Worksheet Solutions: Metal and Non - metals | Chemistry Class 7 ICSE PDF Download
Part A – Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. Metals are generally found in nature in which state?
a) Free state
b) Solid state
c) Liquid state
d) Gaseous state
Answer: a) Free state
Explanation: Metals like gold, silver, and platinum are less reactive, so they exist in the free state in nature. More reactive metals exist as compounds.
Q2. Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity?
a) Wood
b) Copper
c) Plastic
d) Glass
Answer: b) Copper
Explanation: Metals conduct electricity because they have free electrons. Copper is one of the best conductors, which is why it is used in wires.
Q3. Which gas is essential for respiration in living beings?
a) Carbon dioxide
b) Oxygen
c) Nitrogen
d) Hydrogen
Answer: b) Oxygen
Explanation: Oxygen is a non-metal gas. Living beings need oxygen to break down food and release energy.
Q4. Which property is shown by metals but not by non-metals?
a) Brittle
b) Ductile
c) Poor conductor
d) Non-lustrous
Answer: b) Ductile
Explanation: Metals are ductile, meaning they can be drawn into thin wires. Non-metals are brittle and break easily.
Q5. Which of these is a metalloid?
a) Gold
b) Silicon
c) Nitrogen
d) Aluminium
Answer: b) Silicon
Explanation: Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. Silicon conducts electricity like a metal but is brittle like a non-metal.
Part B – Short Answer Questions
Q6. Define corrosion. Why is it harmful?
Answer:
Corrosion is the slow eating away of metals due to reaction with air, moisture, or chemicals.
Example: Iron reacts with oxygen and water to form rust.
Harmful because:
Weakens metal structures (bridges, machinery).
Causes financial losses (replacement needed).
Shortens the life of metals.
Q7. State two differences between metals and non-metals.
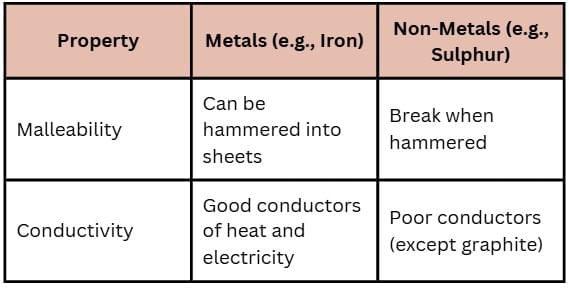
Q8. What conditions are necessary for rusting of iron?
Answer:
Presence of water or moisture.
Presence of oxygen (air).
Both are needed together.
Polluted air with CO₂ or SO₂ speeds up rusting.
Explanation: Rusting is a chemical reaction of iron with both water and oxygen. If one is missing, rusting does not occur.
Q9. Write two uses of aluminium. Why is it used in these ways?
Answer:
Cooking utensils and foils – Aluminium is a good conductor of heat, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant.
Aircraft and automobile bodies – Aluminium alloys are strong, light, and do not corrode easily.
Explanation: The combination of lightweight + strength + resistance to corrosion makes aluminium very useful.
Q10. Give one example each of:
(a) Noble metal
(b) Metalloid
(c) Non-metal used in fertilizers
Answer:
a) Gold – Noble metal, does not corrode easily.
b) Silicon – Metalloid, used in chips and solar cells.
c) Nitrogen – Non-metal, used in fertilizers like urea.
Explanation:
Noble metals resist corrosion.
Metalloids have mixed properties.
Nitrogen is essential for plant growth.
Part C – Long Answer Questions
Q11. List any three physical properties of metals. Give examples.
Answer:
Malleability: Metals like aluminium can be beaten into thin sheets (foil).
Ductility: Copper can be drawn into wires.
Conductivity: Silver and copper conduct heat and electricity well.
Explanation: These properties make metals useful in industries (wires, utensils, machinery).
Q12. How can rusting of iron be prevented?
Answer:
Rusting can be prevented by:
Painting or greasing – Stops contact with air and water.
Galvanisation – Coating iron with zinc to protect from rust.
Alloying – Making stainless steel by mixing iron with chromium and nickel.
Explanation: Rusting needs both air and water. Prevention methods block these from reaching iron.
Q13. Why are gold and platinum called noble metals?
Answer:
Gold and platinum are called noble metals because they do not react easily with air, water, or ordinary chemicals.
They do not rust or corrode.
Example: Gold jewellery shines for years without losing its appearance.
|
33 videos|56 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Metal and Non - metals - Chemistry Class 7 ICSE
| 1. What are the main properties that distinguish metals from non-metals? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of everyday metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How do metals and non-metals react with acids? |  |
| 4. What role do metals and non-metals play in the formation of compounds? |  |
| 5. Why are metals considered to have higher densities compared to non-metals? |  |




















