Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > Mnemonics: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye
Mnemonics: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye | Science Class 8 PDF Download
1. Basic Parts of a Cell
Mnemonic: "Many Cats Nap Calmly"
- Many: Mitochondria — powerhouse of the cell, produces energy.
- Cats: Cytoplasm — jelly-like substance where cell processes occur.
- Nap: Nucleus — controls cell activities and contains genetic material.
- Calmly: Cell membrane — regulates what enters and exits the cell.
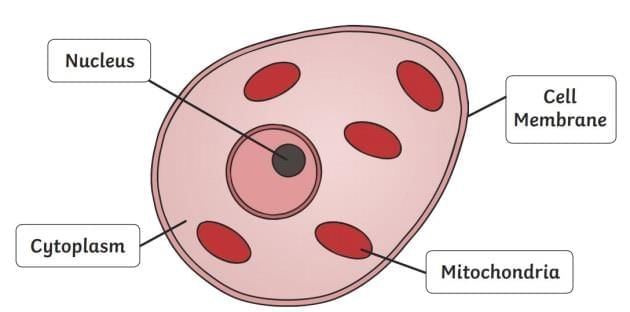 Basic Parts of Cell
Basic Parts of Cell
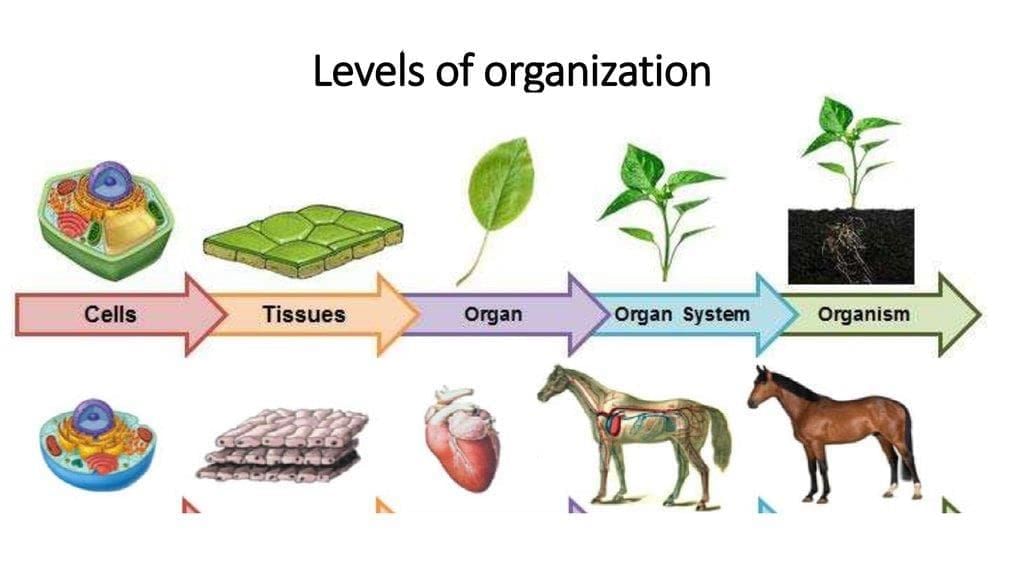
2. Levels of Organisation in Living Organisms
Mnemonic: "Cute Tiny Owls Order Oranges"
- Cute: Cell — basic unit of life.
- Tiny: Tissue — group of similar cells working together.
- Owls: Organ — different tissues form an organ (e.g., heart).
- Order: Organ system — organs working together (e.g., circulatory system).
- Oranges: Organism — complete living entity made of organ systems.
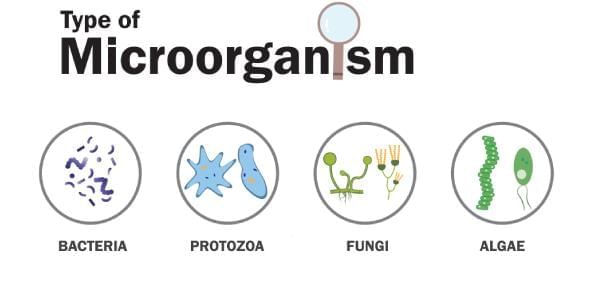
3. Categories of Microorganisms
Mnemonic: "Pink Frogs Bite All"
- Pink: Protozoa — single-celled organisms (e.g., Amoeba, Paramecium).
- Frogs: Fungi — yeast (unicellular) or mould (multicellular), no chlorophyll.
- Bite: Bacteria — unicellular with nucleoid, can be beneficial or harmful.
- All: Algae — often green, photosynthetic microorganisms.
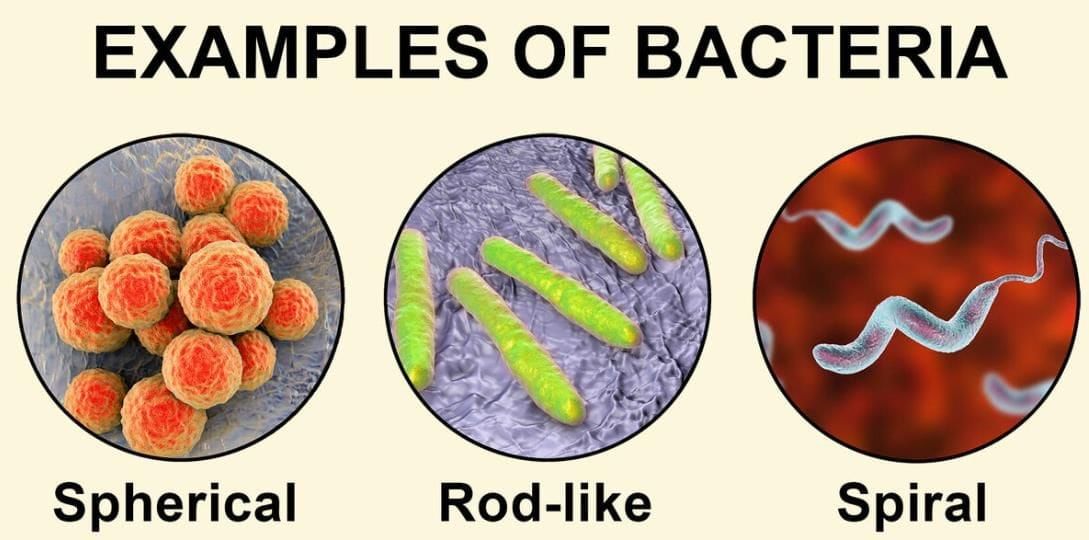
4. Shapes of Bacteria
Mnemonic: "Silly Cats Sing Randomly"
- Silly: Spherical — round-shaped bacteria (e.g., cocci).
- Cats: Comma — comma-shaped bacteria (e.g., vibrio).
- Sing: Spiral — spiral-shaped bacteria (e.g., spirilla).
- Randomly: Rod-shaped — rod-like bacteria (e.g., bacilli).
5. Favourable Conditions for Microorganism Growth
Mnemonic: "Tom And Milk"
- Tom: Temperature — optimal or warm conditions promote growth.
- And: Air — some microbes need oxygen, others thrive without it.
- Milk: Moisture — wet conditions enhance microbial growth.
6. Uses of Microorganisms in Food
Mnemonic: "Big Chefs Invent Cuisines"
- Big: Baking bread — yeast ferments to produce CO₂, making dough rise.
- Chefs: Making cakes/pastries — yeast or bacteria aid in fermentation.
- Invent: Fermentation of idli/dosa batter — microbes ferment batter for texture.
- Cuisines: Curd formation — bacteria like Lactobacillus convert milk to curd.
7. Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Mnemonic: “Pretty Vivid Clever Plants”
- Pretty (P): Plant Cell Wall — present in plant, absent in animal.
- Vivid (V): Vacuole — large in plant, small/absent in animal.
- Clever (C): Chloroplast — present in plant, absent in animal.
- Plants (P): Plant shape fixed (due to cell wall), animal shape variable.
8. Beneficial Roles of Microorganisms
Mnemonic: “Fine Foods Keep Nature Green”
- Fine: Fermentation (bread, cakes, idli, dosa, curd)
- Foods: Food supplements (Spirulina, Chlorella)
- Keep: Keeping environment clean (decomposition, manure)
- Nature: Nitrogen fixation (Rhizobium in legumes)
- Green: Gas production (biogas from waste)
The document Mnemonics: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye | Science Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye - Science Class 8
| 1. Who were the pioneers of microscopy and what were their contributions? |  |
Ans. The pioneers of microscopy are Robert Hooke and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. Robert Hooke is known for his work in the 17th century, where he described cells for the first time in his book "Micrographia." He observed cork and coined the term "cell." Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, often referred to as the "father of microbiology," significantly advanced microscopy by crafting powerful lenses and was the first to observe and describe single-celled organisms, which he referred to as "animalcules."
| 2. What are the basic parts of a cell? |  |
Ans. The basic parts of a cell include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. The cell membrane is a protective barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the cell where various organelles are suspended, and it is the site of many cellular processes. The nucleus contains the cell's genetic material and regulates activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
| 3. What extra elements are found in plant cells compared to animal cells? |  |
Ans. Plant cells contain several extra elements that are not found in animal cells. These include a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large central vacuoles for storage and maintaining cell turgor. The cell wall provides structural support, while chloroplasts enable plants to convert sunlight into energy, a process known as photosynthesis.
| 4. What is the purpose of plastids in plant cells? |  |
Ans. Plastids are organelles found in plant cells that serve various functions. The primary types of plastids include chloroplasts, which are involved in photosynthesis; chromoplasts, which contain pigments that give color to fruits and flowers; and leucoplasts, which are involved in the storage of starch, lipids, or proteins. Plastids play a crucial role in the plant's ability to produce food and store energy.
| 5. How do different cell shapes relate to their functions? |  |
Ans. Different cell shapes are adapted to their specific functions. For example, nerve cells (neurons) have long, branching structures to transmit signals over distances. Red blood cells are biconcave in shape to maximize surface area for oxygen transport. Muscle cells are elongated and can contract to facilitate movement. The shape of a cell is closely tied to its role in the organism, optimizing efficiency and functionality.
Related Searches

















