Important Formulas: Shapes and Patterns | Mathematics for Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Patterns |

|
| Weaving Mats |

|
| Shapes and Their Properties |

|
| Tessellation (Tiling Patterns) |

|
| Types of Triangles |

|
| Quadrilaterals |

|
| Tangram |

|
| Kite |

|
| Circles |

|
| 3D Shapes |

|
Patterns
A pattern is a sequence that repeats in the same way.
Patterns can be made with shapes, numbers, or colours.
Rule of a pattern → helps predict the next item.
Examples:
Colours: red, blue, red, blue → next is red.
Shapes: circle, square, circle, square → keeps repeating.
Numbers: 2, 4, 6, 8 → rule: add 2 each time.
Key Uses of Patterns:
Organise information.
Solve problems easily.
Predict what comes next.
Seen in nature (zebra stripes, honeycombs, petals), art, tiles, and weaving.
Weaving Mats
Weaving rule: Alternate “over–under” rows to form a mat.
Pattern created: Checkerboard / basket design.
Different weaving orders = different patterns.
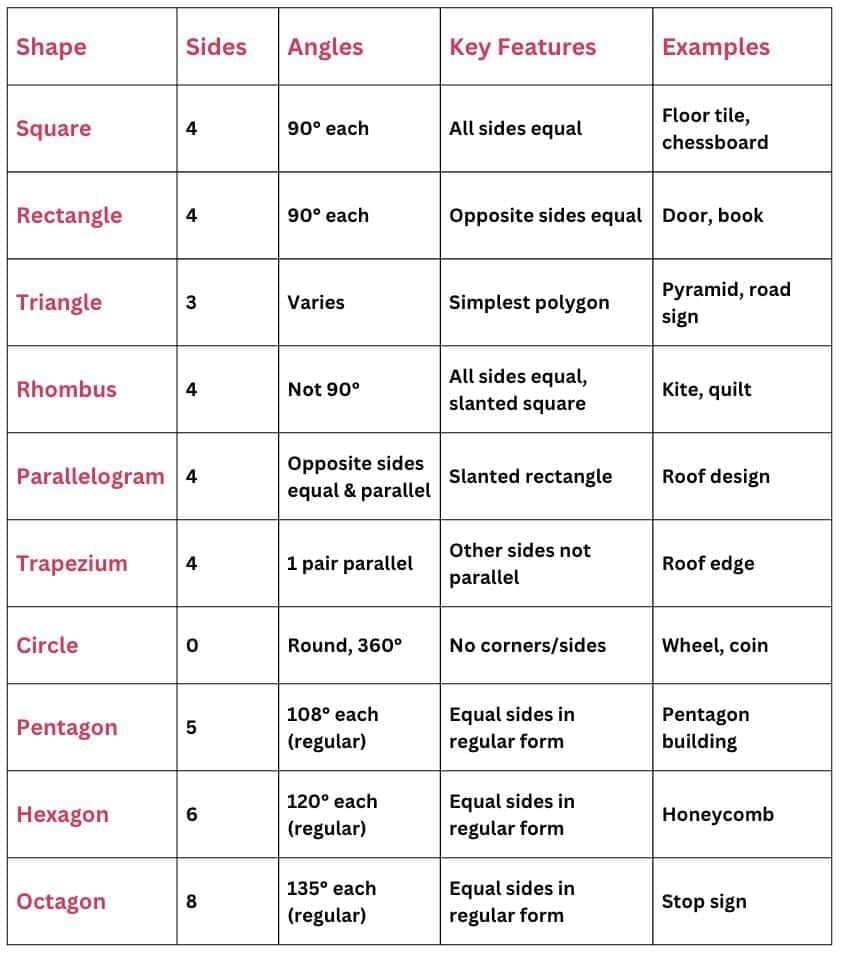
Shapes and Their Properties
Polygons
A polygon is a closed shape made of straight sides.
Tessellation (Tiling Patterns)
Tessellation = covering a surface with shapes without gaps/overlaps.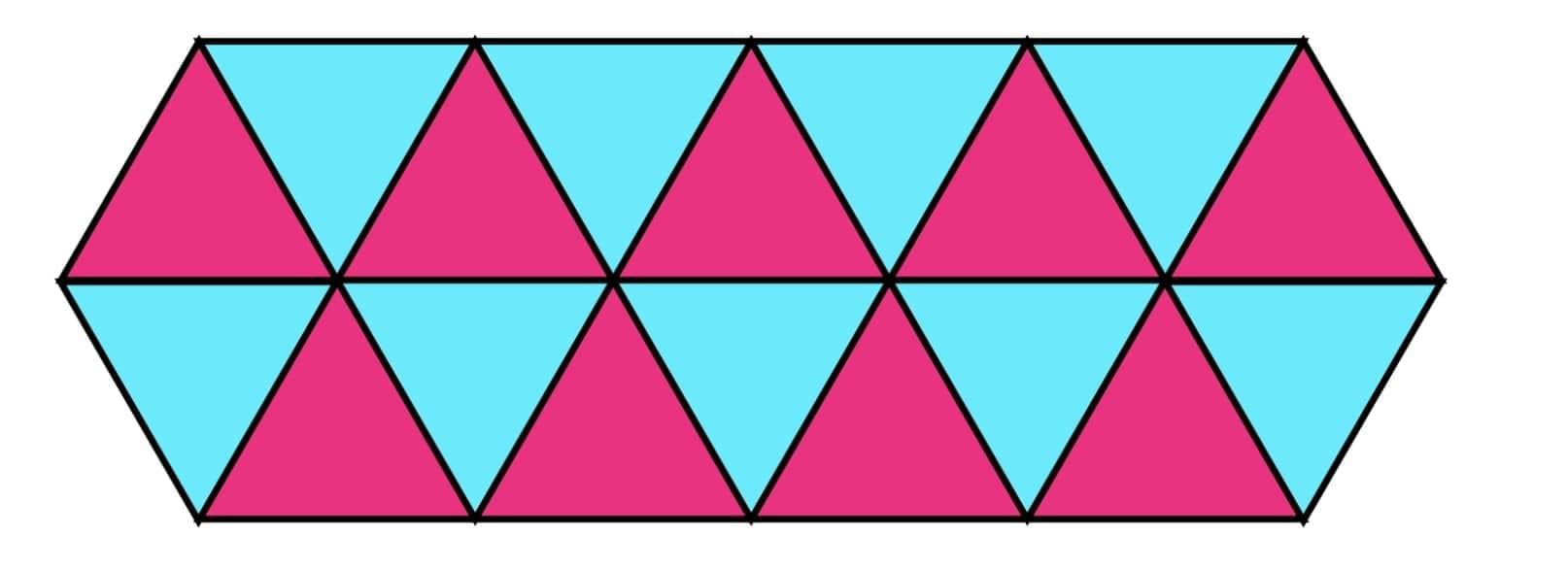
Examples:
Squares → tessellate.
Equilateral triangles → tessellate (6 around a point).
Hexagons → tessellate (3 around a point).
Pentagons & octagons → do not tessellate (leave gaps).
Mixed Tessellation: Shapes like triangles + hexagons, or rhombuses + triangles can combine to tessellate.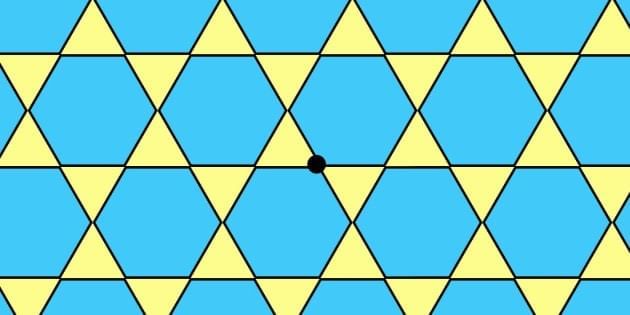
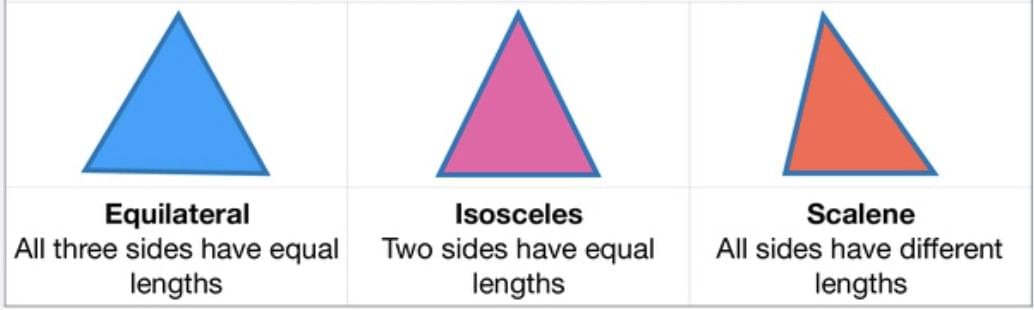
Types of Triangles
Equilateral → 3 equal sides, 3 equal angles (60°).
Isosceles → 2 equal sides, opposite angles equal.
Scalene → All sides and angles different.
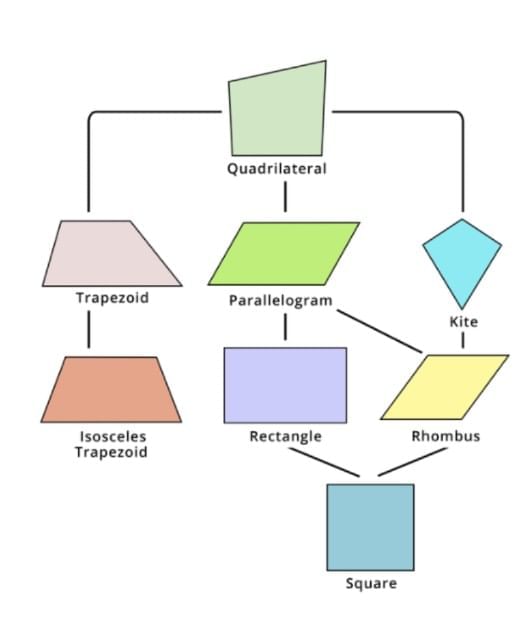
Quadrilaterals
Parallelogram → Opposite sides equal, opposite angles equal.
Rectangle → A parallelogram with all angles = 90°.
Square → A rectangle with all sides equal.
Rhombus → All sides equal, angles not 90°.
Trapezium → One pair of parallel sides.
Tangram
A Tangram has 7 pieces (tans):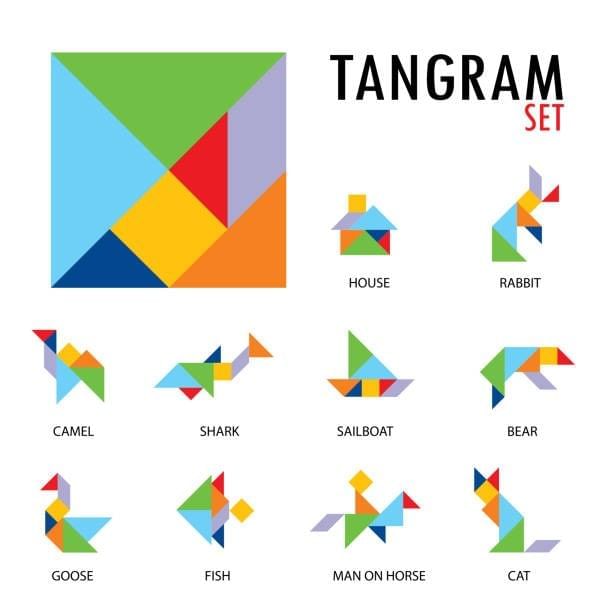
2 Large right-angled isosceles triangles
1 Medium right-angled isosceles triangle
2 Small right-angled isosceles triangles
1 Square
1 Parallelogram
Key Points:
Can form many shapes (bird, fish, square, trapezium, etc.).
Develops spatial thinking and creativity.
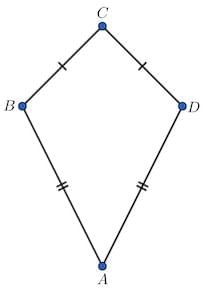
Kite
4-sided quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent equal sides.
Diagonals cross at right angles.
Seen in flying kites, diamond shapes.
Can be made from folding a square.
Circles
Radius (r): Distance from centre to edge.
Diameter (d): Longest distance across circle, d = 2r.
Circumference (C): Distance around circle, C = 2πr.
Area (A): Space inside circle, A = πr².
Angles around circle: 360°.
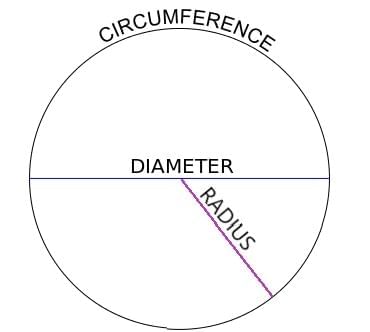
Key Property:
Joining endpoints of two diameters always makes a rectangle (or square if diameters are perpendicular).
3D Shapes
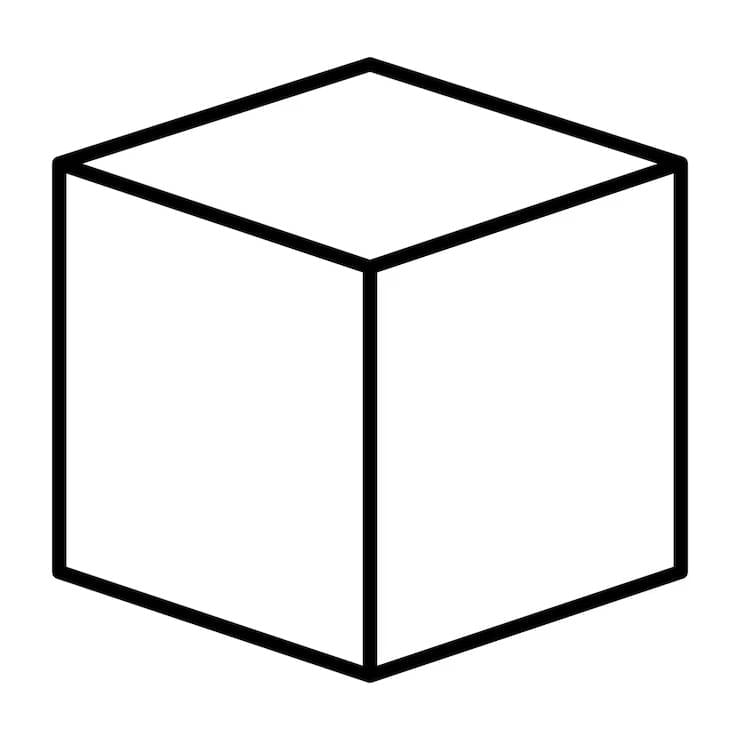
Cube
6 square faces, 12 edges, 8 vertices.
Surface Area = 6 × side²
Volume = side³
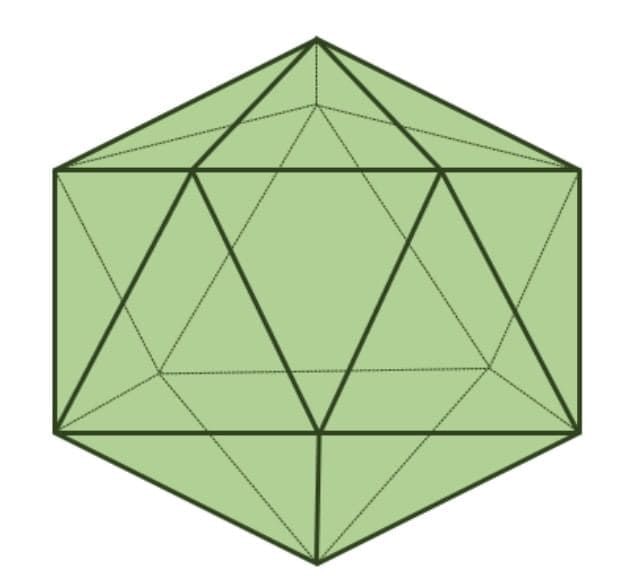
Icosahedron
20 equilateral triangle faces.
30 edges, 12 vertices.
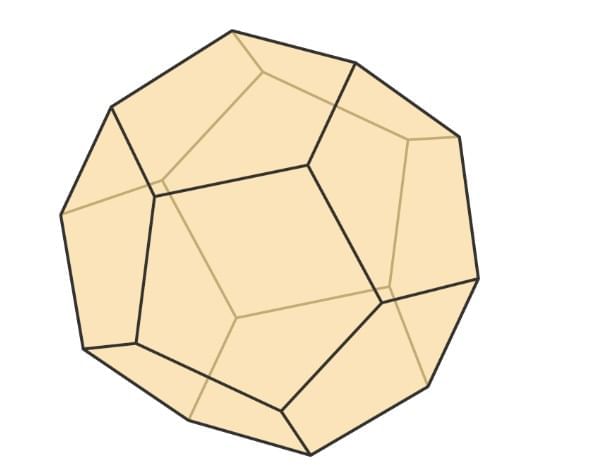
Dodecahedron
12 regular pentagon faces.
30 edges, 20 vertices.
Both are Platonic solids (faces are identical regular polygons, same number of faces meet at each vertex)
|
95 videos|462 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Shapes and Patterns - Mathematics for Class 5
| 1. What are the key properties of different types of triangles? |  |
| 2. What is tessellation and how is it applied in art and architecture? |  |
| 3. How can I differentiate between various quadrilaterals? |  |
| 4. What are the important formulas related to circles and how are they used? |  |
| 5. What is a tangram and what educational benefits does it offer? |  |















