PYQs: Management of Support Services, Institutions and Programmes for Children, Youth and Elderly - Class 10 PDF Download
Q1: In the context of institutes/programmes for vulnerable groups, choose the correct pair:
(a) CARA : Organising rallies
(b) Promotion of Adventure : Child Rights Convention
(c) Observation Home : A kind of home for Children
(d) Promotion of National Integration : Family-based care
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Observation Home : A kind of home for Children
In the context of support services and institutions for vulnerable groups (children, youth, and elderly), various government and non-governmental programs address specific needs like care, protection, rehabilitation, and development. The correct pair must accurately reflect the role or description of the entity.
(a) CARA : Organising rallies: Incorrect. CARA stands for Central Adoption Resource Authority, a statutory body under the Ministry of Women and Child Development, established in 1990 and functioning as the nodal agency for regulating domestic and inter-country adoptions in India. It ensures ethical adoptions, monitors adoption agencies, and maintains a database of adoptable children and prospective parents, but it does not organize rallies. Rallies are typically part of awareness campaigns by other bodies like NGOs or child rights organizations.
(b) Promotion of Adventure : Child Rights Convention: Incorrect. The Promotion of Adventure is a scheme under the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, aimed at encouraging adventure sports and activities among youth (aged 15–29) to build character, resilience, and teamwork. It includes programs like trekking, mountaineering, and camps, often implemented through organizations like the National Adventure Foundation or Youth Hostels Association of India, but it is not linked to the Child Rights Convention (which refers to the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child, 1989, ratified by India in 1992).
(c) Observation Home : A kind of home for Children: Correct. An Observation Home is a residential institution established under Section 47 of the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015, for the temporary reception and care of children in conflict with the law (aged below 18) during the pendency of inquiries or trials. It provides shelter, counseling, education, and vocational training to ensure rehabilitation and protection, making it a specific type of home for vulnerable children.
(d) Promotion of National Integration : Family-based care: Incorrect. Promotion of National Integration is a youth-focused initiative under the National Service Scheme (NSS) and Ministry of Youth Affairs, involving camps, seminars, and cultural exchanges to foster unity in diversity, combat communalism, and promote harmony among diverse groups. It is not related to family-based care, which pertains to child welfare models like foster care or kinship care under schemes like ICPS (Integrated Child Protection Scheme). Thus, option (c) is the accurate pair, aligning with the chapter's emphasis on institutional care for vulnerable children.
Q2: Match the initiatives for children, youth and elderly given in List-I with their related year in List-II.
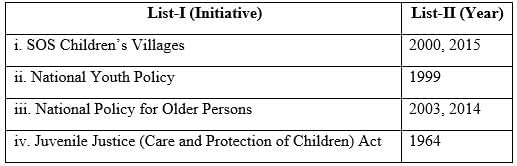
(a) i–4, ii–3, iii–2, iv–1
(b) i–3, ii–4, iii–1, iv–2
(c) i–2, ii–1, iii–4, iv–3
(d) i–3, ii–1, iii–2, iv–4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) i–4, ii–3, iii–2, iv–1
These initiatives are key support services and programs managed by government and NGOs for vulnerable groups, with specific enactment or establishment years marking their evolution. The correct matching is based on historical timelines: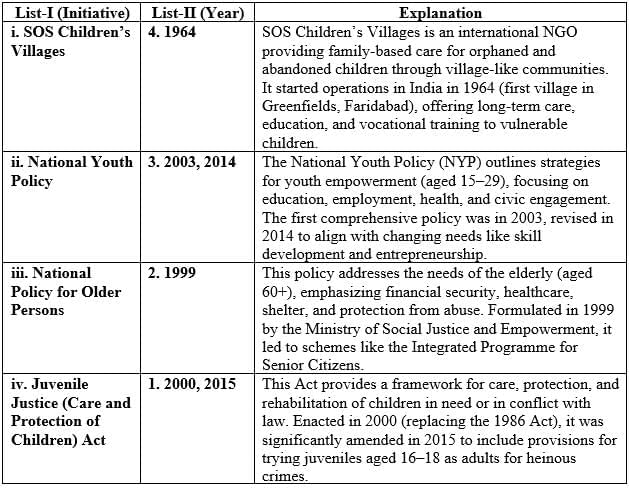
Option (a) (i–4, ii–3, iii–2, iv–1): Correct, as it matches the timelines accurately.
Option (b) (i–3, ii–4, iii–1, iv–2): Incorrect, as SOS is not from 2003–2014, and NYP is not 1964.
Option (c) (i–2, ii–1, iii–4, iv–3): Incorrect, as SOS is not 1999, and NPOP is not 1964.
Option (d) (i–3, ii–1, iii–2, iv–4): Incorrect, as SOS is not 2003–2014, and JJ Act is not 1964.
Q3: Assertion (A): Within the broad category ‘Youth’, there are some groups who are especially vulnerable.
Reason (R): Rural and tribal youth are vulnerable groups.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).Explanation:
- Assertion (A): True. The youth category (aged 15–29 in India) includes subgroups facing heightened risks due to socio-economic, geographic, or cultural factors, such as limited access to education, employment, healthcare, or exposure to exploitation. Programs like the National Youth Policy 2014 recognize this vulnerability and target interventions for groups like rural, tribal, disabled, or migrant youth to ensure inclusive development.
- Reason (R): True. Rural and tribal youth are indeed vulnerable due to challenges like poverty, lack of infrastructure, cultural barriers, and limited opportunities, making them prone to issues like unemployment, migration, or health disparities.
- Relationship: (R) correctly explains (A) by providing specific examples of vulnerable youth groups, illustrating why the broad category has subgroups needing targeted support under schemes like RGNIYD (Rajiv Gandhi National Institute of Youth Development) or tribal youth programs. Thus, option (a) is correct; options (b), (c), and (d) do not fit as both are true and linked.
Q4: Assertion (A): It is necessary to provide for the economic and health needs of the elderly to create a conducive social milieu.
Reason (R): In India, Senior Citizens constitute persons in the age group of 50 years and above.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.Explanation:
- Assertion (A): True. The elderly face challenges like financial insecurity, health issues (e.g., chronic diseases), and social isolation, necessitating provisions like pensions (e.g., Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme), healthcare (e.g., National Programme for Health Care of the Elderly), and community support to foster a respectful, inclusive society as per the National Policy for Older Persons, 1999.
- Reason (R): False. In India, senior citizens are defined as persons aged 60 years and above under laws like the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007, and for benefits like income tax rebates or schemes under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. The age 50 is not the standard threshold (though some schemes may extend benefits from 55–60 for "very senior").
- Relationship: Since (R) is false, it cannot explain (A). Thus, option (c) is correct; options (a), (b), and (d) do not apply.
Q5: Few children of a village have become victims of a natural calamity and are without home. Besides these, which other four types of vulnerable children need care and protection?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Four types of vulnerable children:
- Orphans
- Children with disabilities
- Children of migrant workers
- Children in conflict with the law
Vulnerable children are those at risk of neglect, abuse, exploitation, or deprivation due to circumstances beyond their control, requiring institutional or community-based care under schemes like the Integrated Child Protection Scheme (ICPS) or Juvenile Justice Act, 2015. Besides children affected by natural calamities (e.g., floods, earthquakes leading to homelessness and trauma), the following four types also need protection:
- Orphans: Children who have lost one or both parents (due to death, abandonment, or separation) lack basic support, making them susceptible to poverty, malnutrition, or trafficking. They require foster care, adoption, or institutional homes like SOS Children’s Villages.
- Children with disabilities: Those with physical, intellectual, or sensory impairments face barriers in education, healthcare, and social inclusion, often leading to discrimination or neglect. Specialized institutions and schemes like Deen Dayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme provide assistive devices and training.
- Children of migrant workers: These children experience unstable living conditions, frequent relocations, disrupted education, and exposure to urban risks due to parents' seasonal migration for work. Mobile creches and hostels under ICPS offer protection and continuity.
- Children in conflict with the law: Juveniles involved in offenses (often due to poverty or influence) need rehabilitation rather than punishment. Observation Homes or Special Homes under the JJ Act provide counseling, education, and skill development for reintegration. These categories align with the chapter's focus on managed support services to ensure rights, safety, and development for vulnerable children.
Q6: Sumera lived in a remote village and was never sent to school. Now her parents want to admit her in a residential school. Suggest the name of the scheme by the Government of India meant for such girls. Explain any two other features of this scheme.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya (KGBV) scheme, launched in 2004 by the Ministry of Education (integrated into Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan since 2018), targets out-of-school girls aged 10–18 from remote, rural, or educationally backward blocks (EBBs) with low female literacy or high gender gaps. It provides free residential schooling to bridge educational disparities, especially for girls from SC/ST/OBC/minority/BPL families like Sumera. Two other features include:
- Free residential education with holistic support: It offers education from Class 6 to 12 (extended from initial Class 8), including boarding, lodging, uniforms, textbooks, and stipends, along with accelerated learning programs to address gaps, vocational training, and life skills education for economic empowerment.
- Focus on equity and inclusion: At least 75% enrollment is reserved for girls from disadvantaged groups, with emphasis on health, hygiene, sports, and self-defense training to promote gender equality and reduce dropout rates in underserved areas.
FAQs on PYQs: Management of Support Services, Institutions and Programmes for Children, Youth and Elderly - Class 10
| 1. What is the importance of Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) in child development? |  |
| 2. What are the key components of an effective ECCE program? |  |
| 3. How can parents support their child's early education at home? |  |
| 4. What are some common challenges faced in implementing ECCE programs? |  |
| 5. How does ECCE contribute to social equity and inclusion? |  |













