Important Formulas: Racing Seconds | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Using a Clock |

|
| Measuring Time |

|
| Converting Time Units |

|
| Time Duration (Elapsed Time) |

|
| Time Formats |

|
| Time in a.m. and p.m. |

|
| Special Time Terms |

|
| Practice & Examples |

|

Introduction
Time helps us know when things start, end, and how long they last.
Everyday activities (waking up, going to school, playing, sleeping) happen at specific times.
Units of time: seconds, minutes, hours.
Using a Clock
Hands of a clock:
Hour hand = short → shows hours
Minute hand = long → shows minutes
Second hand = thin → shows seconds
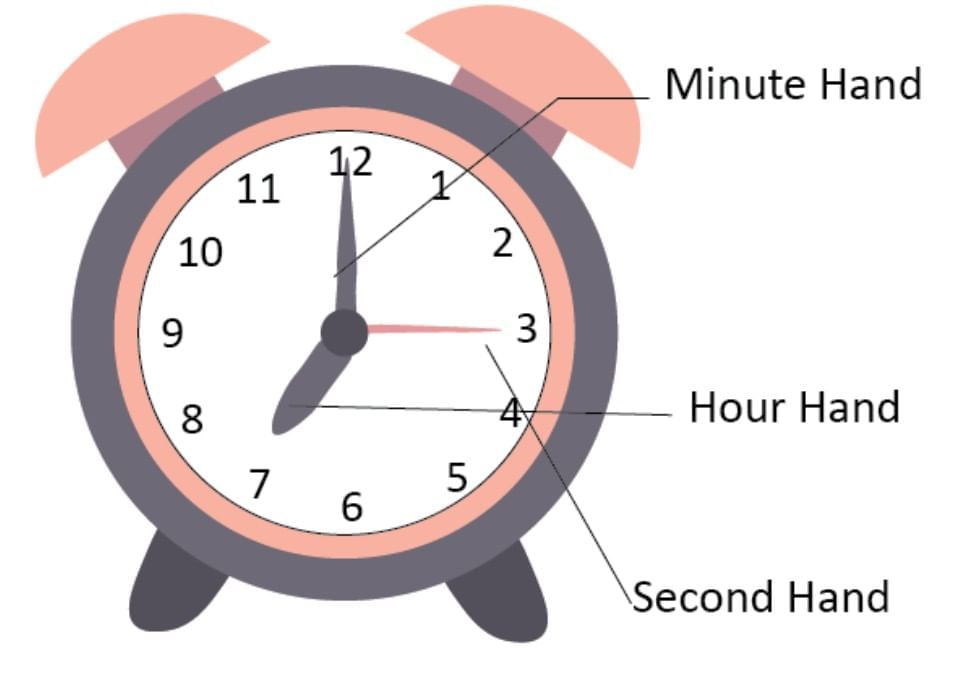
Reading Time:
Check hour hand.
Check minute hand (each number = 5 min.).
Check second hand (each number = 5 sec.).
Example 1: If the minute hand is on 3 and the hour hand is past 11, the time is 11:15 (3 × 5 = 15 minutes), or quarter past 11.
Example 2: If the minute hand is on 10 and the hour hand is past 5, the time is 5:50 or 10 minutes to 6 (12 – 10 = 2 × 5 = 10 minutes).
Measuring Time
Seconds
Smallest commonly used unit of time.
60 seconds = 1 minute.
Examples: blinking, snapping fingers, saying “go!”
Minutes
1 minute = 60 seconds.
Used for short tasks (tying shoelaces, sipping water, reading a paragraph).
Hours
1 hour = 60 minutes = 3,600 seconds.
Used for longer activities (watching cartoons, playing, homework).
Converting Time Units
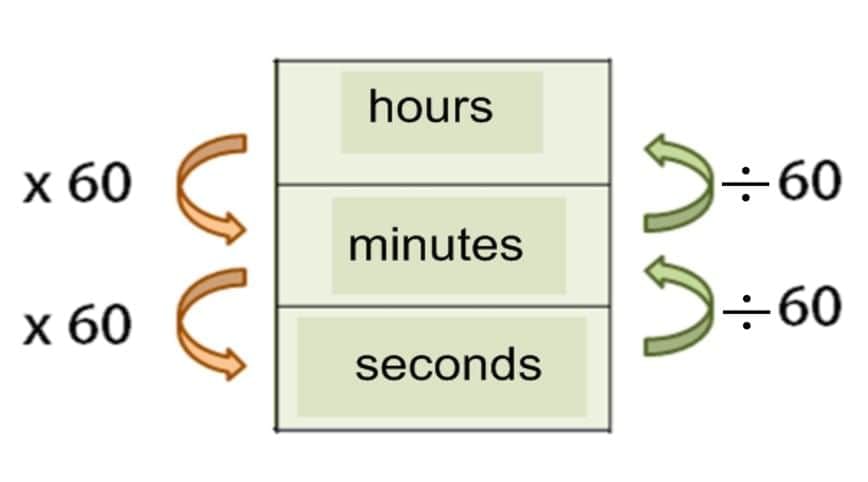
We can convert between hours, minutes, and seconds.
We know:
1 hour = 60 minutes
1 minute = 60 seconds
So,
To go downwards (hours → minutes → seconds), we multiply by 60.
To go upwards (seconds → minutes → hours), we divide by 60.
Example 1: Convert 2 hours into minutes
2 hours = 2 × 60 = 120 minutes
Example 2: Convert 5 minutes into seconds
5 minutes = 5 × 60 = 300 seconds
Example 3: Convert 3600 seconds into hours
Step 1: Convert seconds to minutes
3600 ÷ 60 = 60 minutesStep 2: Convert minutes to hours
60 ÷ 60 = 1 hourSo, 3600 seconds = 1 hour.
2 hours = 2 × 60 = 120 minutes
Time Duration (Elapsed Time)
Definition: How long something lasts.
Formula: Time duration = End time − Start time
Examples:
Football match: 1:15 p.m. – 1:42 p.m. → Duration = 27 min
Yoga: Start 5:35 a.m., End 6:55 a.m. → Duration = 1 h 20 min
Tips: Subtract minutes first, then hours. Borrow 1 hour as 60 minutes if needed.
Time Formats
24-Hour Clock → 12-Hour Clock
Rules:
00:00–00:59 hours → Add a.m. (midnight)
01:00–11:59 hours → Add a.m. directly
12:00–12:59 hours → Add p.m. directly (no change)
13:00–23:59 hours → Subtract 12:00 and add p.m.
Examples:
0045 hours → 12:45 a.m.
1430 hours → 2:30 p.m.
12-Hour Clock → 24-Hour Clock
Rules:
12:00–12:59 a.m. → Subtract 12:00
1:00 a.m.–12:59 p.m. → Write as is
1:00 p.m.–11:59 p.m. → Add 12:00
Examples:
12:20 a.m. → 00:20
5:45 p.m. → 17:45
Why 24-Hour Clock is Useful
No confusion between morning and evening
19:00 is clearly evening, unlike 7:00
Easier to calculate time duration
Example: 09:30 → 14:30 → 5 hours
Time in a.m. and p.m.
1. What is a.m. and p.m.?
a.m. (ante meridiem) → Before midday (from 12 midnight to 12 noon)
p.m. (post meridiem) → After midday (from 12 noon to 12 midnight)
2. Why use a.m. and p.m.?
To avoid confusion between morning and evening times.
Example: 6:00 a.m. = morning
6:00 p.m. = evening
Example:
Hour hand between 4 and 5, minute hand on 3 → 4:15
Morning → 4:15 a.m.
Evening → 4:15 p.m.
Also called quarter past 4
3. Special Rules for 12 o’clock
12:00 noon → midday (not written with a.m./p.m.)
12:00 midnight → night (not written with a.m./p.m.)
Special Time Terms
Quarter past → 15 minutes after the hour
Half past → 30 minutes after the hour
Quarter to → 15 minutes before the next hour
Practice & Examples
Elapsed time:
03:18 p.m. – 08:18 p.m. → 5 h
09:15 a.m. – 11:30 a.m. → 2 h 15 min
Comparing durations:
Who took longest/least time?
Use subtraction of start and end times.
Conversion exercises:
Seconds ↔ minutes ↔ hours
120 sec → 2 min
2 h 15 min → 135 min
|
35 videos|276 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Racing Seconds - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. How do you use a clock to tell time accurately? |  |
| 2. How do I convert time from hours to minutes and vice versa? |  |
| 3. What is elapsed time and how can I calculate it? |  |
| 4. What are the differences between a.m. and p.m. in time notation? |  |
| 5. Can you explain some special terms related to time? |  |
















