Worksheet: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral System | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| True or False |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. What is the minimum age to vote in India?
(a) 16 years
(b) 18 years
(c) 21 years
(d) 25 years
Q2. Which Article of the Indian Constitution ensures the universal adult franchise?
(a) Article 324
(b) Article 21
(c) Article 326
(d) Article 14
Q3. Which body is responsible for conducting free and fair elections in India?
(a) Parliament of India
(b) Supreme Court of India
(c) Election Commission of India
(d) Planning Commission
Q4. How many constituencies are there for Lok Sabha elections?
(a) 545
(b) 500
(c) 543
(d) 520
Q5. Members of the Rajya Sabha are elected by:
(a) The citizens of India directly
(b) Members of State Legislative Assemblies
(c) The President of India
(d) Governors of States
Q6. Which voting system is used in Lok Sabha elections?
(a) Proportional Representation
(b) Single Transferable Vote
(c) First-Past-the-Post
(d) Indirect Voting
Q7. The “Festival of Democracy” refers to:
(a) Cultural festivals in India
(b) General Elections
(c) Independence Day celebrations
(d) Republic Day
Q8. The President of India is elected by:
(a) All Indian citizens
(b) Judges of the Supreme Court
(c) An Electoral College of MPs and MLAs
(d) Only MPs of Lok Sabha
Q9. Who was the Chief Election Commissioner famous for strict electoral reforms in the 1990s?
(a) Sukumar Sen
(b) Rajiv Gandhi
(c) T.N. Seshan
(d) K.R. Narayanan
Q10. One major challenge of India’s elections is:
(a) Small population
(b) Lack of diversity
(c) Money power and criminalization in politics
(d) Limited number of eligible voters
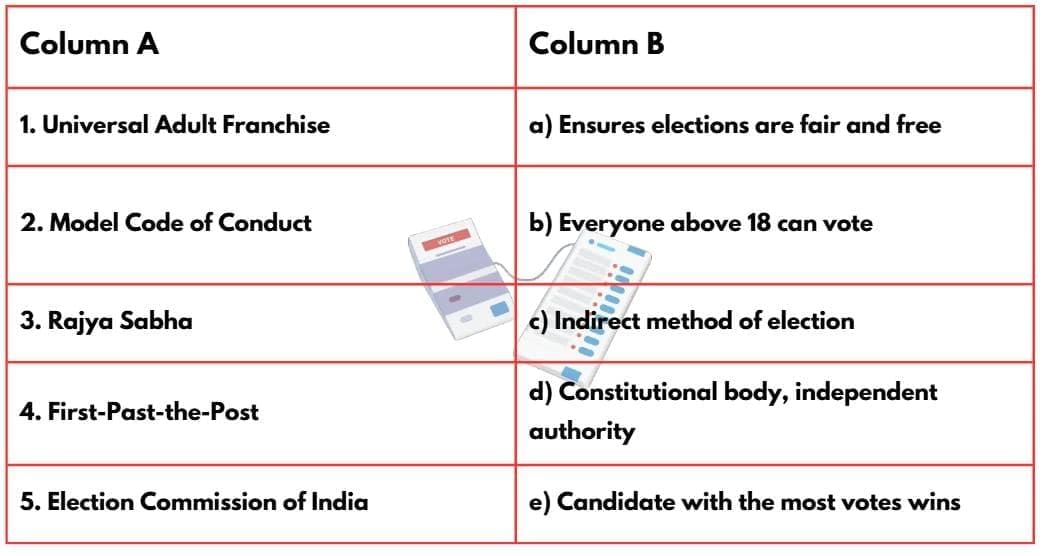
Match the Following
True or False
Q1. Every Indian citizen above 21 years can vote.
Q2. The Lok Sabha has 543 constituencies for elections.
Q3. The Rajya Sabha never dissolves completely.
Q4. Women in India got the right to vote in 1950, much later than Switzerland.
Q5. The Election Commission of India was established in 1950.
Q6. The Model Code of Conduct prevents political leaders from misusing government resources during elections.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1. The right to vote in India is based on ______ adult franchise.
Q2. The Chief Election Commissioner in the 1990s who brought strict reforms was ______.
Q3. Lok Sabha members are also called ______.
Q4. The minimum voting age in India is ______ years.
Q5. Elections in India are often called the “Festival of ______.”
Q6. The Rajya Sabha is also known as the ______ House.
Q7. Article ______ of the Indian Constitution provides for universal adult franchise.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1. Define Universal Adult Franchise in one sentence.
Q2. Who can vote in India?
Q3. What is the value of each vote in India?
Q4. Who conducts the elections in India?
Q5. What is the role of the State Election Commission?
Q6. What do MPs and MLAs stand for?
Q7. Write one key feature of the Model Code of Conduct.
Q8. Why is the Rajya Sabha called the “Permanent House”?
Q9. Which method of voting is used to elect the President of India?
Q10. Mention one challenge faced in conducting elections in India.
You can find Worksheet Solutions here: Worksheet Solutions: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral System
FAQs on Worksheet: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral System - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What is universal franchise and how does it relate to India's electoral system? |  |
| 2. When did India adopt its first Constitution that included universal franchise? |  |
| 3. What are the main features of India's electoral system? |  |
| 4. How does the Election Commission of India ensure free and fair elections? |  |
| 5. What impact does universal franchise have on the political landscape of India? |  |
















