MCQ (Solution) - How Nature Works in Harmony | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Question 1:
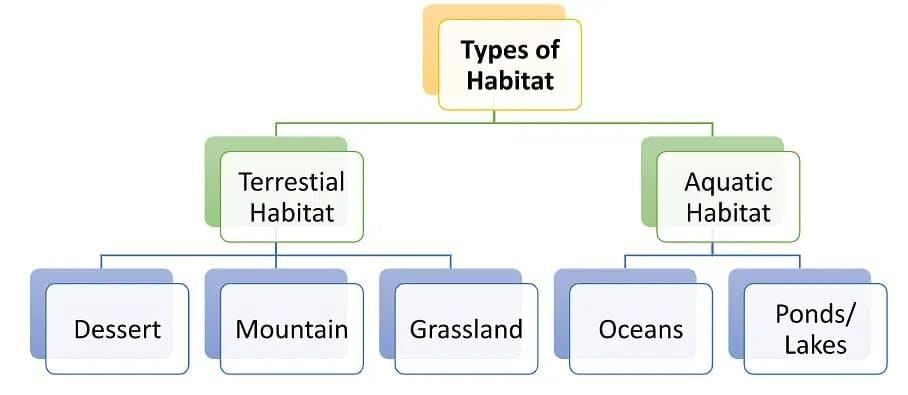
Which option best defines a habitat?
Option A: Only the plants present in a forest
Option B: The place where an organism lives, including living and non-living components
Option C: A group of similar animals living together
Option D: Any human-made area like a farm or park
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- A habitat is the place an organism lives with both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components that provide conditions to survive.
- A and C are subsets; D may be a habitat but is not the definition.
Question 2:
Pond water level drops and many aquatic plants die from pollution. Which change is most likely next within that ecosystem?
Option A: Oxygen in water decreases and fish population drops
Option B: Oxygen in water increases and fish thrive
Option C: Soil moisture rises around the pond
Option D: Decomposers stop working
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Fewer aquatic plants lower dissolved oxygen, stressing fish and reducing their numbers, triggering cascading effects in the community.
Question 3:
In the “pond with fish vs without fish” example, what indirect effect did fish have on nearby flowering plants?
Option A: Fish directly pollinated flowers
Option B: Fish reduced dragonflies, increasing pollinators and seed set
Option C: Fish increased dragonflies, reducing pollinators and seed set
Option D: Fish increased water nutrients taken up by flowers
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Fish prey on dragonfly larvae, lowering dragonfly numbers; fewer dragonflies means more bees/flies/butterflies, improving pollination and seed production.
Question 4:
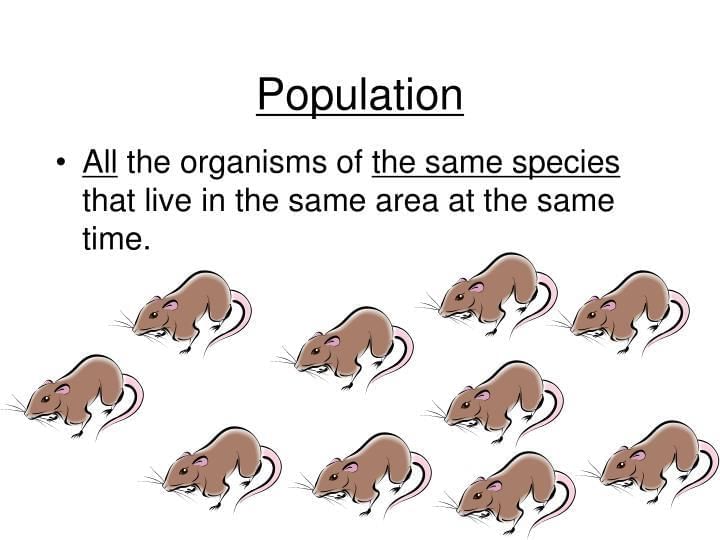
A population is best described as:
Option A: All living and non-living components of an area
Option B: All different species living together
Option C: Individuals of the same species in a given area at a given time
Option D: The abiotic conditions only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Population = one species, defined space and time; B is a community; A is an ecosystem; D misses biotic life.
Question 5:
Which pair correctly matches role and example?
Option A: Producer — deer
Option B: Consumer — mushroom
Option C: Decomposer — fungi/bacteria
Option D: Producer — vulture
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Decomposers (fungi, bacteria) break down dead matter and recycle nutrients; producers are green plants; deer/vulture are consumers.
Question 6:
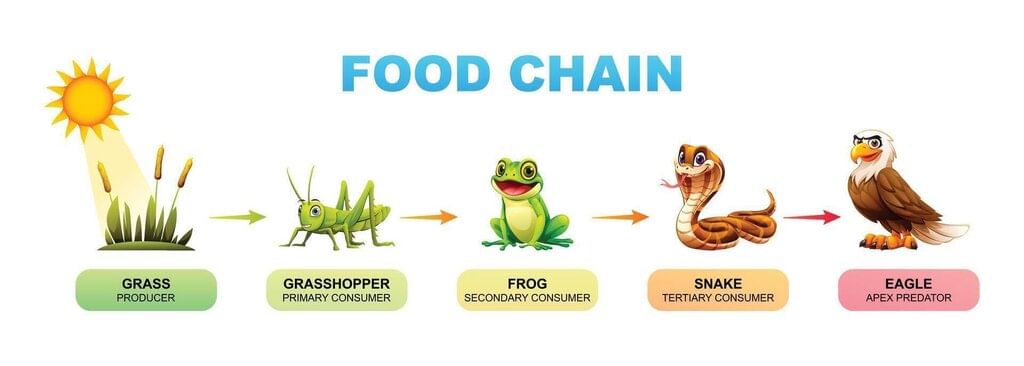
Which example is a correct simple food chain in a grassland?
Option A: Snake → frog → grasshopper → grass
Option B: Grass → hare → fox
Option C: Eagle → snake → frog → grasshopper
Option D: Grasshopper → grass → frog → snake
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Energy flows from producers (grass) to primary consumers (hare) to secondary/tertiary consumers (fox).
Question 7:
In a crop field with millet, mice, and eagles, which trophic level is at the base of the ecological pyramid?
Option A: Eagle
Option B: Mouse
Option C: Millet plants
Option D: Decomposers
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Producers (millet) form the first trophic level and base of the pyramid supporting higher levels (mice, then eagles).
Question 8:
Why are food webs more realistic than single food chains?
Option A: They show abiotic factors only
Option B: Most organisms feed on or are eaten by multiple species, forming interconnected chains
Option C: They exclude decomposers
Option D: They are simpler to draw and read
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Food webs capture the multiple feeding links among species, better representing real ecosystem interactions.
Question 9:
If frogs vanish from a grassland food web, which immediate outcome is most likely?
Option A: Grasshopper population increases; snake population declines
Option B: Grasshopper population decreases; snake population increases
Option C: Both grasshopper and snake populations increase
Option D: No change in other populations
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Fewer frogs reduces predation on grasshoppers (they increase), and reduces food for snakes (they decline), with further cascading effects.
Question 10:
What is the primary ecosystem service of decomposers like mushrooms and bacteria?
Option A: Fix atmospheric nitrogen directly
Option B: Produce glucose by photosynthesis
Option C: Break down dead organic matter, returning nutrients to soil
Option D: Control climate by absorbing CO2 at large scales
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Decomposers recycle nutrients by breaking complex organic matter into simpler forms that plants can reuse, sustaining ecosystem productivity.
Question 11:
Which interaction is correctly matched with its example?
Option A: Mutualism — ticks on dogs
Option B: Commensalism — orchids on tree branches
Option C: Parasitism — bees pollinating flowers
Option D: Mutualism — epiphytes taking space
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Orchids (epiphytes) gain support without harming the tree (commensalism); bees–flowers is mutualism; ticks on dogs is parasitism.
Question 12:
Large-scale harvesting of frogs led to pest outbreaks in fields. Which principle does this illustrate?
Option A: Abiotic factors are more important than biotic ones
Option B: Producers do not affect consumers
Option C: Pesticides enhance biodiversity
Option D: Removing a predator can disrupt balance and increase prey/pest populations
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
- Predators like frogs regulate pest populations; removing them increases pests, often prompting harmful pesticide use and cascading impacts.
Question 13:
Which statement about Sundarbans mangroves is most accurate?
Option A: They only provide timber, not protection
Option B: They buffer coasts against storms and floods, store carbon, and support biodiversity
Option C: They are not threatened by human activities
Option D: They are unimportant to nearby communities
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Mangroves attenuate waves/winds, protect coasts, sequester carbon, and host endangered species; threats include deforestation, pollution, overuse.
Question 14:
Which farming practice is most aligned with sustaining soil health and ecosystem balance?
Option A: Diversified crops, organic amendments/composts, natural pest control
Option B: Continuous monoculture with heavy synthetic inputs
Option C: Increasing pesticide doses to overcome resistance
Option D: Maximizing irrigation and repeated ploughing regardless of soil biota
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Diversity, compost/organic inputs, recycling, and biological pest control support soil organisms, reduce erosion, and enhance long-term productivity.
Question 15:
What is the most complete description of an ecosystem?
Option A: Only the animals and plants in an area
Option B: A community plus its abiotic environment and the interactions among them
Option C: A single food chain in a habitat
Option D: Only human-made systems like farms and parks
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- An ecosystem includes communities of organisms, abiotic factors (air, water, soil, light, temperature), and the network of interactions that link them.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ (Solution) - How Nature Works in Harmony - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key components of nature that work in harmony? |  |
| 2. How does human activity impact the natural harmony of ecosystems? |  |
| 3. What role does biodiversity play in maintaining ecological balance? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of natural phenomena that illustrate harmony in nature? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to preserving the harmony of nature? |  |
















