Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > Mnemonics: Magnetic and Heating Effects
Mnemonics: Magnetic and Heating Effects | Science Class 8 PDF Download
1. Factors Affecting Strength of an Electromagnet
Mnemonic: "More Current Turns Strong Magnet"
- More: Greater electric current → stronger magnetic field.
- Current: Flow of electricity in the coil → generates magnetism.
- Turns: More turns of wire in the coil → increases strength.
- Strong: These factors together strengthen the field.
- Magnet: Electromagnet — a temporary magnet formed by current.
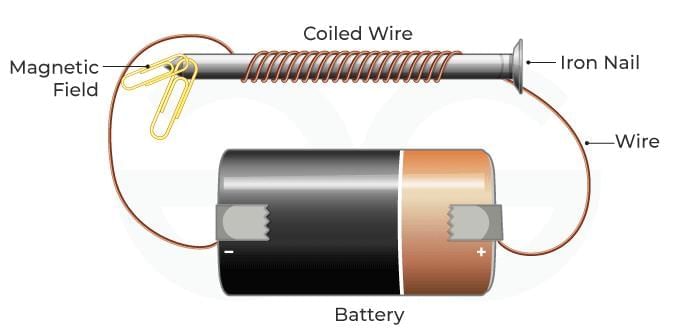 Electromagnet
Electromagnet
2. Factors Affecting Heat Produced in a Conductor
Mnemonic: "Smart Wires Last Longer Time"
- Smart (Material): The type of material decides resistance and heat.
- Wires (Thickness): Thin wires resist more and heat more.
- Last (Length): Longer wires → higher resistance → more heat.
- Time (Time): More time → more heat generated.
3. Parts of a Voltaic Cell
Mnemonic: "Every Plate Loves Energy"
- Every: Electrodes (two metal plates) — conduct electricity.
- Plate: Plates partly dipped in electrolyte — facilitate chemical reaction.
- Loves: Liquid electrolyte (acid or salt solution) — enables ion flow.
- Energy: Produces electric current — generates electricity.
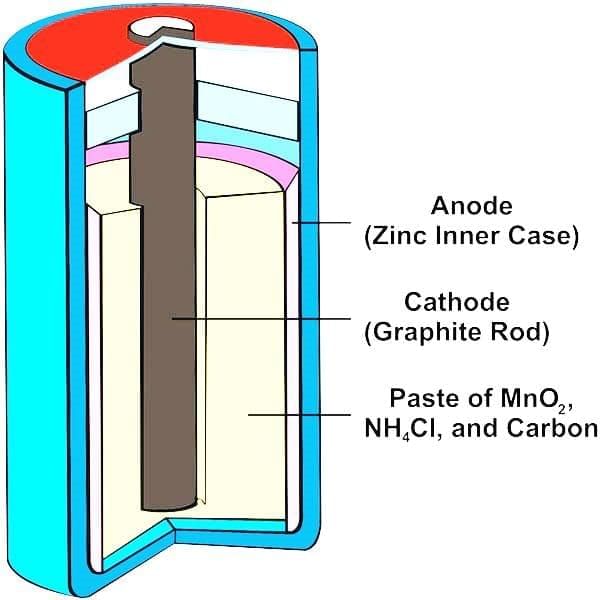
4. Parts of a Dry Cell
Mnemonic: "Zebra Can Eat"
- Zebra: Zinc container (negative terminal) — acts as anode.
- Can: Carbon/ Graphite rod (positive terminal) — acts as cathode.
- Eat: Electrolyte paste — facilitates ion movement.
5. Uses of Electromagnets
Mnemonic: "Lovely Motors Bring Loud Fun"
- Lovely: Lifting electromagnets (cranes, scrap yards) — lift heavy metal objects.
- Motors: Electric motors — convert electrical energy to mechanical motion.
- Bring: Electric bells — use electromagnets for ringing mechanism.
- Loud: Loudspeakers — convert electrical signals to sound.
- Fun: Fans — use electromagnets for rotation.
6. Common Household Appliances Using Heating Effect
Mnemonic: "Hot Room Stays Warm Inside Kettle Hairdryer"
- Hot: Room heater — warms rooms using heating element.
- Room: Electric stove — cooks food with heat from current.
- Stays: Electric kettle — heats water for boiling.
- Warm: Water heater / immersion rod — heats water for bathing or use.
- Inside: Electric iron — smooths clothes with heat.
- Kettle: Kettle (repeated for emphasis in cue) — boils water.
- Hairdryer: Hair dryer — dries hair using heated air.
7. Common Electrodes in Voltaic Cells
Mnemonic: "Zebra Catches Silver Apples In Market Lane"
- Zebra: Zinc — commonly used as an electrode.
- Catches: Copper — frequently used in voltaic cells.
- Silver: Silver — used in specific cell types.
- Apples: Aluminium — lightweight electrode material.
- In: Iron — used in certain voltaic cells.
- Market: Magnesium — reactive electrode material.
- Lane: Lead — used in lead-acid batteries.
8. Advantages of Rechargeable Batteries
Mnemonic: "Reuse Saves Money Often"
- Reuse: Reusable many times — can be recharged and used repeatedly.
- Saves: Reduces wastage — less need for disposable batteries.
- Money: Cost-effective over time — saves money in the long run.
- Often: Common in many devices — widely used in electronics.
The document Mnemonics: Magnetic and Heating Effects | Science Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Magnetic and Heating Effects - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the main factors that affect the strength of an electromagnet? |  |
Ans. The strength of an electromagnet is influenced by several key factors:
1. <b>Current</b>: Increasing the electric current flowing through the coil increases the strength of the electromagnet.
2. <b>Number of Turns</b>: More turns of wire in the coil enhance the magnetic field strength.
3. <b>Core Material</b>: The type of material used as the core (e.g., iron, steel) significantly affects the magnet's strength, as ferromagnetic materials enhance the magnetic field.
4. <b>Coil Configuration</b>: The arrangement of the coils can also impact the magnetic field produced.
| 2. How does the heating effect in a conductor lead to heat production? |  |
Ans. The heating effect in a conductor occurs due to the resistance that opposes the flow of electric current. When current flows through a conductor, electrons collide with the atoms of the conductor, causing them to vibrate more vigorously. This increased atomic vibration results in the generation of heat. The amount of heat produced can be quantified using the formula H = I²Rt, where H is the heat produced, I is the current, R is the resistance, and t is the time for which the current flows.
| 3. What are the essential parts of a voltaic cell? |  |
Ans. A voltaic cell consists of the following essential parts:
1. <b>Anode</b>: The negative electrode where oxidation occurs.
2. <b>Cathode</b>: The positive electrode where reduction takes place.
3. <b>Electrolyte</b>: A substance that allows the flow of ions between the anode and cathode.
4. <b>Salt Bridge</b>: A tube containing electrolyte that connects the two half-cells and maintains electrical neutrality by allowing the flow of ions.
| 4. How does a dry cell differ from a voltaic cell in its components? |  |
Ans. A dry cell is a specific type of voltaic cell that is designed to be portable and non-spillable. Its components typically include:
1. <b>Anode</b>: Usually made of zinc.
2. <b>Cathode</b>: Often composed of carbon or graphite.
3. <b>Electrolyte</b>: A paste-like substance (like ammonium chloride) that is non-liquid, allowing it to be sealed.
4. <b>Separator</b>: A material that keeps the anode and cathode apart to prevent short-circuiting while allowing ionic movement.
| 5. What are some common uses of electromagnets in daily life? |  |
Ans. Electromagnets have various applications in daily life, including:
1. <b>Electric Motors</b>: Used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
2. <b>Magnetic Locks</b>: Utilized in security systems to secure doors.
3. <b>MRI Machines</b>: Employed in medical imaging to create detailed images of the body's internal structures.
4. <b>Speakers</b>: Used to convert electrical signals into sound.
5. <b>Crane Operation</b>: Used to lift heavy ferromagnetic objects in industrial settings.
Related Searches
















