CAT Exam > CAT Notes > Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) > Mind Map: Syllogisms
Mind Map: Syllogisms | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
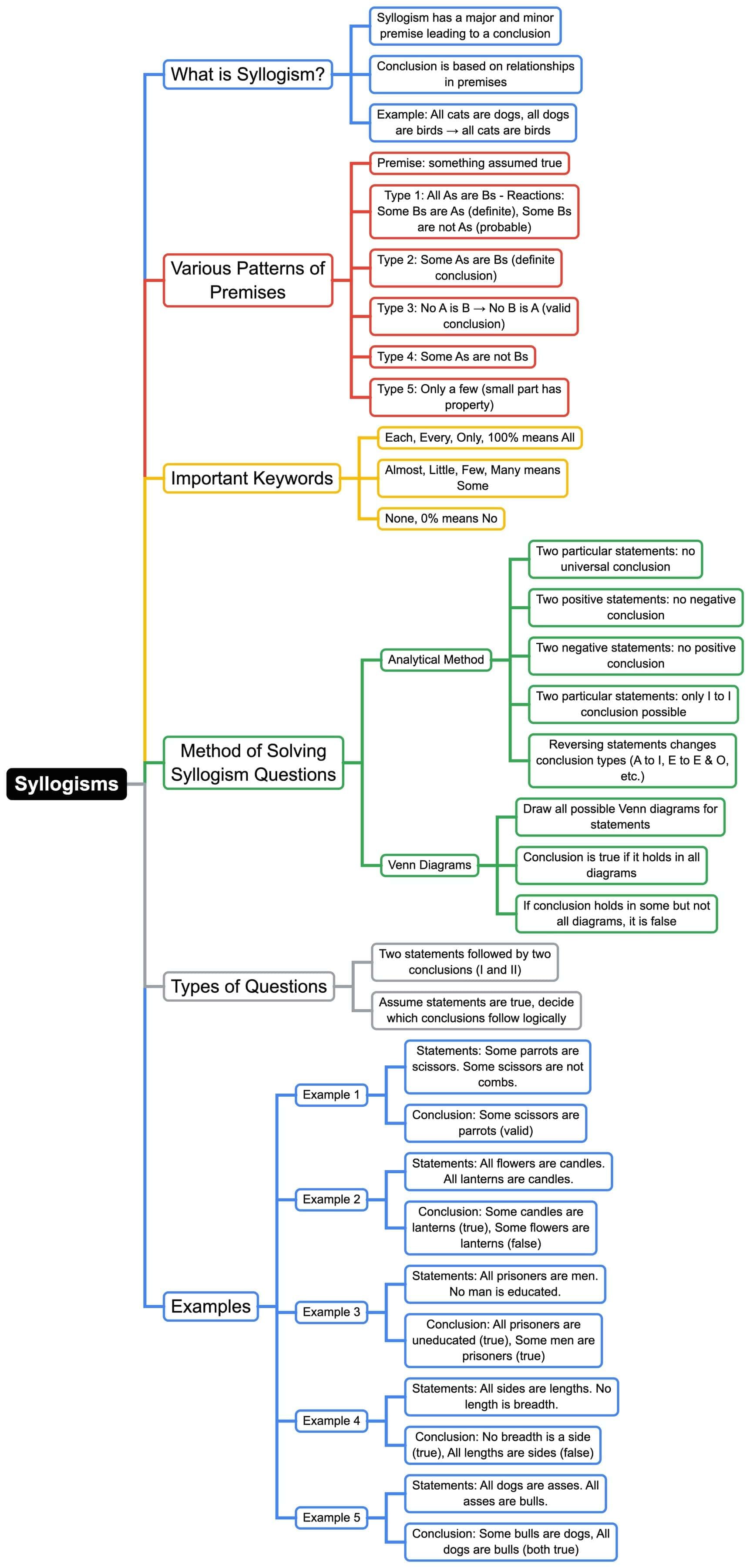
The document Mind Map: Syllogisms | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT is a part of the CAT Course Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI).
All you need of CAT at this link: CAT
|
77 videos|180 docs|96 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Syllogisms - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What is a syllogism and how is it structured? |  |
Ans. A syllogism is a form of logical reasoning that consists of two premises followed by a conclusion. The structure typically involves a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. For example: "All humans are mortal (major premise). Socrates is a human (minor premise). Therefore, Socrates is mortal (conclusion)."
| 2. How can syllogisms be useful in the CAT exam? |  |
Ans. Syllogisms are useful in the CAT exam as they test candidates' logical reasoning skills, which are essential for problem-solving and critical thinking. Understanding syllogistic reasoning can help candidates answer related questions more quickly and accurately, thus boosting their overall performance in the quantitative and verbal sections.
| 3. What are common types of syllogisms found in the CAT exam? |  |
Ans. Common types of syllogisms include categorical syllogisms, which involve statements about categories or classes; hypothetical syllogisms, which involve conditional statements; and disjunctive syllogisms, which involve "either/or" scenarios. Familiarity with these types can aid in identifying the correct conclusions in exam questions.
| 4. What strategies can be employed to solve syllogism questions effectively? |  |
Ans. Effective strategies for solving syllogism questions include breaking down premises into simpler statements, using Venn diagrams to visualize relationships, and practicing with sample questions to improve speed and accuracy. It's also helpful to look for common logical fallacies that may mislead the reasoning process.
| 5. How do negations impact syllogism conclusions? |  |
Ans. Negations can significantly impact syllogism conclusions by altering the truth value of the premises. When a premise is negated, it may change the logical relationship between the statements, potentially leading to a different conclusion. Understanding how to apply negations is crucial for accurately interpreting and answering syllogism questions in the exam.
Related Searches





















