Important Formula: We the Travellers—I | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
1. Place Value System
• This is 1 
• 10 Ones make 1 Ten (10) 
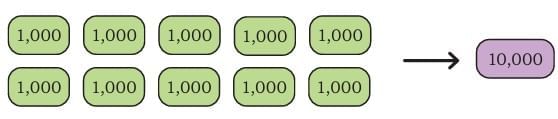
Place Value Order (Indian System):
Ones → Tens → Hundreds → Thousands → Ten Thousands → Lakhs → Ten Lakhs → Crores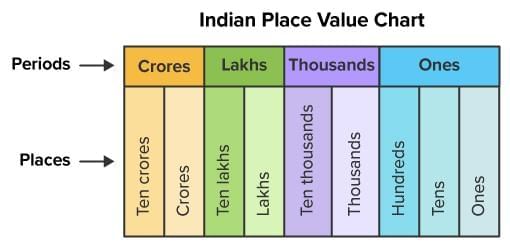
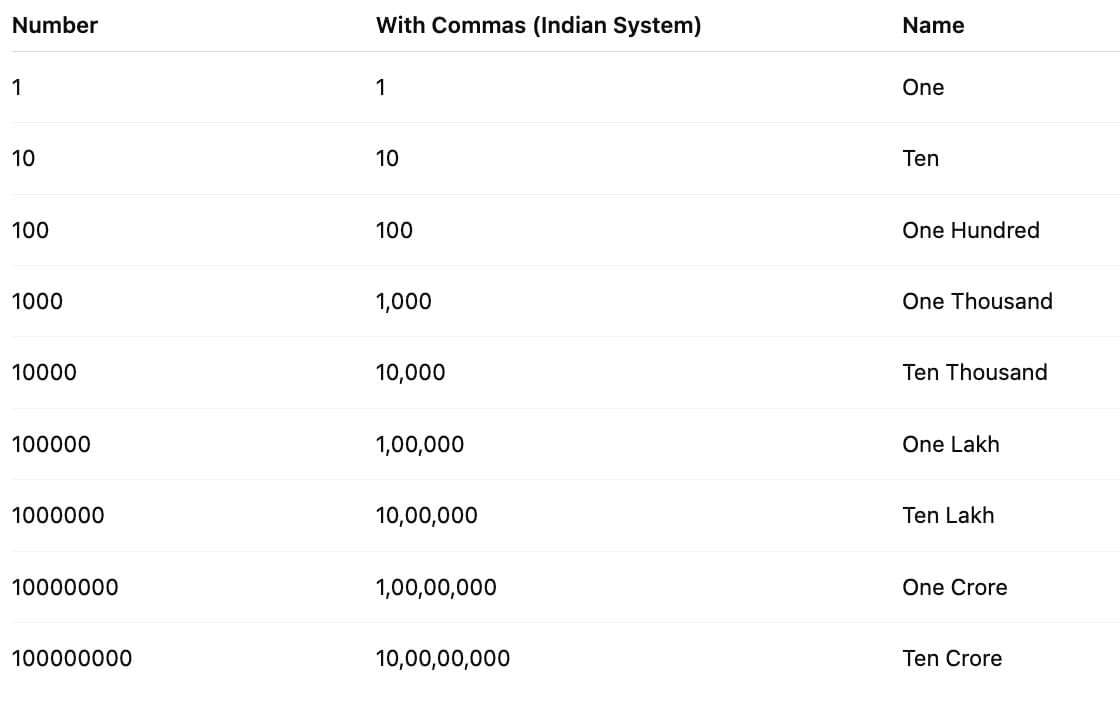
Commas in Large Numbers (Indian System)
First comma after 3 digits from the right.
After that, commas after every 2 digits.
Example: 8045 → 8,045 (Read as Eight thousand forty-five).
Number Naming (Indian System)
Expanded Form
Break a number into place values:
1,380 = 1,000 + 300 + 80 + 0
9,123 = 9,000 + 100 + 20 + 3
General Rule:
Number = (Thousands × 1000) + (Hundreds × 100) + (Tens × 10) + (Ones × 1)
Number Patterns
A number pattern is a sequence of numbers that follow a fixed rule.
Each number in the sequence is obtained from the previous number using that rule.
Example
456 → 567 → 678
Rule: Add 111 each time.
Types of Rules in Number Patterns
1. Repeated Addition
Add the same number again and again.
Example: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 ...
Rule: Add 5 each time.
2. Repeated Subtraction
Subtract the same number again and again.
Example: 100, 90, 80, 70, 60 ...
Rule: Subtract 10 each time.
3. Multiplication by the Same Number
Multiply the previous number by a fixed number.
Example: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 ...
Rule: Multiply by 2 each time.
4. Division by the Same Number
Divide the previous number by a fixed number.
Example: 256, 128, 64, 32, 16 ...
Rule: Divide by 2 each time.
Tip for Students:
Always look for what is happening from one number to the next:
Is the number increasing or decreasing?
Is it changing by addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division?
Rounding Off Rules
1. Nearest 10:
Look at Ones digit.
If Ones ≥ 5 → round up.
If Ones < 5 → round down.
Example: 2,346 → 2,350

2. Nearest 100:
Look at Tens digit.
If Tens ≥ 5 → round up.
If Tens < 5 → round down.
Example: 2,346 → 2,300
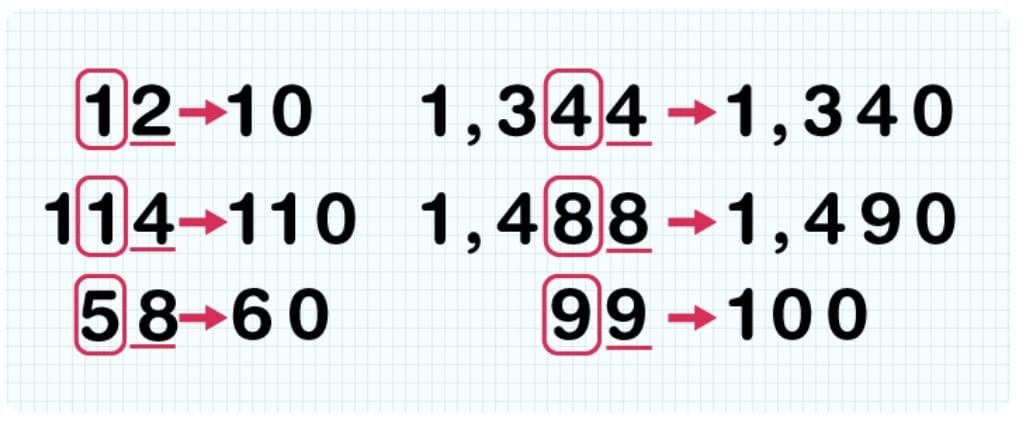
3. Nearest 1000:
Look at Hundreds digit.
If Hundreds ≥ 5 → round up.
If Hundreds < 5 → round down.
Example: 2,346 → 2,000

6. Large Numbers in Daily Life
Numbers we see daily can range from 1-digit to 5-digit (e.g., distances, money, population).
Example: A book with 200 pages × 50 words/page = ~10,000 words.
Units of length: kilometre (km) = 1,000 metres (m).
7. Mathematical Puzzles (Pastime Mathematics)
(a) River Crossing Puzzle
Objects: Lion, Sheep, Grass with the Boatman.
 Boatman
BoatmanRules:
Boat carries only 1 item at a time.
Lion & sheep alone → lion eats sheep.
Sheep & grass alone → sheep eats grass.
Solution (7 trips):
Take sheep across → return alone → take lion → bring sheep back → take grass → return alone → take sheep.
Key Idea: Logical sequencing and safe grouping.
(b) Pile of Pebbles Game
Two piles, each with 7 pebbles.
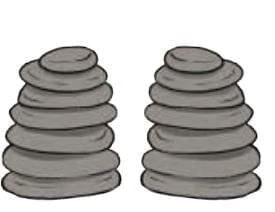
On each turn, a player can take any number of pebbles from one pile only.
Winning Strategy:
If piles are equal → second player wins by copying moves.
If piles unequal → first player can win by making them equal.
Key Idea: Patterns and strategy in game theory.
(c) The Number Puzzle
Start with any two digits → form two 2-digit numbers → subtract smaller from larger → repeat with digits of result.
Pattern: Always ends at 9.
Example:
73 – 37 = 36 → 63 – 36 = 27 → 72 – 27 = 45 → 54 – 45 = 9.
Why? Differences are always multiples of 9.
Key Idea: Hidden number patterns and divisibility by 9.
(d) King’s Horses Puzzle
King has 20 horses, 1 stolen → only 19 left.
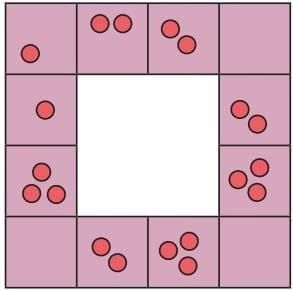
Caretaker arranges horses in a square with horses at corners.
When king counts each side (5 per side × 4 sides = 20), he double-counts the corner horses.
Trick: Corner horses counted twice.
Key Idea: Counting principles and visual tricks.
|
35 videos|318 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formula: We the Travellers—I - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the place value system, and why is it important in understanding large numbers? |  |
| 2. How are large numbers grouped in the Indian numbering system? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the expanded form of a number with an example? |  |
| 4. What are rounding off rules, and how do they apply to numbers? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between speed, distance, and time, and how can it be calculated? |  |
















