NCERT Based Activity: How Nature Works in Harmony | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Activity 12.1: Let us explore
Caution: Explore the habitat in groups with your teacher.
- Identify two habitats in your surroundings.
- These could be any two of the following: a pond, a forest, an agricultural farm, or even a large tree like banyan, mango, or pilkhan (white fig) tree.
- List the living beings and non-living things that you observe in these habitats.
- Record your observations in Table 12.1.
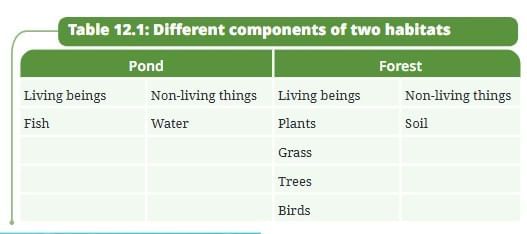
Table 12.1: Different components of two habitats (example: Pond and Forest, completed with sample observations):
| Pond | Forest | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Living beings | Non-living things | Living beings | Non-living things |
| Fish | Water | Plants | Soil |
| Frogs | Sunlight | Grass | Air |
| Snakes | Temperature | Trees | Rock |
| Dragonflies | Mud | Birds | Water (streams) |
| Mosquitos | Deer | ||
| Snails | Insects | ||
| Ducks | Snakes | ||
| Algae | Fungi | ||
| Diatoms | |||
| Duckweeds | |||
| Lotus | |||
Q. What common characteristics do you observe in the two habitats in Activity 12.1?
Ans: Both habitats have living beings (biotic components) as well as non-living things (abiotic components), but the types of living beings and non-living things vary, offering different living conditions.
Activity 12.2: Let us record
We can understand the population of a particular type of plant by counting them at a given place and time.
- Divide students into four to five groups.
- Each group may identify any two organisms, plant(s) or animal(s).
- Mark an area of 1 m × 1 m in your school garden.
- Identify four organisms in this area, and count their numbers.
- Record the number of the organisms in Table 12.2.
- Compile the data from all groups.
Table 12.2: Number of particular organisms at a given space and time (sample completed):
| Name of organism | Population (Number of individual organisms) |
|---|---|
| Plant 1: Grass | 20 |
| Plant 2: Weed | 05 |
| Animal 1: Ant | 15 |
| Animal 2: Earthworm | 03 |
Q. In the given example, there is a population of 20 ______ plants and is only 5 ______ plants in the same 1×1 m2 area.
Ans: There is a population of 20 grass plants and only 5 weed plants in the same 1×1 m² area.
Activity 12.3: Let us read
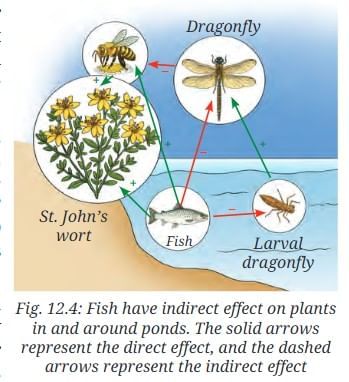
- Researchers conducted a study to see how fish in ponds affect seed production in the plants nearby. They observed two ponds—A with fish and large number of flowering plants around it; B without fish and fewer flowering plants around it (Fig. 12.3). Think of a reason for these observations.

Ans: Pond A has more flowering plants because fish reduce dragonfly larvae, leading to fewer dragonflies, more pollinators (bees, butterflies), and better pollination/seed production. Pond B has more dragonflies, fewer pollinators, and less seed production. - Compare the number of dragonflies, bees, and butterflies in both the ponds. Do you find any relationship between the number of dragonflies and bees/butterflies?
Ans: Pond A (with fish): Fewer dragonflies, more bees/butterflies. Pond B (without fish): More dragonflies, fewer bees/butterflies. Relationship: More dragonflies reduce bees/butterflies (as dragonflies eat them). - We observed that in Pond A (with fish) the number of dragonflies were less as compared to Pond B. Why?
Ans: Fish eat dragonfly larvae, so Pond A has fewer dragonflies. - What does this study show? How does the population of fish in a pond affect the seed production in nearby plants?
Ans: The study shows interactions between biotic (fish, dragonflies, pollinators, plants) and abiotic components. Fish reduce dragonflies, increasing pollinators, which boost seed production in plants. - This study shows how biotic components (fish, dragonflies, pollinators, plants) and abiotic components (temperature, water, nutrients) interact with and affect each other (Fig. 12.4). Similarly, can overfishing by humans change this balance? How do you think it may affect the living and non-living parts of the habitat?
Ans: Overfishing reduces fish, increasing dragonflies, decreasing pollinators, reducing seed production. This affects plant growth (biotic), nutrient cycling, water quality (abiotic), and overall habitat balance.
Activity 12.4: Let us relate and identify
- Based on the given criteria, identify and describe the interactions between biotic and abiotic components shown in Fig. 12.5.

- Criterion 1: Interactions between abiotic and biotic components. These may influence life processes like nutrition, respiration, and reproduction in biotic components.
- Criterion 2: Interaction between two abiotic components these may influence the physical characteristics of a habitat.
- Criterion 3: Interaction among the biotic components. These may influence the availability of resources needed for life processes like nutrition, respiration, and reproduction.
- Relate your learning with your observations.
- Record your observations in Table 12.3 at the appropriate places. Table 12.3 is filled with examples for your reference.
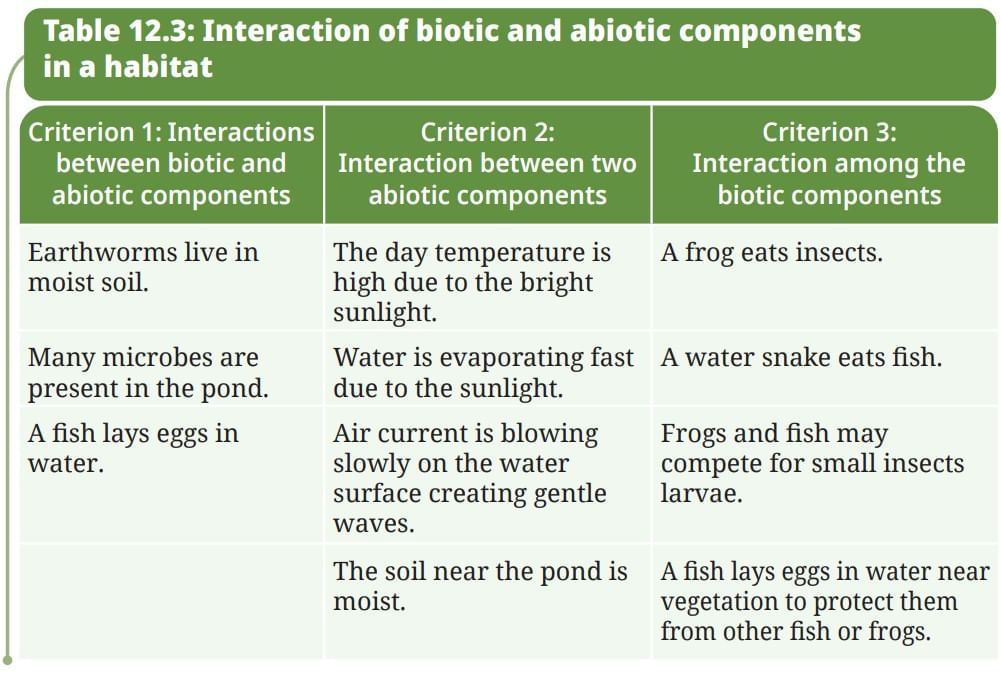
Table 12.3: Interaction of biotic and abiotic components in a habitat (completed with additional examples):
| Criterion 1: Interactions between biotic and abiotic components | Criterion 2: Interaction between two abiotic components | Criterion 3: Interaction among the biotic components |
|---|---|---|
| Earthworms live in moist soil. | The day temperature is high due to the bright sunlight. | A frog eats insects. |
| Many microbes are present in the pond. | Water is evaporating fast due to the sunlight. | A water snake eats fish. |
| A fish lays eggs in water. | Air current is blowing slowly on the water surface creating gentle waves. | Frogs and fish may compete for small insects larvae. |
| The soil near the pond is moist. | A fish lays eggs in water near vegetation to protect them from other fish or frogs. | |
| Plants absorb sunlight for photosynthesis. | Soil absorbs water, affecting humidity. | Birds compete with squirrels for fruits. |
| Frogs breathe oxygen from air. | Wind influences temperature. | Plants provide shelter to insects. |
Activity 12.5: Let us classify
- Observe Fig 12.1b, which illustrates a forest ecosystem.

- Study the picture carefully and spot the organisms listed in Table 12.4.
- Using the internet or your school library, find out what do these organisms eat.
- Record your observations in Table 12.4 by identifying whether each organism feeds only on plants and plant products, only on animals, or on both.
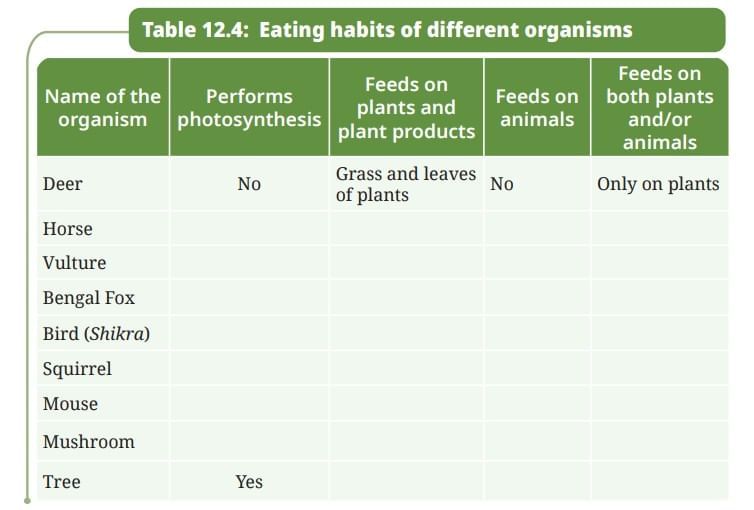
Table 12.4: Eating habits of different organisms (completed):
| Name of the organism | Performs photosynthesis | Feeds on plants and plant products | Feeds on animals | Feeds on both plants and/or animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deer | No | Grass and leaves of plants | No | Only on plants |
| Horse | No | Grass, hay | No | Only on plants |
| Vulture | No | No | Dead animals (carrion) | Only on animals |
| Bengal Fox | No | Fruits, berries | Small animals, insects | Both |
| Bird (Shikra) | No | No | Small birds, rodents | Only on animals |
| Bird | No | Seeds, fruits | Insects | Both |
| Squirrel | No | Nuts, seeds | No | Only on plants |
| Mouse | No | Seeds, grains | Insects occasionally | Both |
| Mushroom | No | Dead organic matter (not plants directly) | No | Decomposer |
| Tree | Yes | No | No | Producer |
Q. List the heterotrophs from Table 12.4.
Ans: Deer, Horse, Vulture, Bengal Fox, Bird (Shikra), Bird, Squirrel, Mouse, Mushroom (consumers/decomposers).
Activity 12.6: Let us link (relate)
- Take an example of a grassland ecosystem.
- Consider the following organisms that we can spot in a grassland ecosystem: grass, frog, hare, fox, grasshopper, snake, and eagle.
- In Fig. 12.8, a relationship of who eats whom is shown among some of the organisms.
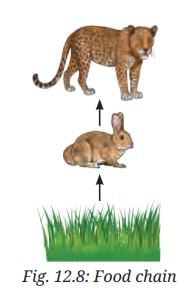
- Draw the feeding relationships for the remaining organisms by adding arrows, similar to those in Fig. 12.8.
Ans: Grass → Grasshopper; Grasshopper → Frog; Frog → Snake; Snake → Eagle; Grass → Hare; Hare → Fox; Grasshopper → Snake (possible); Bird (if present) → Grasshopper/Frog.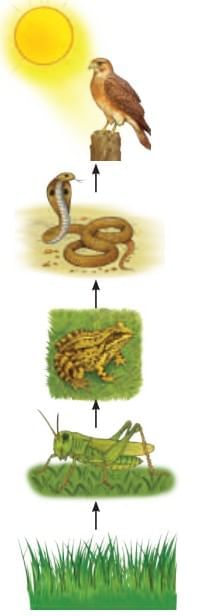
- Which is another food chain that can be drawn for the organisms given in this activity? One example may be as follows: Grass, Grasshopper, Frog, Snake, Eagle
Ans: Another food chain: Grass → Hare → Fox → Eagle (if eagle eats fox, though eagle typically eats snakes/small mammals).
Activity 12.7: Let us draw
Fig. 12.10a represents a crop field with millets, mouse, and eagle.
- Count the number of each type of organism in Fig. 12.10a.
Ans: Assume sample counts: Millets: 50 plants, Mouse: 10, Eagle: 1 - Make a table and set a number in the table against each of the organisms.
| Organism | Number |
|---|---|
| Millets | 50 |
| Mouse | 10 |
| Eagle | 1 |
- Arrange the numbers in the ascending order, consider the highest number at the base and the lowest at the top.
Ans: Base: 50 (millets), Middle: 10 (mouse), Top: 1 (eagle). - Place the mouse, millet, and eagle appropriately in Fig. 12.10b.
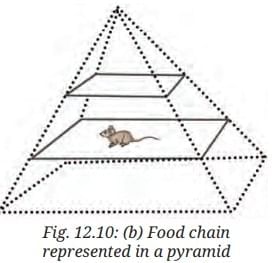
Ans: Base: Millets, Middle: Mouse, Top: Eagle. - What figure do you get? It looks like a pyramid. Complete the pyramid in Fig. 12.10b.
Ans: The figure is a pyramid of numbers, showing decreasing population from producers (millets) to herbivores (mouse) to carnivores (eagle).
Activity 12.8: Let us trace and link
- Look at Fig. 12.11.
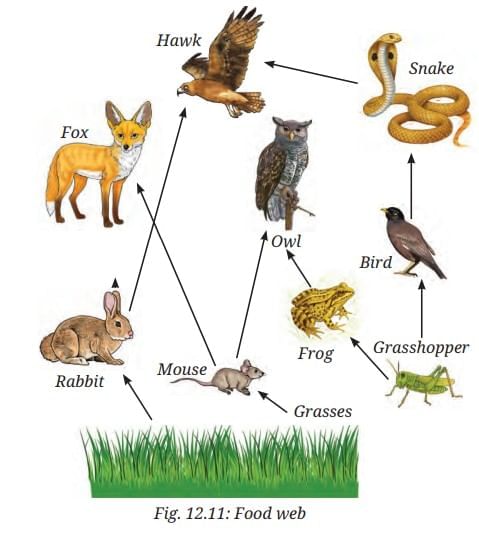
- Look at the figure and put more arrows for the missing relationship of ‘who eats whom’.
Ans: Additional arrows: Grasses → Rabbit; Grasses → Mouse; Grasshopper → Bird; Grasshopper → Frog; Rabbit → Fox; Mouse → Fox; Mouse → Owl; Mouse → Snake; Frog → Owl; Frog → Hawk; Snake → Hawk; Snake → Owl; Bird → Snake; Bird → Hawk. - How many other organisms might be connected to one organism through a feeding relationship in an ecosystem?
Ans: One organism can be connected to multiple (e.g., mouse eaten by fox, owl, snake; grasses eaten by grasshopper, rabbit, mouse).
Activity 12.9: Let us read
- In the 1980s, India was a significant exporter of frog legs, especially of the Indian bullfrog (Hoplobatrachus tigerinus) (Fig. 12.14). This large-scale harvesting led to a decline in frog populations. Since frogs eat insects, their reduced numbers resulted in a rise in agricultural pests. This forced farmers to use more synthetic pesticides, which harmed the environment, soil and water quality, and affected the overall environmental and human health. The Government of India banned the export of frog legs to prevent further ecological damage.
(No explicit questions, but implied: What does this show about ecosystem balance?)
Ans: This shows that disrupting one species (frogs) affects pest control, increasing pesticide use, harming environment/health. Balance requires stable populations/resources.
Activity 12.10: Let us survey
- Visit a nearby farm with your parents or teacher/interact with farmers in your community to find out about the farming practices they adopt.
- Prepare a list of questions for farmers to find out the pesticides and other farm inputs they use, and whether they reuse or recycle materials to improve their crops. Here are some sample questions:
- How have your farming practices changed over time? And why?
Ans: Changed from organic to synthetic fertilizers/pesticides for higher yields, but now shifting back due to soil degradation. - What effects do you notice when using synthetic fertilisers and pesticides?
Ans: Increased yields initially, but soil fertility decreased, pests resistant, health issues. - Have you seen any changes in soil health after using these synthetic fertilisers and pesticides?
Ans: Soil became harder, less fertile, fewer earthworms. - Interact with farmers based on these questions. Based on your findings, prepare a report.
Ans: Report: Synthetic inputs improved production but harmed soil/microbes; sustainable practices like organic farming needed. - What inference do you draw from your interactions with farmers?
Ans: Overuse of synthetics degrades soil, increases pests; eco-friendly methods sustain long-term health.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: How Nature Works in Harmony - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key principles of how nature works in harmony? |  |
| 2. How does human activity impact the harmony of nature? |  |
| 3. What role do ecosystems play in maintaining environmental harmony? |  |
| 4. Why is biodiversity important for the harmony of nature? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to the harmony of nature in their daily lives? |  |





















