Unit Test: Keeping Time with the Skies | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
Q1: The Moon shines in our sky because it (1 Mark)
(i) emits its own light
(ii) reflects sunlight
(iii) glows due to heat from Earth
(iv) shines only during night
 Moon in Sky
Moon in Sky
Q2: The changing visible shapes of the Moon as seen from Earth are called (1 Mark)
(i) eclipses
(ii) seasons
(iii) phases of the Moon
(iv) lunations
Q3: The period when the bright part of the Moon decreases day by day is called (1 Mark)
(i) waxing (Shukla Paksha)
(ii) waning (Krishna Paksha)
(iii) eclipse season
(iv) tropical period
Q4: On a full Moon day, the Moon is positioned nearly (1 Mark)
(i) between Earth and Sun
(ii) in the same direction as the Sun
(iii) opposite the Sun in the sky
(iv) at the Earth’s North Pole
Q5: The mean solar day (used to define 24 hours) is the average time between (1 Mark)
(i) two consecutive sunrises
(ii) sun’s highest position (noon) on successive days
(iii) two moonrises
(iv) two midnights
Q6: Why do we see the Moon in different positions at the same clock time on successive days? (2 Marks)
Q7: State two observational differences between waxing and waning periods of the Moon that help locate it in the sky. (2 Marks)
Q8: The phases of the Moon are NOT caused by Earth’s shadow. Explain briefly. (2 Marks)
Q9: In Activity with ball, lamp, observer, identify which ball positions correspond to full Moon and new Moon. Justify. (3 Marks)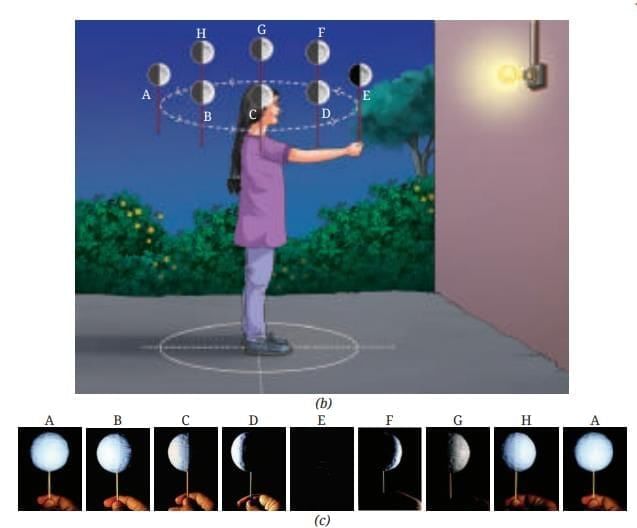
Q10: Define Shukla Paksha and Krishna Paksha. Approximately how long is each and how do the visible shapes change? (3 Marks)
Q11: A student claims, “The Moon always rises when the Sun sets.” Is this correct? Explain with an example. (3 Marks)
Q12: Calendars and timekeeping. (5 Marks)
(a) Name and define the natural cycles that underpin a day, a month, and a year.
(b) Why does a Gregorian leap year occur and what special century rule is followed?
(c) State one key difference between lunar and solar calendars in aligning with seasons.
Q13: Luni-solar practice, national calendar, and festivals. (5 Marks)
(a) What is a luni-solar calendar and how does it keep in step with seasons?
(b) State two features of the Indian National Calendar (Shaka Era) structure and its start date relative to the Gregorian calendar.
(c) Why do many Indian festivals fall on different Gregorian dates each year? Give one lunar and one solar-based example.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test: Keeping Time with the Skies - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the significance of the sky in understanding timekeeping? |  |
| 2. How did ancient civilizations use celestial navigation for timekeeping? |  |
| 3. What are some traditional methods of timekeeping based on the sky? |  |
| 4. How has the study of astronomy influenced modern timekeeping? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand the relationship between time and the sky in today's society? |  |
















