Unit Test (Solutions): Clothes — How Things are Made | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 45 Minutes
M.M.: 20
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 7 to 9 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 10 carries 5 marks.
Q1. The process of twisting fibres to make yarn is called:
(a) Weaving
(b) Spinning
(c) Stitching
(d) Knitting
Ans: (b) Spinning
Spinning
Q2. Fill in the blanks:
In weaving, threads cross ______ and ______ to make fabric.
Ans: over, under
Q3. True or False:
Silk thread comes from the cocoon of the silk moth.
Ans: True
Q4. Name any one natural fibre mentioned in the chapter.
Ans: Cotton (or wool/silk/linen/jute/bamboo)
Cotton
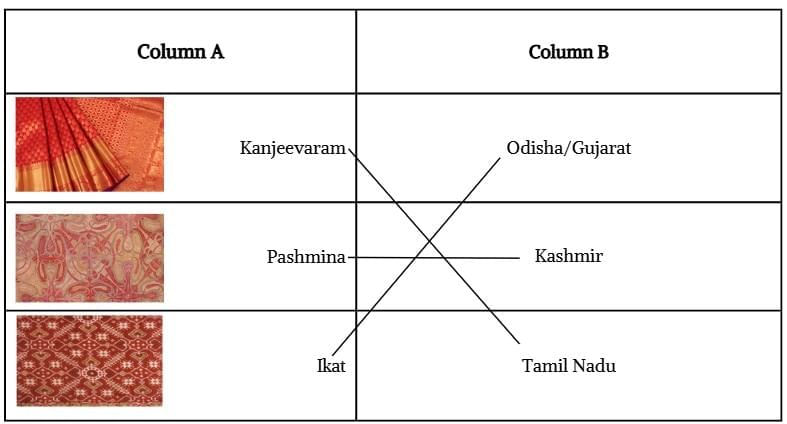
Q5. Match the following: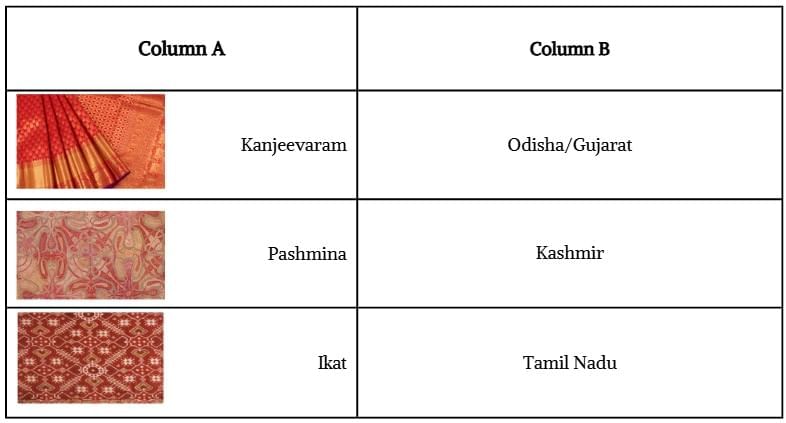
Ans:
Q6. Which stitch did you learn as a basic joining stitch?
(a) Chain stitch
(b) Buttonhole stitch
(c) Running stitch
(d) Cross stitch
Ans: (c) Running stitch
Q7. Explain the difference between natural and synthetic fibres with one example each.
Ans: 1. Natural fibres are breathable/biodegradable; synthetic fibres often dry fast and are durable.
2. Natural fibres come from plants/animals (e.g., cotton from a plant).
3. Synthetic fibres are man-made (e.g., polyester).
Q8. Why is handloom weaving important for people and culture? Give three reasons.
Ans:
handloom weaving
1. Provides livelihoods to many families/artisans.
2. Preserves traditional skills and regional designs.
3. Uses low energy and supports sustainable practices.
Q9. Suggest three ways to reduce cloth waste at home/school.
Ans: 1. Reuse/repurpose old clothes into bags/mats/quilts.
2. Repair (stitch buttons, mend tears) instead of throwing.
3. Donate wearable clothes to those in need.
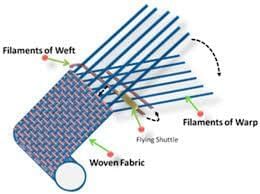
Q10. Draw and label a simple weaving mat pattern and explain in 4–5 sentences how weaving forms fabric.
Ans:
- Two sets of strips/threads: vertical (warp) and horizontal (weft).
- Pass the weft over–under the warp repeatedly.
- The interlacing holds threads together to form a strong sheet.
- Using threads instead of paper creates cloth.
- Patterns change with colours and the over–under order.
|
14 videos|234 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Clothes — How Things are Made - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main processes involved in making clothes? |  |
| 2. What different types of fabrics are commonly used in clothing? |  |
| 3. How has the clothing manufacturing process evolved over time? |  |
| 4. What are the environmental impacts of clothing production? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of clothing in different cultures? |  |