Worksheet Solutions: Factors of Production | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| True or False |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
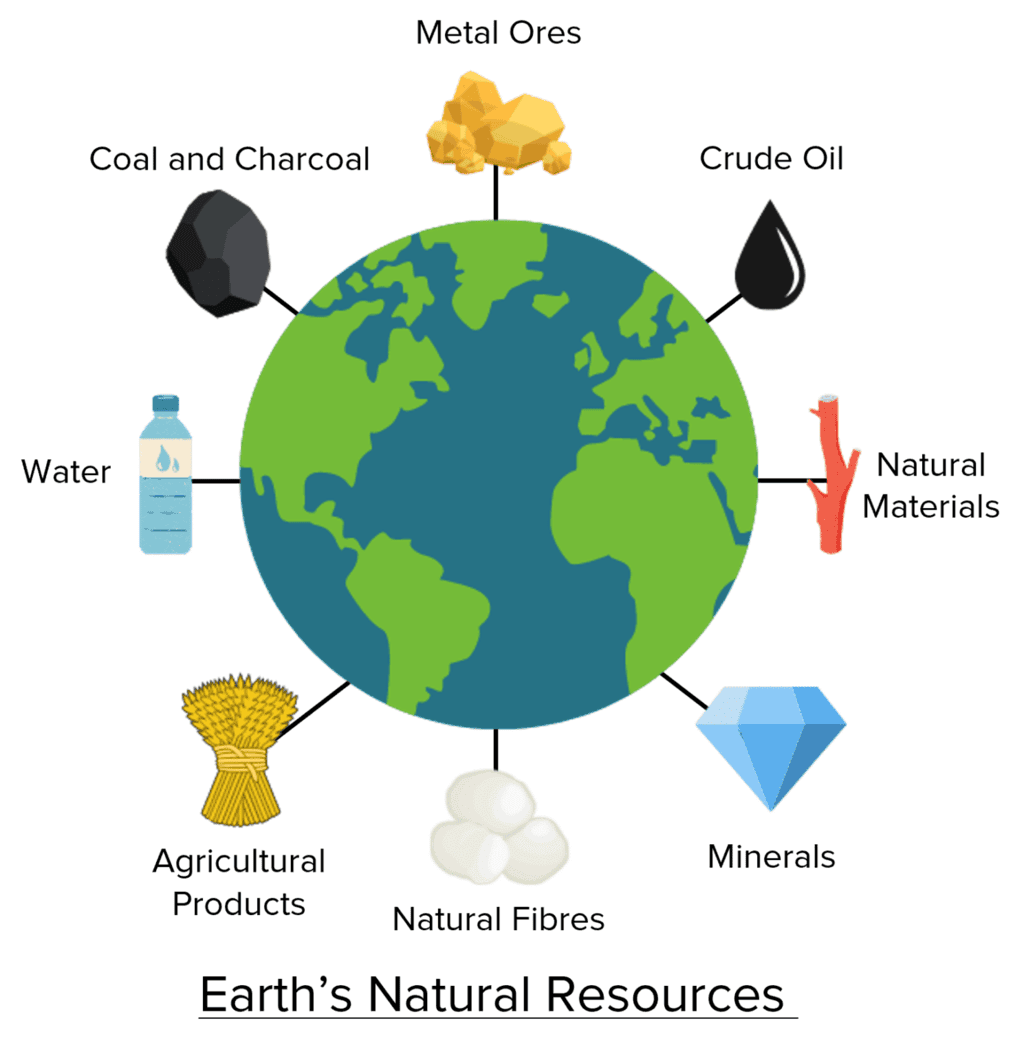
Q1. Which of the following is an example of a natural resource used in production?
(a) Computer software
(b) Minerals and forests
(c) Workers’ skills
(d) Bank loans
Ans: (b) Minerals and forests
These are natural resources, part of land in economics.
Q2. In a production process, the physical and mental effort applied by humans is called—
(a) Capital
(b) Technology
(c) Labour
(d) Land
Ans: (c) Labour
Labour refers to the physical and mental effort applied in production.
Q3. Human capital refers to—
(a) Money invested in business
(b) Machines and tools
(c) Land and natural resources
(d) The quality, skills, and knowledge of workers
Ans: (d) The quality, skills, and knowledge of workers
Human capital is the specialised knowledge, skills, and abilities of workers.
Q4. Which of the following best illustrates entrepreneurship?
(a) A farmer planting crops
(b) A person starting a food delivery startup
(c) A teacher giving online classes
(d) A factory worker assembling phones
Ans: (b) A person starting a food delivery startup
Entrepreneurship involves creating a new business to solve a problem and taking risks.
Q5. Which two main facilitators help improve human capital?
(a) Education and healthcare
(b) Minerals and forests
(c) Loans and machinery
(d) Technology and land
Ans: (a) Education and healthcare
Education improves skills; healthcare ensures workers are healthy and productive.
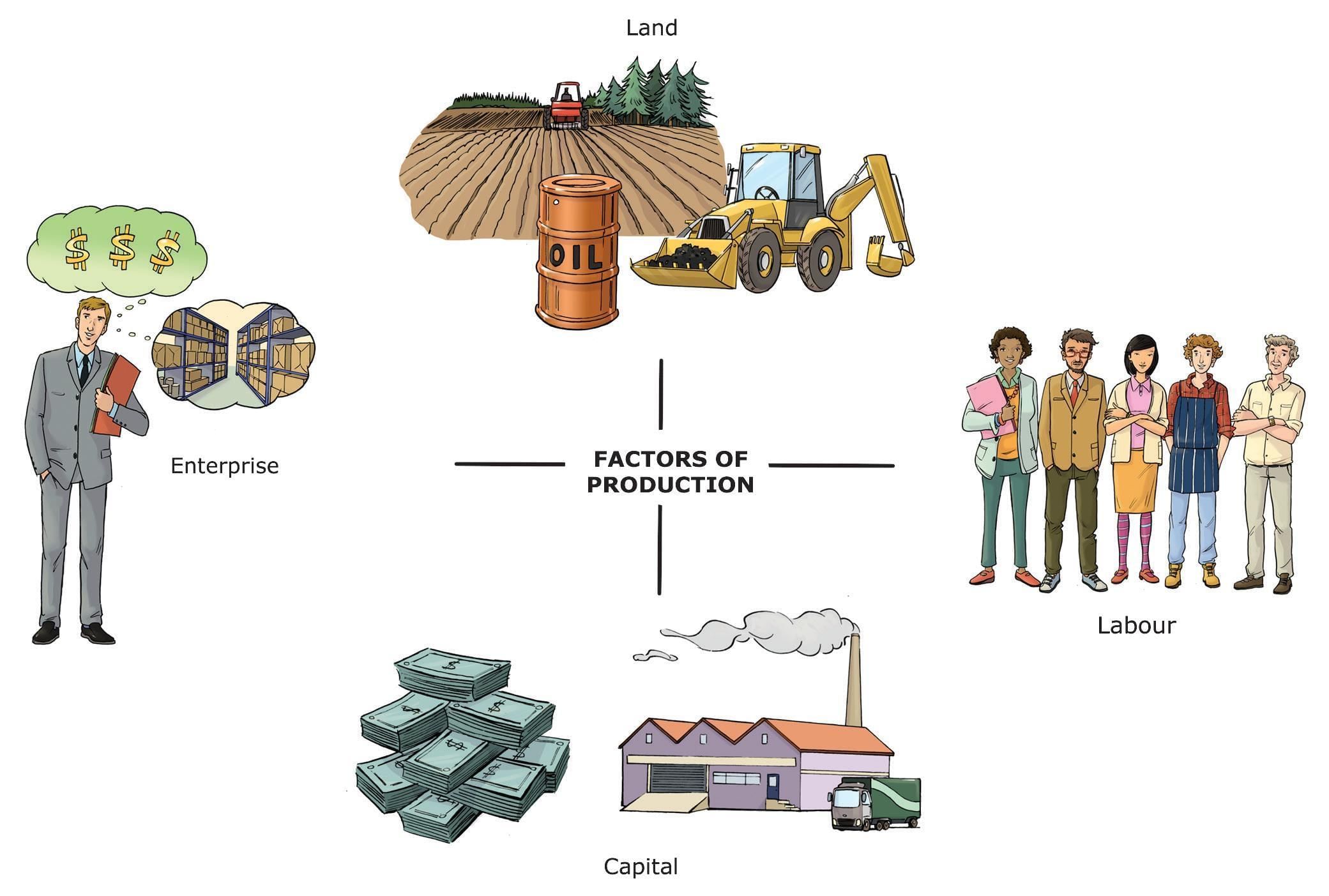
Q6. Capital in economics includes—
(a) Only money
(b) Only land
(c) Machines, tools, buildings, and money
(d) Only labour
Ans: (c) Machines, tools, buildings, and money
Capital includes both financial and physical assets used in production.
Q7. Who among the following started India’s first airline in 1932?
(a) Ratan Tata
(b) Dhirubhai Ambani
(c) J.R.D. Tata
(d) Verghese Kurien
Ans: (c) J.R.D. Tata
J.R.D. Tata founded Tata Airlines in 1932, which later became Air India.
Q8. Which technological innovation helps farmers improve crop health today?
(a) Email communication
(b) Drones spraying fertilisers
(c) Pulley systems
(d) Sewing machines
Ans: (b) Drones spraying fertilisers
Modern technology helps farmers improve crop health through drones.
Q9. The Japanese concept of continuous improvement is called—
(a) Kaizen
(b) Demographic dividend
(c) CSR
(d) SWAYAM
Ans: (a) Kaizen
Kaizen is the Japanese concept of continuous improvement.
Q10. What is the main goal of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
(a) Increase profits only
(b) Avoid taxes
(c) Pay workers less
(d) Benefit society and the environment
Ans: (d) Benefit society and environment
CSR focuses on social and environmental responsibility, not just profits.
Match the Following
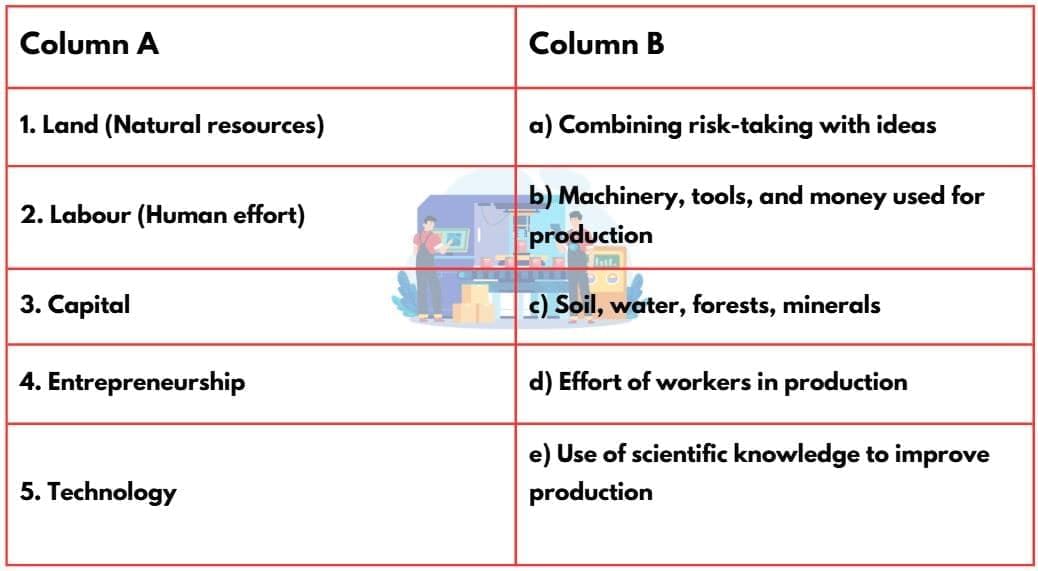
Ans: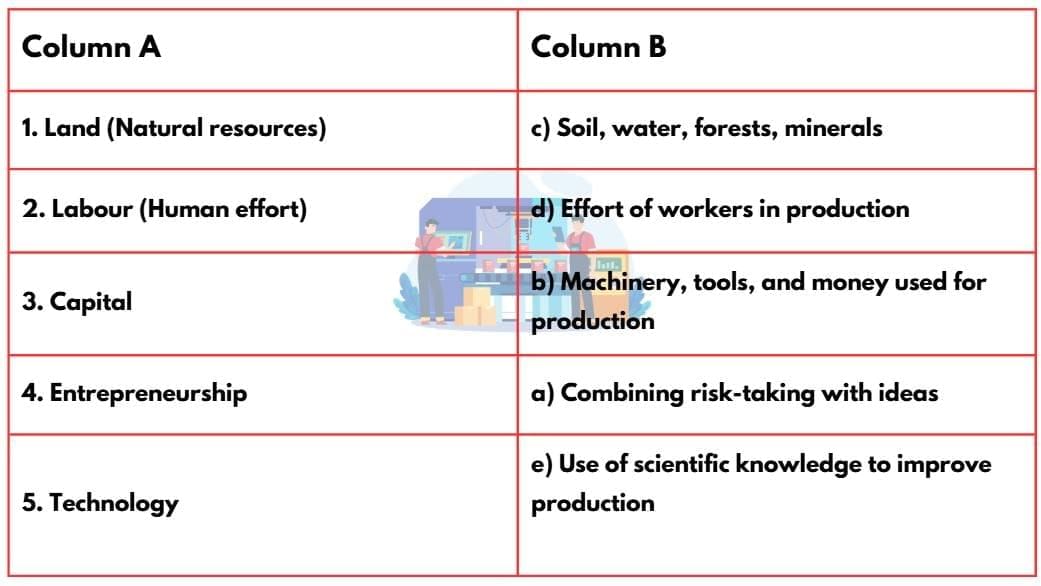
True or False
Q1. Technology is only about machines; it cannot include software.
Ans: False
Technology includes both machines and software.
Q2. Workers’ training and education improve productivity.
Ans: True
Education and training improve productivity.
Q3. Ancient Indians used stitching techniques to build ships.
Ans: True
Ancient Indians used stitching techniques for shipbuilding.
Q4. Entrepreneurs create job opportunities for society.
Ans: True
Entrepreneurs create jobs and contribute to society.
Q5. Supply chain disruption can halt production.
Ans: True
Supply chain disruption can halt production.
Q6. CSR ignores environmental protection and worker welfare.
Ans: False
CSR promotes environmental protection and employee welfare.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1. The four main factors of production are land, labour, capital, and ______.
Ans: Entrepreneurship
Q2. Skills, knowledge, and expertise that improve labour’s efficiency are called ______ capital.
Ans: Human
Q3. Businesses must adopt ______ practices to protect natural resources.
Ans: Sustainable
Q4. J.R.D. Tata founded ______ Airlines in 1932.
Ans: Tata
Q5. The network of individuals, organisations, and resources involved in producing goods is called the ______.
Ans: Supply chain
Q6. Money borrowed from a bank must be repaid with ______.
Ans: Interest
Q7. Online platforms like_______ provide access to online learning opportunities.
Ans: SWAYAM
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1. Define the term “production process”.
Ans: The production process is the sequence of steps through which inputs like land, labour, and capital are combined to create goods or services.
Example: Making a mobile phone involves designing, assembling parts, testing, and packaging.
Q2. Give two examples of technology used in modern production.
Ans: Examples:
- Drones spraying fertilisers in agriculture.
- Robots are assisting in surgeries or assembling products in factories.

Q3. What is human capital, and how is it different from labour?
Ans: Labour is the human effort, physical and mental, used in production. Human capital is the knowledge, skills, and expertise that make labour more effective and efficient.
Example: A trained software engineer vs. an untrained worker doing the same task.
Q4. Name two responsibilities of businesses towards their employees.
Ans: Two responsibilities of businesses towards their employees:
- Providing fair wages and safe working conditions.
- Offering training and skill development opportunities.
Q5. Give an example of entrepreneurship in your local area.
Ans: Starting a roadside food stall, a tailoring shop, a mobile repair service, or a small grocery store.
Q6. Why is education important for building human capital?
Ans: Education equips individuals with knowledge and problem-solving skills, making them productive and capable of performing complex tasks.
Example: Civil engineering students learning construction principles.
Q7. Explain the concept of demographic dividend.
Ans: When a country has a large working-age population and fewer dependents, it can achieve higher economic growth through increased production and consumption.
Q8. Mention one ancient Indian skill or technique used in production.
Ans: The ship stitching technique, where wooden planks were stitched together with cords instead of nails to build flexible maritime vessels.
Q9. What is the purpose of supply chain management in production?
Ans: It ensures the smooth flow of materials, labour, and technology from suppliers to production units to deliver goods efficiently and on time.
Q10. Why should factors of production be used responsibly?
Ans: To prevent resource depletion, environmental pollution, and ensure sustainable production for future generations.
Example: Recycling old electronics and reducing industrial wastewater.
You can find Worksheet Solutions here: Worksheet Solutions: Factors of Production
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Factors of Production - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What are the main factors of production? |  |
| 2. How does the factor of production 'land' contribute to the economy? |  |
| 3. What role does labor play in the production process? |  |
| 4. Why is entrepreneurship considered a vital factor of production? |  |
| 5. How do changes in the factors of production impact economic growth? |  |