Unit Test: Particulate Nature of Matter | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
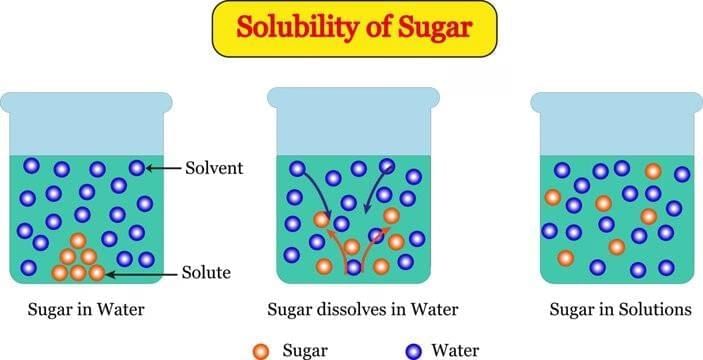
Q1: Which statement best explains why sugar “disappears” when dissolved in water? (1 Mark)
(i) Sugar is destroyed during stirring.
(ii) Sugar changes into air bubbles.
(iii) Sugar breaks into tiny constituent particles that spread in spaces between water particles.
(iv) Water particles convert sugar into water.
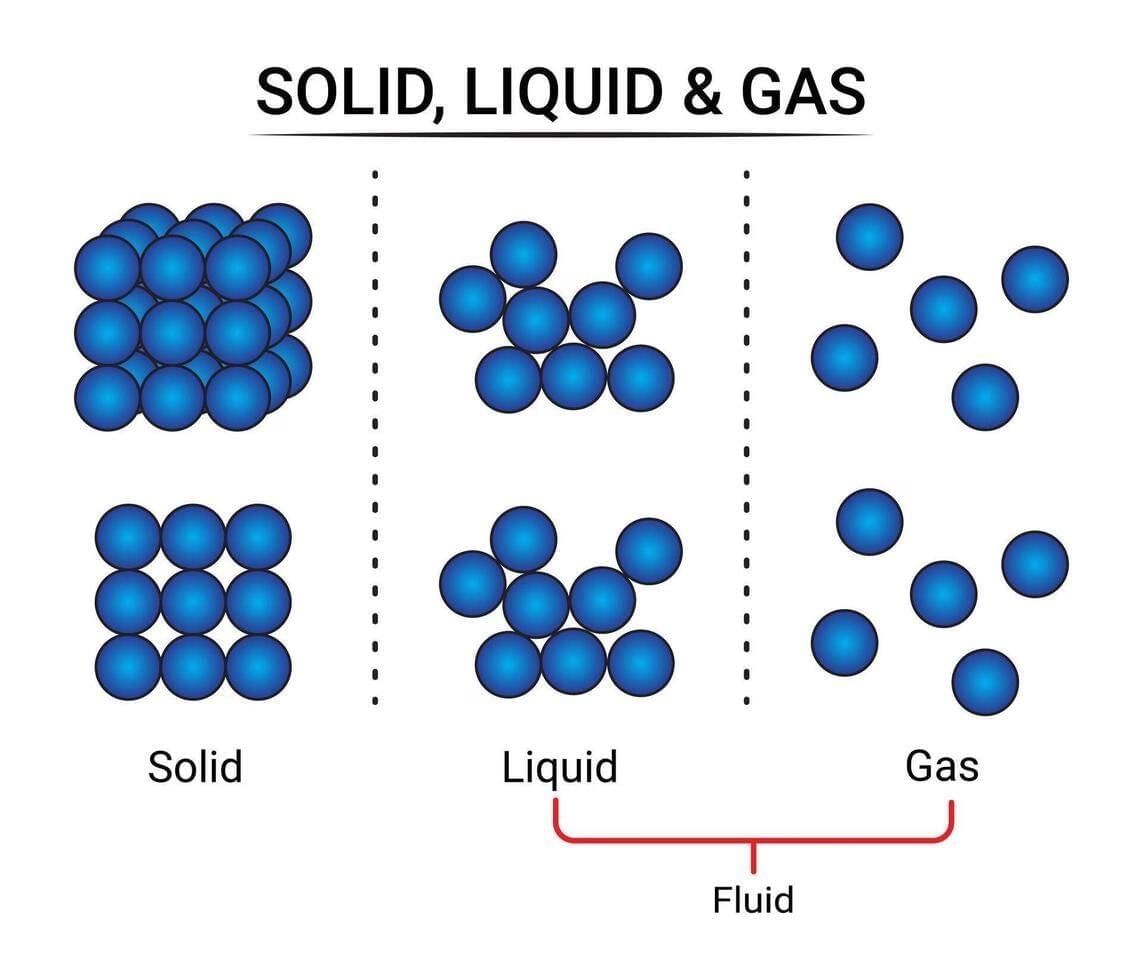
Q2: Solids have a definite shape mainly because (1 Mark)
(i) their particles are far apart.
(ii) their interparticle attractions are very strong and particles vibrate about fixed positions.
(iii) their particles move freely in all directions.
(iv) they have no particles.
Q3: Which pair correctly matches the state with particle spacing? (1 Mark)
(i) Solid — maximum spacing
(ii) Liquid — negligible spacing
(iii) Gas — maximum spacing
(iv) Solid — particles free to move throughout
Q4: The temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid at atmospheric pressure is called the (1 Mark)
(i) boiling point
(ii) melting point
(iii) condensation point
(iv) sublimation point
Q5: Smoke/iodine vapour filling an inverted gas jar demonstrates that gases (1 Mark)
(i) have fixed volume
(ii) do not move
(iii) expand to occupy available space and take container’s shape
(iv) only rise upward
Q6: State two observations from classroom activities that support “matter is made of extremely small particles.” (2 Marks)
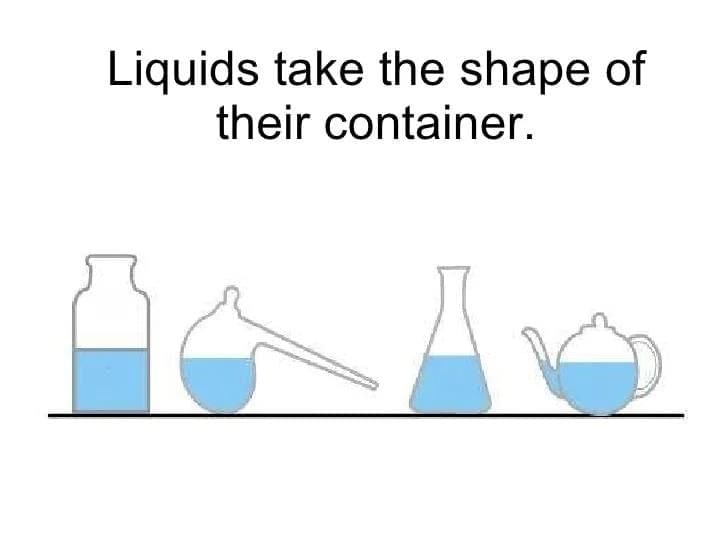
Q7: Explain why liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape, using particle ideas. (2 Marks)
Q8: A syringe without a needle is filled with air and sealed by a thumb; pushing the plunger makes the volume smaller. What does this reveal about gases? (2 Marks)
Q9: Differentiate among solids, liquids, and gases based on
(a) interparticle attraction,
(b) interparticle spacing,
(c) particle motion. (3 Marks)
Q10: Define melting point and boiling point; describe particle-level changes at each. (3 Marks)
Q11: In a clean vessel, water at 200 mL receives two spoons of sugar; level rises then after dissolving, it slightly falls below the mark. Explain. (3 Marks)
Q12:
(a) With suitable labeled sketches, explain how particle arrangement changes when ice melts and then boils into steam.
(b) Why does potassium permanganate spread fastest in hot water compared to cold water?
(c) Sand does not dissolve in water. Using particles, explain the observed volume change when sand is added to water. (5 Marks)
Q13: Answer the following application questions.
(a) Gases mix easily whereas solids usually do not—justify using interparticle attractions and spacing.
(b) Milk spreads when spilled but the glass cup retains its shape—explain.
(c) “If all constituent particles were removed from a chair, nothing of the chair would remain.” Defend this statement. (5 Marks)
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test: Particulate Nature of Matter - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the particulate nature of matter? |  |
| 2. How does temperature affect the movement of particles in matter? |  |
| 3. What are the three states of matter, and how do they differ based on the arrangement of particles? |  |
| 4. What evidence supports the particulate nature of matter? |  |
| 5. How does the concept of the particulate nature of matter relate to everyday life? |  |





















