Unit Test: How Nature Works in Harmony | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
Chapter 12: How Nature Works in Harmony — Unit Test with Detailed Solutions
Q1: A habitat consists of (1 Mark)
(i) only living (biotic) components
(ii) only non-living (abiotic) components
(iii) both living and non-living components interacting together
(iv) only producers and consumers
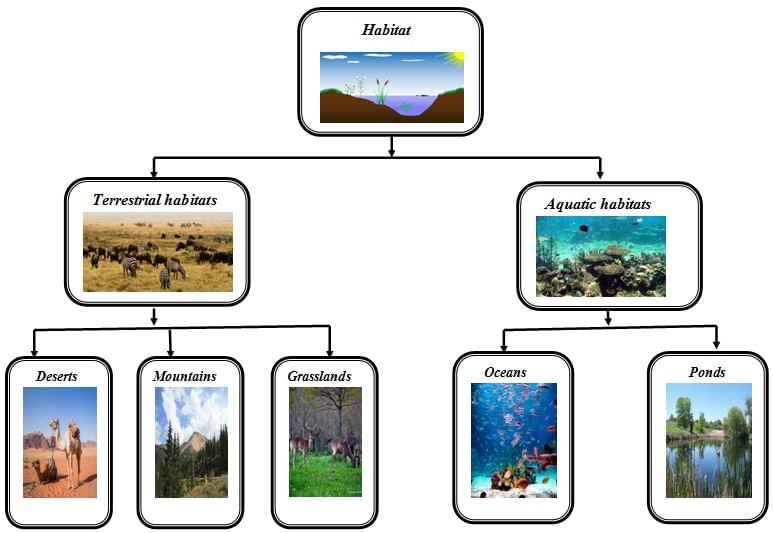
Q2: In a pond, fish obtain oxygen mainly from (1 Mark)
(i) air above the pond surface only
(ii) dissolved oxygen in water
(iii) plants only
(iv) soil
Q3: A population refers to (1 Mark)
(i) different species living together in a habitat
(ii) organisms of the same species in a given area and time
(iii) all living and non-living components in an area
(iv) only producers in a habitat
Q4: Which sequence is a correct food chain in a grassland? (1 Mark)
(i) Eagle → Snake → Frog → Grasshopper → Grass
(ii) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
(iii) Grasshopper → Grass → Frog → Snake → Eagle
(iv) Grass → Snake → Frog → Grasshopper → Eagle
Q5: Mushrooms growing on dead logs are best classified as (1 Mark)
(i) producers
(ii) herbivores
(iii) decomposers (saprotrophs)
(iv) omnivores
Q6: Distinguish between biotic and abiotic components with one example each from a pond. (2 Marks)
Q7: Define community and population, and state how they are related. (2 Marks)
Q8: Why are wildlife corridors (like elephant corridors) important for ecosystem balance? (2 Marks)
Q9: In a pond study, fish reduced dragonfly numbers; pollinators increased near fish ponds and seed set in plants was higher. Explain the indirect effect of fish on plants. (3 Marks)
Q10: Fill the trophic levels in order and give one example for each from a forest. (3 Marks)
(a) 1st trophic level (Producers): _______
(b) 2nd trophic level (Primary consumers): _______
(c) 3rd trophic level (Secondary consumers): _______
(d) 4th trophic level (Tertiary/top carnivores): _______
Q11: Differentiate mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism with one example each from the chapter context. (3 Marks)
Q12: Ecosystem functioning and disruption. (5 Marks)
(a) Explain why decomposers are essential to ecosystem health.
(b) Using the “one change leads to another” idea, describe a plausible chain of impacts if pond plants die due to pollution.
(c) Suggest two human actions to prevent such cascades.
Q13: Sustainable farming and ecosystem services. (5 Marks)
(a) List two drawbacks of overusing synthetic fertilisers and pesticides highlighted by farmers’ experiences.
(b) Propose three eco-friendly practices that enhance soil health and biodiversity in farms.
(c) Explain how natural predators and pollinators support sustainable yields.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test: How Nature Works in Harmony - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key components that contribute to the harmony of nature? |  |
| 2. How do human activities impact the harmony of nature? |  |
| 3. Why is biodiversity important for the sustainability of ecosystems? |  |
| 4. What role do decomposers play in maintaining ecological balance? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to preserving the harmony of nature? |  |















