Unit Test (Solutions): Journey of a River | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 45 Minutes
M.M.: 20
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 7 to 9 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 10 carries 5 marks.
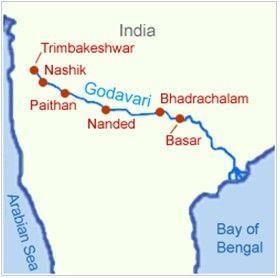
Q1. The Godavari River begins at which place?
(a) Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh
(b) Trimbakeshwar, Brahmagiri Hills, Maharashtra
(c) Gangotri, Uttarakhand
(d) Mahabaleshwar, Maharashtra
Ans: (b) Trimbakeshwar, Brahmagiri Hills, Maharashtra
Q2. Fill in the blanks:
The Godavari is India’s __________-longest river and flows for about __________ km.
Ans: second; 1,465 km
Q3. True or False:
The Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary lies in the Godavari delta near Kakinada and has mangrove forests.
Ans: True
Q4. Rivers like Manjira, Indravati, and Sabari that join the Godavari are called __________.
Ans: tributaries
Q5. Match the following:
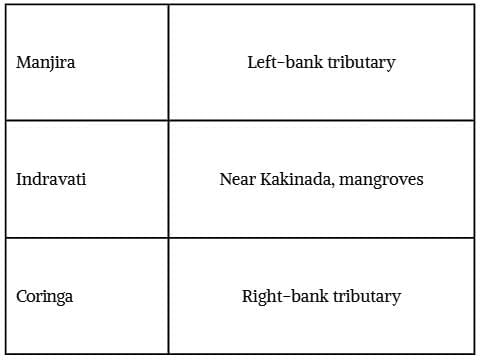
Ans:
Q6. The Godavari is also called “Dakshina Ganga” because it is a major sacred river of southern India. This statement is:
(a) Always false
(b) True
(c) True only during monsoon
(d) True only in Maharashtra
Ans: (b) True
Q7. List any three ways the Godavari supports human life and briefly explain each.
Ans: 1. Drinking Water: The Godavari gives water to drink and use at home for cooking and washing.
2. Farming: Farmers use river water to grow crops like rice and fruits, which we eat.
3. Industries/Work: Many industries use river water to produce things. People catch fish or take tourists on boat rides, earning money to live.
Q8. Explain how dams help people and also how they can cause problems. Give one point for each help and each problem.
Ans: Dams help people, and at the same time, also create problems
Help: Dams save water in big lakes so we can use it for drinking, growing crops, or making electricity.
Problem: Dams can flood villages and forests, making people and animals move away.
Additional Effect: Dams can stop the river’s flow, which hurts fish and plants downstream.
Q9. Why is the Godavari delta around Coringa important for wildlife, and how do mangroves help during storms or floods?
Ans: Importance of Godavari Delta:
- Wildlife value: The Godavari delta near Coringa has mangroves where birds, fish, and other animals live happily.
- Mangrove role: Mangrove roots hold the soil tight and stop waves from washing it away.
- Protection: Mangroves act like a wall to protect land from big storms and floods.
Q10. A school near the Godavari plans an eco-club project to keep the river clean. Design a 5-point action plan that students can do without harming the environment. Include at least one awareness activity, one waste-reduction step, one monitoring step, and one community partnership.
Ans: 5-point action plan for students:
1. Awareness Activity: Make colourful posters with slogans like “Save Our Godavari!” and show them in a school play to tell everyone to keep the river clean.
2. Waste Reduction: Use cloth bags and steel water bottles instead of plastic; hold a “no-plastic day” at school.
3. Monitoring Step: Walk near the river once a month with a teacher to check for garbage or dirty water and write it in a notebook.
4. Community Partnership: Team up with a local shop or cleaning group to pick up litter near the river safely.
5. Follow-up: Share what you found in the school assembly and promise to use less water at home, like turning off taps while brushing.
|
11 videos|211 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Journey of a River - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main stages in the journey of a river? |  |
| 2. How does a river contribute to the ecosystem? |  |
| 3. What are some human activities that impact rivers? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of rivers to human civilization? |  |
| 5. How can we protect and preserve rivers? |  |