Practice Question - 78 (Scheduling) | 100 DILR Questions for CAT Preparation PDF Download
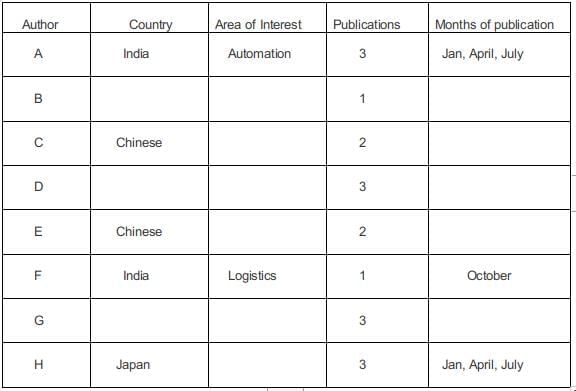
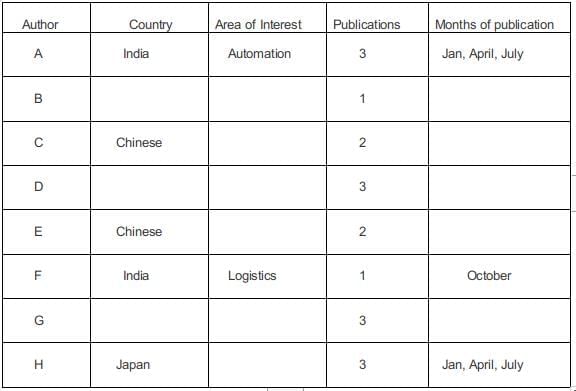
A journal plans to publish 18 research papers, written by eight authors (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H) in four issues of the journal scheduled in January, April, July and October. Each of the research papers was written by exactly one of the eight authors. Five papers were scheduled in each of the first two issues, while four were scheduled in each of the last two issues. Every author wrote at least one paper and at most three papers. The total number of papers written by A, D, G and H was double the total number of papers written by the other four authors. Four of the authors were from India and two each were from Japan and China. Each author belonged to exactly one of the three areas — Manufacturing, Automation, and Logistics. Four of the authors were from the Logistics area and two were from the Automation area. As per the journal policy, none of the authors could have more than one paper in any issue of the journal.
The following facts are also known.
- F, an Indian author from the Logistics area, wrote only one paper. It was scheduled in the October issue.
- A was from the Automation area and did not have a paper scheduled in the October issue.
- None of the Indian authors were from the Manufacturing area and none of the Japanese or Chinese authors were from the Automation area.
- A and H were from different countries, but had their papers scheduled in exactly the same issues.
- C and E, both Chinese authors from different areas, had the same number of papers scheduled. Further, E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues of the journal but C did not.
- B, from the Logistics area, had a paper scheduled in the April issue of the journal.
- B and G belonged to the same country. None of their papers were scheduled in the same issue of the journal.
- D, a Japanese author from the Manufacturing area, did not have a paper scheduled in the July issue.
- C and H belonged to different areas.
Q1: What is the correct sequence of number of papers written by B, C, E and G, respectively?
(a) 1, 2, 2, 3
(b) 1, 3, 3, 1
(c) 3, 1, 1, 3
(d) 1, 2, 2, 1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
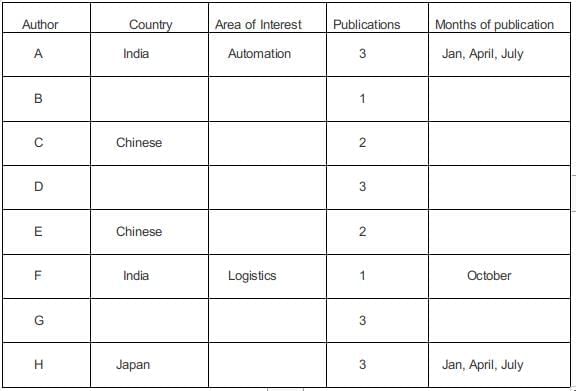
In the information, it is provided that there are four authors in the logistics department, 2 authors in automation, and 2 authors in manufacturing. There are 4 Indian authors, 2 Chinese authors, and 2 Japanese authors.
The total issues publicized were 18 of which the publications done by A, D, G, H are twice the papers written by the other four authors. Hence A + D + G + H has written 12 papers in total and B + C + E + F has written 6 in total. Since an author can write a minimum of 4 papers and a maximum of 3 papers. Each of A, D, G, H must have written 3 papers each.
In statement 3 it was provided that none of the Indian authors were from the Manufacturing area and none of the Japanese or Chinese authors were from the Automation area.
Since none of the Japanese and Chinese authors belonged to automation. Hence the two automation authors must be from India. In statement 1 it was given that F an Indian author is from logistics.
Of the remaining 5 authors 3 from logistics and 2 from manufacturing, in statement 5 it is given that the two Chinese authors are from different areas and hence they must be from manufacturing and logistics.
Of the remaining 3 authors 2 in logistics and 1 in manufacturing, in statement 8 is given that a Japanese author belonged to manufacturing, and hence of the remaining 2 in logistics one of them was from India and the other from Japan.
Of the four Indian authors, 2 belonged to logistics and 2 automation. Of the two authors from Japan, one belonged to manufacturing and one logistics. Of the two Chinese authors, one of them belonged to logistics and the other manufacturing.
Five papers were scheduled in each of the January and April issues, while four were scheduled in each of July and October issues.
Using statement 1, F an Indian author wrote a single paper in logistics published in October.
Using statement 2, A was from Automation and did not have a paper scheduled in October. Since A wrote 3 papers in total he must have written in the other three months and since only Indian authors worked in Automation he must have been from India.
Using statement 5, C, E are Chinese and wrote an equal number of papers. Since B + C + E + F have written a total of 6 papers. The two possibilities are 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 or 3 + 1 + 1 + 1.. Since it was given that E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues and C did not. So the only possible case is C = 2, E = 2, F = 1, B = 1.
Using statement 4, A and H were from different countries and wrote papers in the same months. Hence H must be Japanese and must have written in Jan, April, July.
In statement 6, B, from the Logistics area, had a paper scheduled in the April issue of the journal.
In statement 7, B and G belonged to the same country. None of their papers were scheduled in the same issue of the journal. Since B and G belonged to the same country the only possibility is that both of them belonged to the same country and since they published Journals in different months. G must have published in January, July, and October.
In statement 8, D, a Japanese author from the Manufacturing area, did not have a paper scheduled in the July issue. Hence he must have had the three issues in Jan, April, Oct. The other Japanese author H must have written in logistics.
The fourth Indian author G must have written a paper in Automation.
In January, one more paper needs to be publicized, one in April, 1 in July, and one in October.
In statement 5, E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues of the journal but C did not.
Hence C must have written in Jan and October, and E in April and July.
In statement 9, C and H belonged to different areas. Hence C must be from Manufacturing and E must be from Logistics.
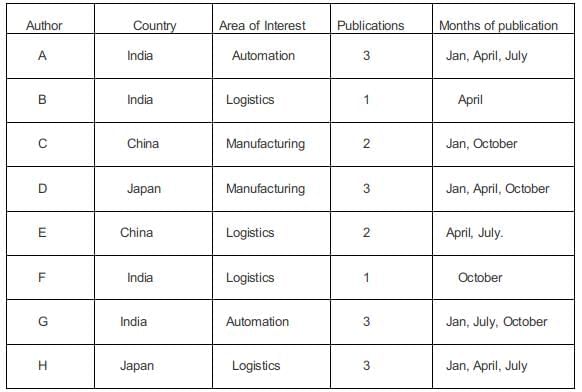
Number of papers written by B, C, E, and G are: 1, 2, 2, 3.
Q2: How many papers were written by Indian authors?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 8
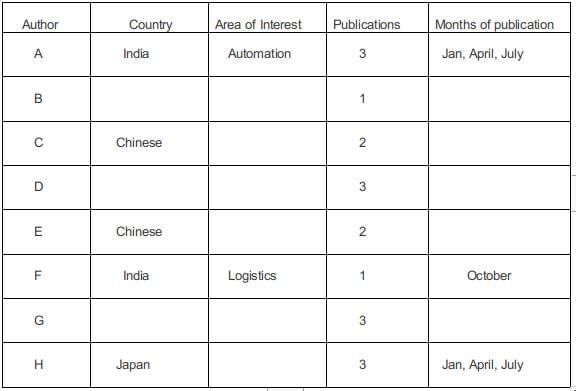
In the information, it is provided that there are four authors in the logistics department, 2 authors in automation, and 2 authors in manufacturing. There are 4 Indian authors, 2 Chinese authors, and 2 Japanese authors.
The total issues publicized were 18 of which the publications done by A, D, G, H are twice the papers written by the other four authors. Hence A + D + G + H has written 12 papers in total and B + C + E + F has written 6 in total. Since an author can write a minimum of 4 papers and a maximum of 3 papers. Each of A, D, G, H must have written 3 papers each.
In statement 3 it was provided that none of the Indian authors were from the Manufacturing area and none of the Japanese or Chinese authors were from the Automation area.
Since none of the Japanese and Chinese authors belonged to automation. Hence the two automation authors must be from India. In statement 1 it was given that F an Indian author is from logistics.
Of the remaining 5 authors 3 from logistics and 2 from manufacturing, in statement 5 it is given that the two Chinese authors are from different areas and hence they must be from manufacturing and logistics.
Of the remaining 3 authors 2 in logistics and 1 in manufacturing, in statement 8 is given that a Japanese author belonged to manufacturing, and hence of the remaining 2 in logistics one of them was from India and the other from Japan.
Of the four Indian authors, 2 belonged to logistics and 2 automation. Of the two authors from Japan, one belonged to manufacturing and one logistics. Of the two Chinese authors, one of them belonged to logistics and the other manufacturing.
Five papers were scheduled in each of the January and April issues, while four were scheduled in each of July and October issues.
Using statement 1, F an Indian author wrote a single paper in logistics published in October.
Using statement 2, A was from Automation and did not have a paper scheduled in October. Since A wrote 3 papers in total he must have written in the other three months and since only Indian authors worked in Automation he must have been from India.
Using statement 5, C, E are Chinese and wrote an equal number of papers. Since B + C + E + F have written a total of 6 papers. The two possibilities are 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 or 3 + 1 + 1 + 1.. Since it was given that E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues and C did not. So the only possible case is C = 2, E = 2, F = 1, B = 1.
Using statement 4, A and H were from different countries and wrote papers in the same months. Hence H must be Japanese and must have written in Jan, April, July.
In statement 6, B, from the Logistics area, had a paper scheduled in the April issue of the journal.
In statement 7, B and G belonged to the same country. None of their papers were scheduled in the same issue of the journal. Since B and G belonged to the same country the only possibility is that both of them belonged to the same country and since they published Journals in different months. G must have published in January, July, and October.
In statement 8, D, a Japanese author from the Manufacturing area, did not have a paper scheduled in the July issue. Hence he must have had the three issues in Jan, April, Oct. The other Japanese author H must have written in logistics.
The fourth Indian author G must have written a paper in Automation.
In January, one more paper needs to be publicized, one in April, 1 in July, and one in October.
In statement 5, E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues of the journal but C did not.
Hence C must have written in Jan and October, and E in April and July.
In statement 9, C and H belonged to different areas. Hence C must be from Manufacturing and E must be from Logistics.
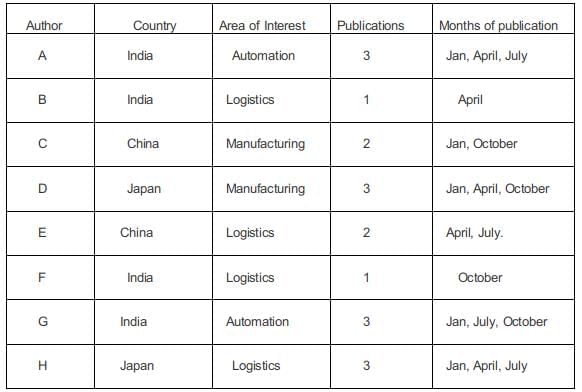
Indian authors wrote a total of 3 + 1 + 1 + 3 = 8 papers
Q3: Which of the following statement(s) MUST be true?
Statement A: Every issue had at least one paper by author(s) from each country.
Statement B: Every issue had at most two papers by author(s) from each area.
(a) Both the statements
(b) Only Statement B
(c) Only Statement A
(d) Neither of the statements
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
In the information, it is provided that there are four authors in the logistics department, 2 authors in automation, and 2 authors in manufacturing. There are 4 Indian authors, 2 Chinese authors, and 2 Japanese authors.
The total issues publicized were 18 of which the publications done by A, D, G, H are twice the papers written by the other four authors. Hence A + D + G + H has written 12 papers in total and B + C + E + F has written 6 in total. Since an author can write a minimum of 4 papers and a maximum of 3 papers. Each of A, D, G, H must have written 3 papers each.
In statement 3 it was provided that none of the Indian authors were from the Manufacturing area and none of the Japanese or Chinese authors were from the Automation area.
Since none of the Japanese and Chinese authors belonged to automation. Hence the two automation authors must be from India. In statement 1 it was given that F an Indian author is from logistics.
Of the remaining 5 authors 3 from logistics and 2 from manufacturing, in statement 5 it is given that the two Chinese authors are from different areas and hence they must be from manufacturing and logistics.
Of the remaining 3 authors 2 in logistics and 1 in manufacturing, in statement 8 is given that a Japanese author belonged to manufacturing, and hence of the remaining 2 in logistics one of them was from India and the other from Japan.
Of the four Indian authors, 2 belonged to logistics and 2 automation. Of the two authors from Japan, one belonged to manufacturing and one logistics. Of the two Chinese authors, one of them belonged to logistics and the other manufacturing.
Five papers were scheduled in each of the January and April issues, while four were scheduled in each of July and October issues.
Using statement 1, F an Indian author wrote a single paper in logistics published in October.
Using statement 2, A was from Automation and did not have a paper scheduled in October. Since A wrote 3 papers in total he must have written in the other three months and since only Indian authors worked in Automation he must have been from India.
Using statement 5, C, E are Chinese and wrote an equal number of papers. Since B + C + E + F have written a total of 6 papers. The two possibilities are 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 or 3 + 1 + 1 + 1.. Since it was given that E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues and C did not. So the only possible case is C = 2, E = 2, F = 1, B = 1.
Using statement 4, A and H were from different countries and wrote papers in the same months. Hence H must be Japanese and must have written in Jan, April, July.
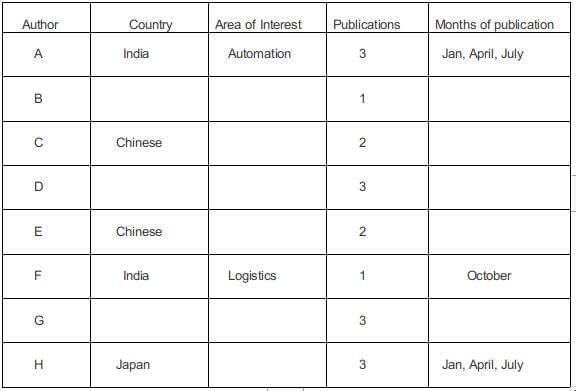
In statement 6, B, from the Logistics area, had a paper scheduled in the April issue of the journal.
In statement 7, B and G belonged to the same country. None of their papers were scheduled in the same issue of the journal. Since B and G belonged to the same country the only possibility is that both of them belonged to the same country and since they published Journals in different months. G must have published in January, July, and October.
In statement 8, D, a Japanese author from the Manufacturing area, did not have a paper scheduled in the July issue. Hence he must have had the three issues in Jan, April, Oct. The other Japanese author H must have written in logistics.
The fourth Indian author G must have written a paper in Automation.
In January, one more paper needs to be publicized, one in April, 1 in July, and one in October.
In statement 5, E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues of the journal but C did not.
Hence C must have written in Jan and October, and E in April and July.
In statement 9, C and H belonged to different areas. Hence C must be from Manufacturing and E must be from Logistics.
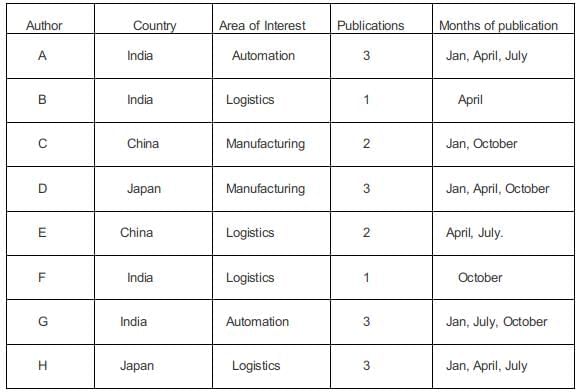
The publication of April has three authors from logistics. Hence false
Q4: Which of the following statements is FALSE?
(a) Every issue had at least one paper by author(s) from Automation area.
(b) Every issue had exactly one paper by a Chinese author.
(c) Every issue had exactly two papers by authors from Logistics area.
(d) Every issue had exactly two papers by Indian authors.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
In the information, it is provided that there are four authors in the logistics department, 2 authors in automation, and 2 authors in manufacturing. There are 4 Indian authors, 2 Chinese authors, and 2 Japanese authors.
The total issues publicized were 18 of which the publications done by A, D, G, H are twice the papers written by the other four authors. Hence A + D + G + H has written 12 papers in total and B + C + E + F has written 6 in total. Since an author can write a minimum of 4 papers and a maximum of 3 papers. Each of A, D, G, H must have written 3 papers each.
In statement 3 it was provided that none of the Indian authors were from the Manufacturing area and none of the Japanese or Chinese authors were from the Automation area.
Since none of the Japanese and Chinese authors belonged to automation. Hence the two automation authors must be from India. In statement 1 it was given that F an Indian author is from logistics.
Of the remaining 5 authors 3 from logistics and 2 from manufacturing, in statement 5 it is given that the two Chinese authors are from different areas and hence they must be from manufacturing and logistics.
Of the remaining 3 authors 2 in logistics and 1 in manufacturing, in statement 8 is given that a Japanese author belonged to manufacturing, and hence of the remaining 2 in logistics one of them was from India and the other from Japan.
Of the four Indian authors, 2 belonged to logistics and 2 automation. Of the two authors from Japan, one belonged to manufacturing and one logistics. Of the two Chinese authors, one of them belonged to logistics and the other manufacturing.
Five papers were scheduled in each of the January and April issues, while four were scheduled in each of July and October issues.
Using statement 1, F an Indian author wrote a single paper in logistics published in October.
Using statement 2, A was from Automation and did not have a paper scheduled in October. Since A wrote 3 papers in total he must have written in the other three months and since only Indian authors worked in Automation he must have been from India.
Using statement 5, C, E are Chinese and wrote an equal number of papers. Since B + C + E + F have written a total of 6 papers. The two possibilities are 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 or 3 + 1 + 1 + 1.. Since it was given that E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues and C did not. So the only possible case is C = 2, E = 2, F = 1, B = 1.
Using statement 4, A and H were from different countries and wrote papers in the same months. Hence H must be Japanese and must have written in Jan, April, July.
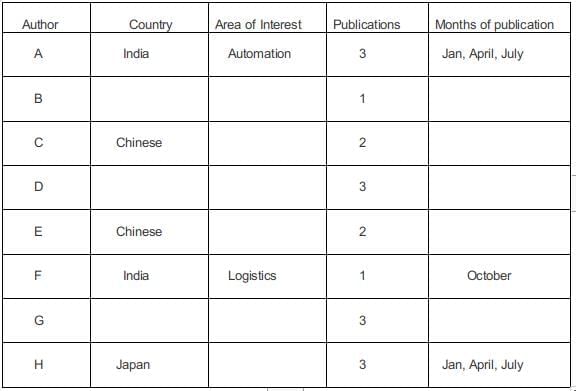
In statement 6, B, from the Logistics area, had a paper scheduled in the April issue of the journal.
In statement 7, B and G belonged to the same country. None of their papers were scheduled in the same issue of the journal. Since B and G belonged to the same country the only possibility is that both of them belonged to the same country and since they published Journals in different months. G must have published in January, July, and October.
In statement 8, D, a Japanese author from the Manufacturing area, did not have a paper scheduled in the July issue. Hence he must have had the three issues in Jan, April, Oct. The other Japanese author H must have written in logistics.
The fourth Indian author G must have written a paper in Automation.
In January, one more paper needs to be publicized, one in April, 1 in July, and one in October.
In statement 5, E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues of the journal but C did not.
Hence C must have written in Jan and October, and E in April and July.
In statement 9, C and H belonged to different areas. Hence C must be from Manufacturing and E must be from Logistics.
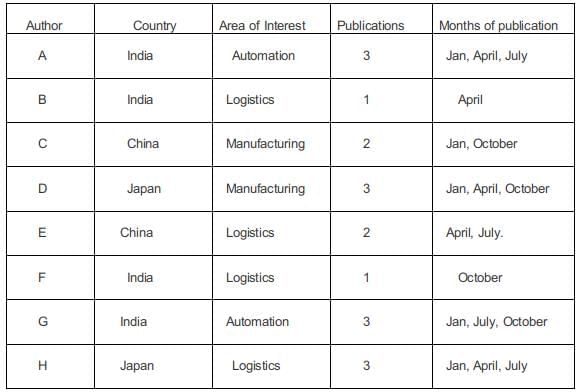
Option C is false in the issue of April there were three authors from logistics department.
Q5: Which of the following statements is FALSE?
(a) There were exactly two papers by authors from Manufacturing area in the January issue.
(b) There was exactly one paper by an author from Manufacturing area in the April issue.
(c) There was exactly one paper by an author from Logistics area in the October issue.
(d) There were exactly two papers by authors from Manufacturing area in the July issue.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
In the information, it is provided that there are four authors in the logistics department, 2 authors in automation, and 2 authors in manufacturing. There are 4 Indian authors, 2 Chinese authors, and 2 Japanese authors.
The total issues publicized were 18 of which the publications done by A, D, G, H are twice the papers written by the other four authors. Hence A + D + G + H has written 12 papers in total and B + C + E + F has written 6 in total. Since an author can write a minimum of 4 papers and a maximum of 3 papers. Each of A, D, G, H must have written 3 papers each.
In statement 3 it was provided that none of the Indian authors were from the Manufacturing area and none of the Japanese or Chinese authors were from the Automation area.
Since none of the Japanese and Chinese authors belonged to automation. Hence the two automation authors must be from India. In statement 1 it was given that F an Indian author is from logistics.
Of the remaining 5 authors 3 from logistics and 2 from manufacturing, in statement 5 it is given that the two Chinese authors are from different areas and hence they must be from manufacturing and logistics.
Of the remaining 3 authors 2 in logistics and 1 in manufacturing, in statement 8 is given that a Japanese author belonged to manufacturing, and hence of the remaining 2 in logistics one of them was from India and the other from Japan.
Of the four Indian authors, 2 belonged to logistics and 2 automation. Of the two authors from Japan, one belonged to manufacturing and one logistics. Of the two Chinese authors, one of them belonged to logistics and the other manufacturing.
Five papers were scheduled in each of the January and April issues, while four were scheduled in each of July and October issues.
Using statement 1, F an Indian author wrote a single paper in logistics published in October.
Using statement 2, A was from Automation and did not have a paper scheduled in October. Since A wrote 3 papers in total he must have written in the other three months and since only Indian authors worked in Automation he must have been from India.
Using statement 5, C, E are Chinese and wrote an equal number of papers. Since B + C + E + F have written a total of 6 papers. The two possibilities are 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 or 3 + 1 + 1 + 1.. Since it was given that E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues and C did not. So the only possible case is C = 2, E = 2, F = 1, B = 1.
Using statement 4, A and H were from different countries and wrote papers in the same months. Hence H must be Japanese and must have written in Jan, April, July.
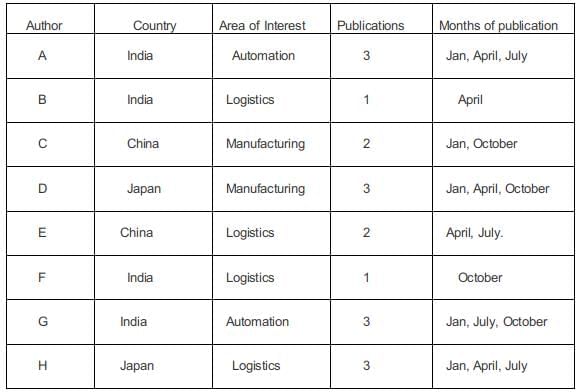
In statement 6, B, from the Logistics area, had a paper scheduled in the April issue of the journal.
In statement 7, B and G belonged to the same country. None of their papers were scheduled in the same issue of the journal. Since B and G belonged to the same country the only possibility is that both of them belonged to the same country and since they published Journals in different months. G must have published in January, July, and October.
In statement 8, D, a Japanese author from the Manufacturing area, did not have a paper scheduled in the July issue. Hence he must have had the three issues in Jan, April, Oct. The other Japanese author H must have written in logistics.
The fourth Indian author G must have written a paper in Automation.
In January, one more paper needs to be publicized, one in April, 1 in July, and one in October.
In statement 5, E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues of the journal but C did not.
Hence C must have written in Jan and October, and E in April and July.
In statement 9, C and H belonged to different areas. Hence C must be from Manufacturing and E must be from Logistics.
There are no authors from Manufacturing in the July issue and hence option D is false.
Q6: Which of the following is the correct sequence of number of papers by authors from Automation, Manufacturing and Logistics areas, respectively?
(a) 6, 5, 7
(b) 6, 6, 6
(c) 6, 7, 5
(d) 5, 6, 7
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
In the information, it is provided that there are four authors in the logistics department, 2 authors in automation, and 2 authors in manufacturing. There are 4 Indian authors, 2 Chinese authors, and 2 Japanese authors.
The total issues publicized were 18 of which the publications done by A, D, G, H are twice the papers written by the other four authors. Hence A + D + G + H has written 12 papers in total and B + C + E + F has written 6 in total. Since an author can write a minimum of 4 papers and a maximum of 3 papers. Each of A, D, G, H must have written 3 papers each.
In statement 3 it was provided that none of the Indian authors were from the Manufacturing area and none of the Japanese or Chinese authors were from the Automation area.
Since none of the Japanese and Chinese authors belonged to automation. Hence the two automation authors must be from India. In statement 1 it was given that F an Indian author is from logistics.
Of the remaining 5 authors 3 from logistics and 2 from manufacturing, in statement 5 it is given that the two Chinese authors are from different areas and hence they must be from manufacturing and logistics.
Of the remaining 3 authors 2 in logistics and 1 in manufacturing, in statement 8 is given that a Japanese author belonged to manufacturing, and hence of the remaining 2 in logistics one of them was from India and the other from Japan.
Of the four Indian authors, 2 belonged to logistics and 2 automation. Of the two authors from Japan, one belonged to manufacturing and one logistics. Of the two Chinese authors, one of them belonged to logistics and the other manufacturing.
Five papers were scheduled in each of the January and April issues, while four were scheduled in each of July and October issues.
Using statement 1, F an Indian author wrote a single paper in logistics published in October.
Using statement 2, A was from Automation and did not have a paper scheduled in October. Since A wrote 3 papers in total he must have written in the other three months and since only Indian authors worked in Automation he must have been from India.
Using statement 5, C, E are Chinese and wrote an equal number of papers. Since B + C + E + F have written a total of 6 papers. The two possibilities are 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 or 3 + 1 + 1 + 1.. Since it was given that E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues and C did not. So the only possible case is C = 2, E = 2, F = 1, B = 1.
Using statement 4, A and H were from different countries and wrote papers in the same months. Hence H must be Japanese and must have written in Jan, April, July.
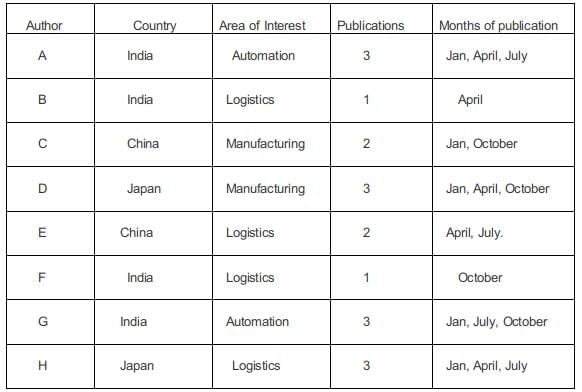
In statement 6, B, from the Logistics area, had a paper scheduled in the April issue of the journal.
In statement 7, B and G belonged to the same country. None of their papers were scheduled in the same issue of the journal. Since B and G belonged to the same country the only possibility is that both of them belonged to the same country and since they published Journals in different months. G must have published in January, July, and October.
In statement 8, D, a Japanese author from the Manufacturing area, did not have a paper scheduled in the July issue. Hence he must have had the three issues in Jan, April, Oct. The other Japanese author H must have written in logistics.
The fourth Indian author G must have written a paper in Automation.
In January, one more paper needs to be publicized, one in April, 1 in July, and one in October.
In statement 5, E had papers scheduled in consecutive issues of the journal but C did not.
Hence C must have written in Jan and October, and E in April and July.
In statement 9, C and H belonged to different areas. Hence C must be from Manufacturing and E must be from Logistics.
In Automation, there are a total of 6 papers, Logistics 7 papers, and Manufacturing a total of 5 papers.
|
102 videos|123 docs|121 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Question - 78 (Scheduling) - 100 DILR Questions for CAT Preparation
| 1. What is the significance of scheduling in time management? |  |
| 2. How can one effectively create a study schedule for exam preparation? |  |
| 3. What are common scheduling techniques that can be applied in daily life? |  |
| 4. How does technology assist in scheduling and time management? |  |
| 5. What are the consequences of poor scheduling on productivity? |  |















