convex lenses can concentrate parallel sun rays to a small area, raising temperature enough to char or ignite paper (principle of solar concentrators).
- Why others are incorrect: A, C, D do not describe the optical focusing mechanism.
Question 11:
Looking through a thin, flat glass plate at text produces what change compared to looking through a convex lens?
Option A: Flat glass enlarges; convex lens leaves size unchanged
Option B: Flat glass leaves size unchanged; convex lens can enlarge for close objects
Option C: Both always diminish
Option D: Both always invert
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- A thin flat window simply transmits light without magnification; a convex lens can produce an erect, enlarged image for close viewing.
- Why others are incorrect: A reverses; C and D are false in general use.
Question 12:
Which pairing is correct for “optical element → beam behavior” with parallel incident rays?
Option A: Plane mirror → diverge
Option B: Concave mirror → converge
Option C: Convex mirror → remain parallel
Option D: Concave lens → converge
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Parallel rays reflect to converge for concave mirrors; remain parallel for plane mirrors; diverge for convex mirrors; concave lenses diverge transmitted rays.
- Why others are incorrect: A, C, D mismatch observed beam behavior.
Question 13:
If a light ray falls on a plane mirror along the normal, then:
Option A: Angle of incidence is 0° and the ray reflects back on itself
Option B: Angle of incidence is 90° and no reflection occurs
Option C: The reflected ray is perpendicular to the incident ray
Option D: The ray gets absorbed completely
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Incidence along the normal implies ∠i=0°, so ∠r=0°; the ray retraces its path.
- Why others are incorrect: B misstates the angle; C is not general; D contradicts the reflective behavior.
Question 14:
Why do convex mirrors give a larger field of view than plane mirrors of the same size?
Option A: They magnify everything
Option B: Their outward curvature allows them to capture rays from a wider angular region
Option C: They focus light to a point
Option D: They block peripheral rays
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Convex curvature lets more peripheral rays reflect towards the observer, showing a wider scene (basis for use in vehicles and safety mirrors).
- Why others are incorrect: A is false (they diminish); C describes concave focusing; D is opposite of wider view.
Question 15:
Which matching of lens type with consistently observed image property for real objects is correct?
Option A: Convex lens — always erect and enlarged
Option B: Concave lens — always erect and diminished
Option C: Convex lens — always inverted and diminished
Option D: Concave lens — sometimes inverted and enlarged
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- A concave (diverging) lens always produces erect, diminished, virtual images of real objects; a convex lens can produce erect enlarged (near) or inverted images (far), so its behavior varies with distance.
- Why others are incorrect: A and C wrongly claim “always” for convex; D is contrary to concave lens behavior.
|
59 videos|235 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ (Solution) - Light: Mirrors and Lenses - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the basic principles of reflection and how do they apply to mirrors? |  |
| 2. How do convex and concave mirrors differ in terms of their images? |  |
| 3. What is the role of lenses in focusing light and how do they differ from mirrors? |  |
| 4. How do we determine the focal length of a lens or mirror? |  |
| 5. What practical applications do mirrors and lenses have in everyday life? |  |
















