Case Based Questions: Exploring Magnets | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Q1: Read the source and answer the question that follows
Kiran and Ayaan are in their schoolyard testing how magnets interact. They each hold a bar magnet and bring them close together. Kiran notices that when they bring the north pole of one magnet close to the south pole of the other, the magnets attract and pull towards each other. However, when they bring like poles (north-north or south-south) together, they repel each other and push away.
Priya, who is also watching, asks why magnets behave like this. Ayaan explains that magnets have two poles—North and South. Opposite poles attract each other, while similar poles repel. They also try the same experiment with smaller magnets and see the same effect, reinforcing the idea that the force between magnets depends on the poles facing each other.
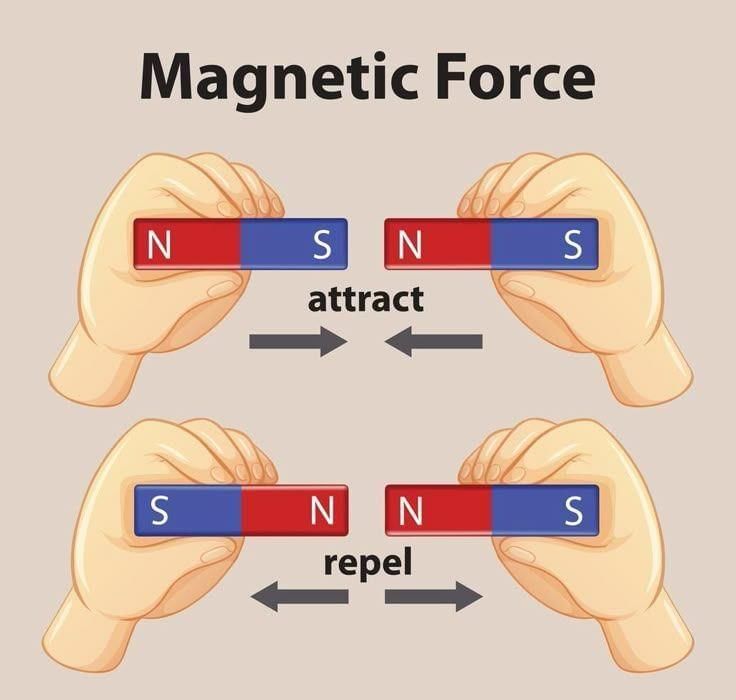 Q1. What happens when two magnets with the same poles facing each other are brought close?
Q1. What happens when two magnets with the same poles facing each other are brought close?
A) They attract each other
B) They repel each other
C) They do not interact
D) They form a single magnet
Ans: B) They repel each other
Q2. How do magnets help in everyday life, based on their attractive and repulsive properties?
Ans: Magnets are used in devices like motors, door locks, and magnetic levitation systems, utilizing the attraction and repulsion between magnets to function efficiently.
Q3. What happens when opposite poles of two magnets are brought close together?
Ans: When opposite poles (north-south) of two magnets are brought together, they attract each other and pull towards each other.
Q2: Read the source and answer the question that follows
Neha and Arjun are in their school science lab, where they are learning about magnetic and non-magnetic materials. They bring several objects to test which ones are attracted to a magnet. They place a magnet next to a metal paperclip, and to their surprise, it sticks to the magnet. Ravi wonders why non-metals, like plastic and wood, are not attracted to the magnet.
Neha explains that magnetic materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt are attracted to magnets because these materials contain magnetic properties. Arjun tests more items, and they discover that materials such as wood, plastic, and glass are non-magnetic, as they do not interact with the magnet at all.
Q1. Which of the following materials will be attracted to a magnet?
A) Wood
B) Glass
C) Iron
D) Rubber
Ans: C) Iron
Q2. Explain why wood and plastic are not attracted to magnets, while metals like iron are.
Ans: Wood and plastic are non-magnetic materials because they do not have the magnetic properties that allow them to be attracted to magnets.
Q3. What makes certain materials magnetic?
Ans: Certain materials are magnetic because they contain magnetic properties that allow them to be attracted to magnets, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
Q3: Read the source and answer the question that follows
Riya and Rahul are learning about the magnetic compass in their history class. They experiment by creating a simple compass using a magnetized needle and a small piece of cork. They place the cork in a bowl of water, and the needle floats, rotating until it points in the North-South direction. Rahul explains that the needle aligns with Earth's magnetic field, which makes it point north.
Maya asks how sailors used compasses for navigation. Riya explains that sailors used similar devices to determine directions when traveling at sea. They also discuss how a compass needle can rotate freely to point to the magnetic North, making it a reliable tool for finding directions.

Q1. Why does a magnetized needle in a compass point in the North-South direction?
Ans: A magnetized needle points in the North-South direction because it aligns with Earth's magnetic field, which has its magnetic poles in the north and south.
Q2. What is the main purpose of a magnetic compass?
A) To measure magnetic strength
B) To find directions (North-South)
C) To generate electricity
D) To store energy
Ans: B) To find directions
Q3. How did sailors use a magnetic compass in the past?
Ans: Sailors used the magnetic compass to determine directions by aligning the needle, which always pointed north, helping them navigate at sea.
|
86 videos|376 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Case Based Questions: Exploring Magnets - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of magnets? |  |
| 2. How do magnets work? |  |
| 3. What are some everyday uses of magnets? |  |
| 4. Can magnets lose their magnetism? If so, how? |  |
| 5. What materials are attracted to magnets? |  |
















