Unit Test: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions - Class 8 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
Q1: A solution is defined as (1 Mark)
(i) any mixture of two solids
(ii) a uniform mixture in which components are evenly distributed
(iii) a non-uniform mixture where components settle
(iv) only liquids mixed with liquids
Q2: In the solution of salt in water, salt is the ______ and water is the ______. (1 Mark)
(i) solvent, solute
(ii) solute, solvent
(iii) suspension, colloid
(iv) liquid, solid

Q3: When no more solute can dissolve in a solution at a given temperature, the solution is (1 Mark)
(i) dilute
(ii) concentrated
(iii) saturated
(iv) supersaturated at all temperatures
Q4: Generally, the solubility of most solids in liquids ______ with increase in temperature, while the solubility of gases in liquids ______. (1 Mark)
(i) decreases, increases
(ii) increases, decreases
(iii) unchanged, unchanged
(iv) decreases, decreases
Q5: Density is defined as (1 Mark)
(i) mass × volume
(ii) volume/mass
(iii) mass/volume
(iv) weight/area
Q6: State the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated solution with one example from class activities. (2 Marks)
Q7: Give one reason why air is considered a solution. Identify the solvent in air. (2 Marks)
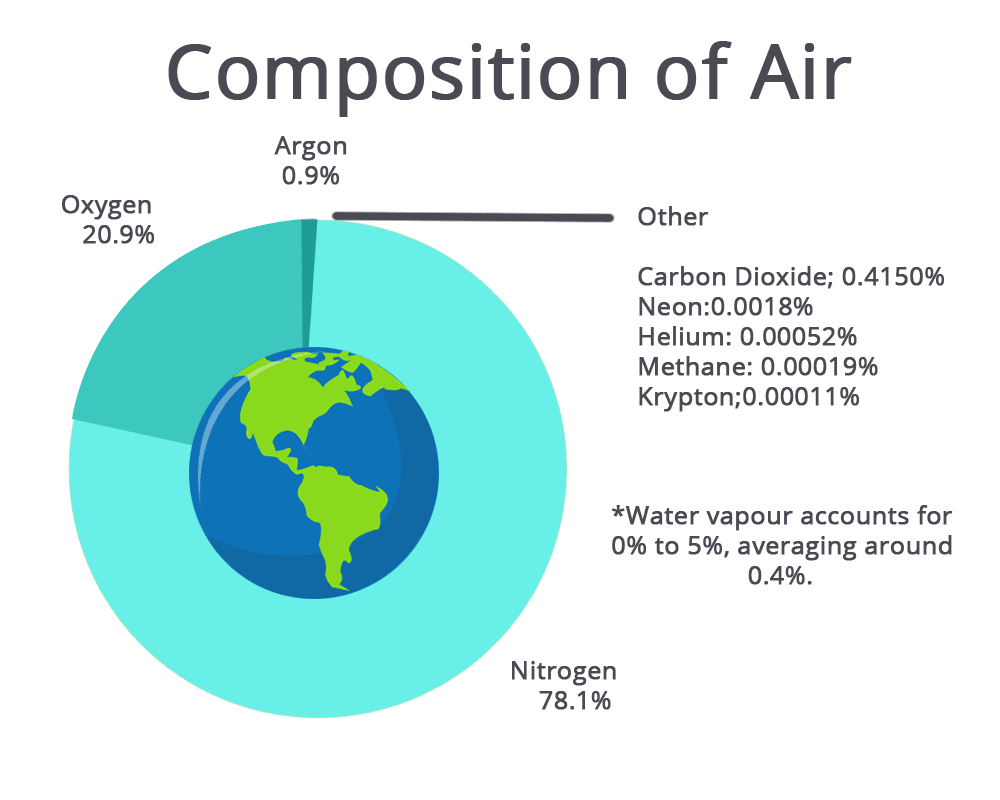
Q8: Explain why oxygen dissolves more in cold water than in hot water. How is this important for aquatic life? (2 Marks)
Q9: In an experiment, baking soda is added to water at 20 °C until some remains undissolved. On heating to 50 °C, the undissolved part disappears. Explain what this shows about solubility and the status of the solution at the higher temperature. (3 Marks)
Q10: Define concentration in simple terms. Which is more concentrated and why: (a) 2 spoons of salt in 100 mL water or (b) 4 spoons of salt in 50 mL water? (3 Marks)
Q11: A student mixes sawdust in water and notices it floats, while sand sinks. Use density ideas to explain both observations. (3 Marks)
Q12: Measurement and density applications. (5 Marks)
(a) Describe how to measure 50 mL of water accurately in a measuring cylinder (mention meniscus and eye position).
(b) A stone has mass 16.400 g. Using water displacement, its volume increases from 50 mL to 55 mL after immersion. Calculate its density.
(c) Predict qualitatively how heating a liquid generally affects its density and why.
Q13: (a) Give one everyday example showing that solutions can be formed from gases too; identify solute and solvent.
(b) An unpeeled orange floats while a peeled one sinks. Explain.
(c) A 2 L bottle currently holds 500 mL of water. How much more water can it hold? If filled completely, what mass of water would it contain approximately at room temperature? (5 Marks)
FAQs on Unit Test: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions - Class 8
| 1. What are solutes, solvents, and solutions? |  |
| 2. How do temperature and pressure affect solubility? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated solution? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of solutions in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What is the role of solubility in chemical reactions? |  |



















