MCQ (Solution) - Our Home: Earth, a Unique Life Sustaining Planet | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Question 1:
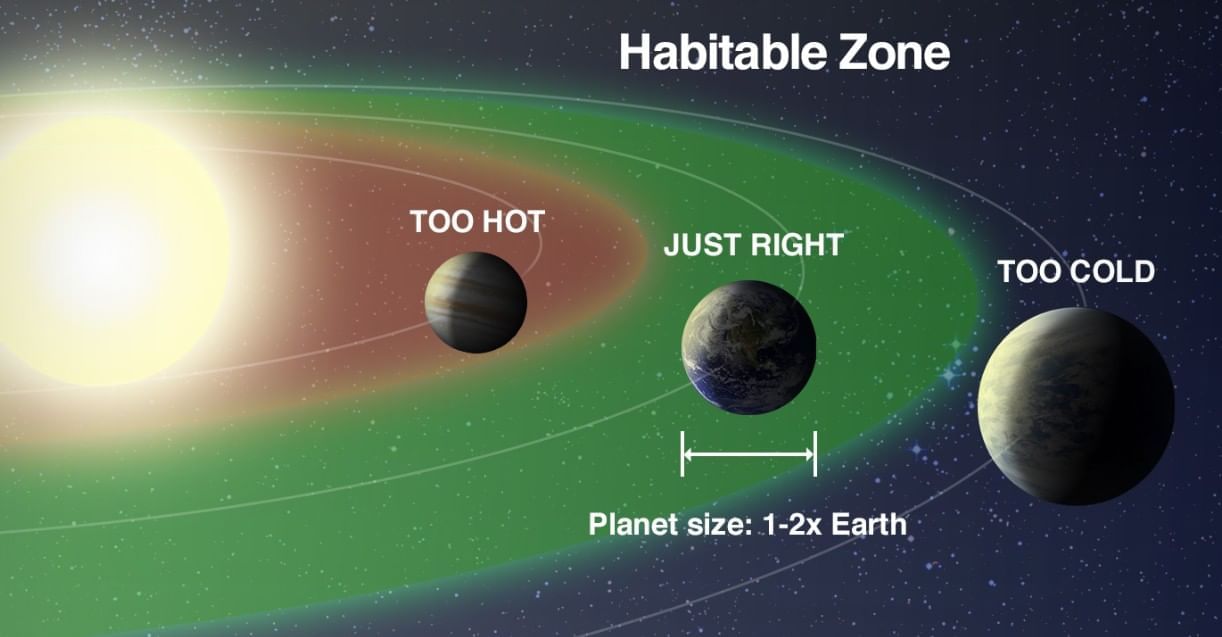
Which combination best explains why Earth can sustain liquid water on its surface?
Option A: Far from the Sun, thin atmosphere, no magnetic field
Option B: Very large size, no atmosphere, strong solar wind
Option C: Very close to the Sun, thick clouds, no ozone layer
Option D: Right distance (habitable zone), suitable atmospheric greenhouse effect, nearly circular orbit
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
- Earth’s position in the habitable zone, mild greenhouse effect, and nearly circular orbit keep surface temperatures in a range where water remains liquid.
- Distance alone is insufficient; stable insolation and heat retention are also required.
Question 2:
Why is Venus hotter than Mercury on average despite being farther from the Sun?
Option A: It receives more sunlight due to its rotation
Option B: Its thick CO₂ atmosphere causes an intense greenhouse effect
Option C: Mercury has no atmosphere to reflect sunlight
Option D: Venus has a stronger magnetic field trapping heat
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Venus’s dense CO₂ atmosphere traps outgoing infrared radiation, creating extreme surface temperatures surpassing Mercury’s.
Question 3:
If Earth were significantly smaller (same density), which outcome is most likely?
Option A: Weaker gravity, atmosphere escapes more readily
Option B: Stronger gravity, thicker atmosphere
Option C: No change to atmospheric retention
Option D: Instant formation of oceans
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Smaller mass implies weaker surface gravity, reducing the planet’s ability to retain atmospheric gases over geologic timescales.
Question 4:
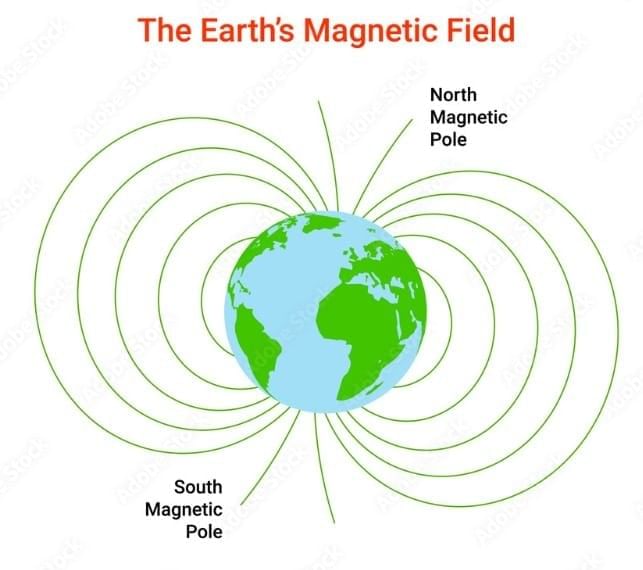
Which protective role does Earth’s magnetic field primarily play?
Option A: Keeps oceans from evaporating by cooling air
Option B: Blocks harmful UV radiation directly
Option C: Deflects charged particles from the Sun and space, helping protect the atmosphere
Option D: Traps oxygen near the surface
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- The magnetosphere deflects solar wind and cosmic particles, reducing atmospheric erosion and preserving conditions favorable to life.
Question 5:
Which statement correctly distinguishes the atmospheric “greenhouse effect” from a plant greenhouse?
Option A: Both trap air with glass walls
Option B: Atmospheres absorb and re-emit infrared; greenhouses mainly limit air exchange and convection
Option C: Both reflect UV back to space
Option D: Neither warms surfaces
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Greenhouse gases absorb Earth’s IR and re-emit it, while plant greenhouses reduce convective heat loss by enclosure.
Question 6:
Which Earth system pairing is correctly matched to its main components?
Option A: Atmosphere — rocks and minerals
Option B: Biosphere — nitrogen and oxygen gases only
Option C: Geosphere — plants, animals, microbes
Option D: Hydrosphere — liquid, solid, and vapor water reservoirs
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
- Hydrosphere includes oceans, lakes, rivers, groundwater, ice, and atmospheric water vapor; geosphere is rock/soil; biosphere is life; atmosphere is gases.
Question 7:
Which factor makes Earth’s orbit especially favorable for climate stability?
Option A: Highly elongated orbit causing strong seasonal extremes
Option B: Nearly circular orbit limiting insolation swings through a year
Option C: Retrograde orbit around the Sun
Option D: No axial tilt, so no seasons
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Low eccentricity orbits reduce annual variation in solar energy, supporting climate stability alongside other factors.
Question 8:
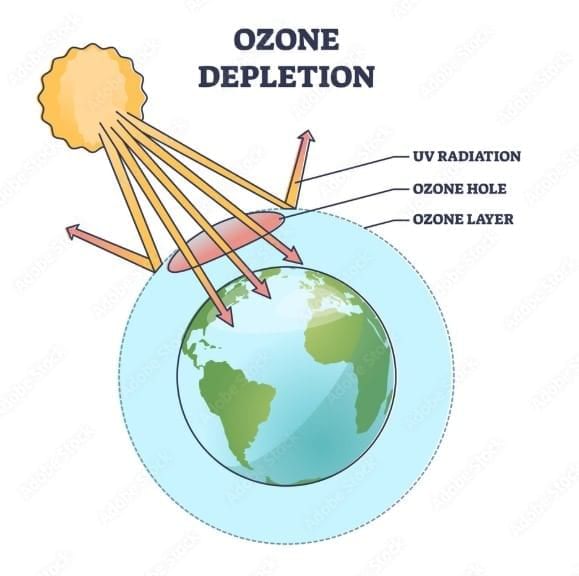
Which best explains why the ozone layer is vital to surface life?
Option A: It absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation
Option B: It deflects solar wind particles
Option C: It produces greenhouse gases
Option D: It generates Earth’s magnetic field
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Stratospheric ozone absorbs much of the Sun’s UV-B and UV-C, reducing biological damage at Earth’s surface.
Question 9:
Which statement about geodiversity is correct?
Option A: It refers to the variety of animal species
Option B: It is the diversity of climate types only
Option C: It includes the variety of landforms, rocks, soils, and geological processes
Option D: It is the number of lakes and rivers alone
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Geodiversity comprises physical Earth features and processes that shape habitats and influence biodiversity.
Question 10:
Which pairing of reproduction type and description is correct?
Option A: Asexual — offspring are genetic mixes of two parents
Option B: Sexual — one parent produces identical copies
Option C: Asexual — one parent produces genetically identical offspring
Option D: Sexual — no gametes involved
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Asexual reproduction involves one parent; offspring are clones (barring mutations). Sexual reproduction mixes genetic material from two parents via gametes.
Question 11:
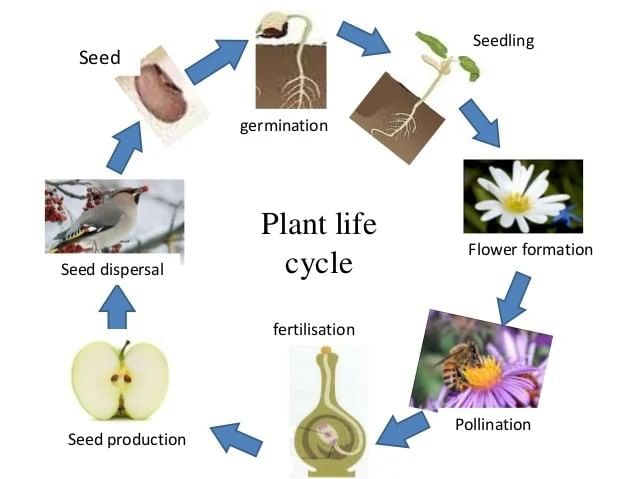
Which sequence correctly describes sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
Option A: Germination → pollination → fertilisation → seed
Option B: Seed → fruit → fertilisation → pollination
Option C: Fertilisation → pollination → fruit → seed
Option D: Pollination → fertilisation → seed formation → fruit development
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
- Pollen transfer (pollination) precedes fusion of gametes (fertilisation), forming a seed; surrounding tissues develop into fruit.
Question 12:
Which is an example of vegetative (asexual) propagation?
Option A: Seed formation in mango
Option B: Potato sprouting from “eyes” forming new plants
Option C: Pollination by bees in mustard
Option D: Internal fertilisation in mammals
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- New plants can grow from potato buds (eyes), ginger rhizomes, or stem cuttings (e.g., money plant), without seeds.
Question 13:
Which set correctly lists the “triple planetary crisis” discussed in the chapter?
Option A: Deforestation, overfishing, desertification
Option B: Climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution
Option C: Ozone formation, photosynthesis, respiration
Option D: Earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- These three interlinked global challenges threaten the stability of natural systems and human well-being worldwide.
Question 14:
Which global treaty pairing is correctly matched with its primary goal?
Option A: Montreal Protocol — reduce ozone-depleting substances
Option B: Paris Agreement — remove all CO₂ from the air immediately
Option C: Kyoto Protocol — protect whale populations
Option D: Earth Summit — ban all fossil fuels instantly
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Montreal Protocol targeted CFCs and related chemicals to protect the ozone layer; Paris aims to limit warming; Kyoto set emission targets.
Question 15:
Why do sexually reproducing offspring differ from their parents and siblings?
Option A: They receive identical gene copies as each parent
Option B: They receive a unique combination of genes via gametes from both parents
Option C: Environment rewrites their genetic instructions after birth
Option D: All siblings inherit the same gene mix each time
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Gametes carry half-sets that combine uniquely at fertilisation, producing genetic variation among offspring.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ (Solution) - Our Home: Earth, a Unique Life Sustaining Planet - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key features that make Earth a unique life-sustaining planet? |  |
| 2. How do human activities impact the sustainability of Earth? |  |
| 3. What role does the water cycle play in sustaining life on Earth? |  |
| 4. Why is biodiversity important for the health of our planet? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to protecting Earth's environment? |  |















