Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions- 1 | Sample Papers For Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 Hours
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions
This question paper consists of 31 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1–7 are multiple-choice questions and each carries 1 mark.
- Questions 8–16 are very short-answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 17–26 are short-answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 27–31 are long-answer questions and each carries 5 marks.
Section - A
Q1. Which of the following is a renewable source of energy? (1 mark)
(a) Coal
(b) Solar energy
(c) Natural gas
(d) Petroleum
Ans: (b)
Solar energy comes from the sun and can be renewed naturally, unlike coal, natural gas, or petroleum, which are limited and take millions of years to form.
Q2. Which process is used to separate grains from husk? (1 mark)
(a) Filtration
(b) Winnowing
(c) Sieving
(d) Decantation
Ans: (b)
Winnowing separates grains from husk by blowing air, as husk is lighter and gets carried away, while grains fall back down.
Q3. Which part of the cell is responsible for controlling its activities? (1 mark)
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus
(c) Cell membrane
(d) Vacuole
Ans: (b)
The nucleus Hawkins controls the cell’s activities, like growth and division, because it contains the cell’s genetic material.
Q4. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of sound waves? (1 mark)
(a) Frequency
(b) Amplitude
(c) Temperature
(d) Wavelength
Ans: (c)
Sound waves have frequency, amplitude, and wavelength as characteristics. Temperature affects the speed of sound, but it isn’t a feature of the wave itself.
Q5. Which gas is primarily responsible for the greenhouse effect? (1 mark)
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Helium
Ans: (c)
Carbon dioxide traps heat in the atmosphere, causing the greenhouse effect, which warms the Earth. Other gases like oxygen or helium don’t have this effect.
Q6. Which of the following is a biodegradable material? (1 mark)
(a) Plastic bottle
(b) Vegetable peel
(c) Aluminium can
(d) Glass jar
Ans: (b)
Vegetable peels can be broken down by microorganisms, making them biodegradable. Plastic, aluminium, and glass are not easily decomposed.
Q7. What is the SI unit of force? (1 mark)
(a) Newton
(b) Joule
(c) Watt
(d) Kelvin
Ans: (a)
The SI unit of force is the Newton, which measures how much an object is pushed or pulled. Joule is for energy, Watt for power, and Kelvin for temperature.
Section - B
Q8. Name two sustainable agricultural practices used in India. (2 mark)
Ans: Organic farming uses natural fertilisers like compost to enrich soil without harmful chemicals, and crop rotation grows different crops like rice and pulses in sequence to improve soil fertility and reduce pests.
Q9. How do microorganisms help in waste management? (2 mark)
Ans: Microorganisms break down organic waste into compost by decomposing food scraps into nutrient-rich manure, and they ferment waste in biogas plants to produce eco-friendly energy.
Q10. What is the difference between contact and non-contact forces? Give one example of each. (2 mark)
Ans: Contact forces act when objects touch, like friction slowing a sliding book, while non-contact forces act without touching, like gravity pulling a ball downward.
Q11. Why do we see a rainbow after rain? (2 mark)
Ans: Raindrops act like prisms, refracting and reflecting sunlight in water droplets to split it into colours, forming a rainbow after rain.
Q12. Why is CNG considered a cleaner fuel compared to petrol or diesel? (2 mark)
Ans:
- CNG burns more completely and produces less smoke.
- It emits fewer harmful gases like carbon monoxide and sulphur oxides.
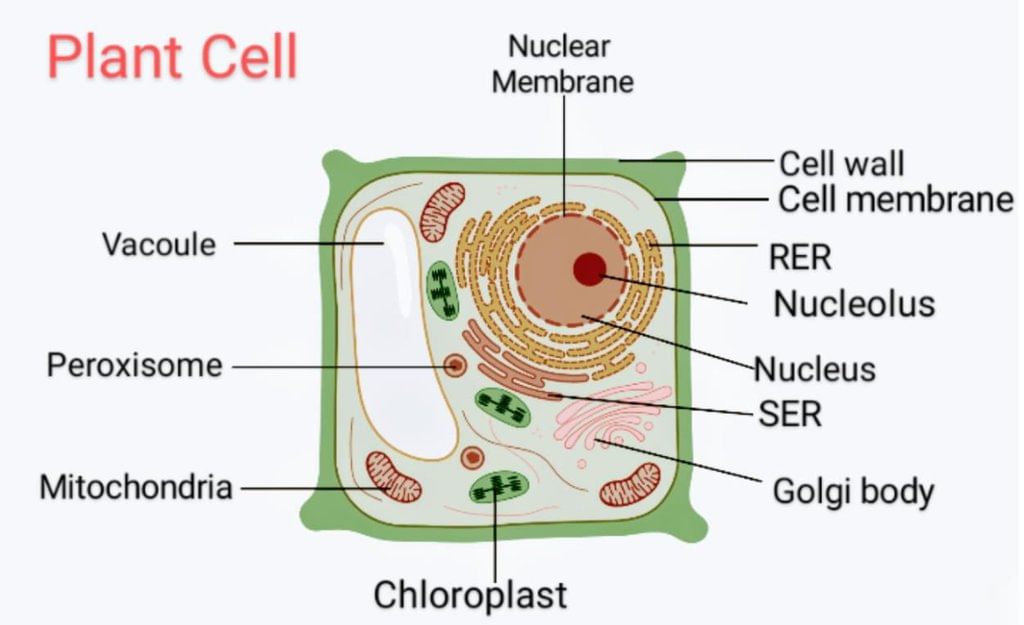
Q13. Draw a labelled diagram of a plant cell. (2 mark)
Ans:
Q14. Write two differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Prokaryotic cells do not have a well-defined nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus with a nuclear membrane.
- Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler, whereas eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex.
Q15. How does recycling help the environment? (2 mark)
Ans: Recycling reduces waste in landfills to decrease pollution and saves resources like trees by reusing materials such as paper.
Q16. Why is CNG considered a cleaner fuel compared to petrol or diesel? (2 mark)
Ans:
- CNG burns more completely and produces less smoke.
- It emits fewer harmful gases like carbon monoxide and sulphur oxides.
Section - C
Q17. Explain how winnowing and sieving can be used to separate components of a mixture. Give one example for each. (3 mark)
Ans: Winnowing separates lighter components from heavier ones by blowing air, like separating husk from grains when farmers toss the mixture and the wind carries the husk away. Sieving separates particles of different sizes using a mesh, such as sieving flour to remove coarse impurities. Both methods rely on physical properties like weight or size to separate mixtures effectively.
Q18. How does pressure vary with depth in a liquid? Explain with an example. (3 mark)
Ans: Pressure in a liquid increases with depth because the weight of the liquid above exerts more force. At greater depths, more liquid presses down, increasing pressure. For example, when diving deeper in a swimming pool, a diver feels more pressure on their ears due to the increased weight of water above, demonstrating how pressure grows with depth.
Q19. Why is composting considered an eco-friendly practice? (3 mark)
Ans: Composting is eco-friendly because it recycles organic waste like vegetable peels into nutrient-rich manure, reducing landfill waste and pollution. It enriches soil naturally, decreasing the need for chemical fertilisers that harm the environment. By promoting microbial activity, composting supports sustainable agriculture and reduces greenhouse gas emissions from waste decomposition, making it an environmentally beneficial practice.
Q20. Describe the role of the ozone layer in protecting life on Earth. (3 mark)
Ans: The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, protecting living organisms from skin cancer and eye damage. It shields plants from UV harm, ensuring healthy growth, and maintains ecosystems. For example, without the ozone layer, excessive UV radiation could harm marine life like plankton, disrupting food chains and affecting life on Earth.
Q21. How do camels adapt to survive in deserts? (3 mark)
Ans: Camels adapt to deserts by storing fat in their humps for energy when food is scarce, and they conserve water by producing concentrated urine and minimal sweat. Their thick fur protects against the sun and cold, and their wide feet prevent sinking in sand. For example, camels can drink large amounts of water at once, storing it to survive long periods without drinking in harsh desert conditions.
Q22. Explain the process of pollination in plants with an example. (3 mark)
Ans: Pollination is the transfer of pollen from a flower’s anther to its stigma, enabling fertilisation and seed production. It occurs through agents like wind, insects, or birds. For example, in mustard plants, bees carry pollen from one flower to another’s stigma while collecting nectar, aiding reproduction. This process ensures plants produce seeds and fruits, supporting plant reproduction and food production.
Q23. How does sound travel through different media? Give one example. (3 mark)
Ans: Sound travels as vibrations through solids, liquids, and gases, moving fastest in solids due to closely packed particles and slowest in gases. In solids, like a metal rod, vibrations travel quickly; in liquids, like water, they travel more slowly; and in air, slowest. For example, a dolphin’s sound travels through water to communicate, showing how sound moves effectively through a liquid medium.
Q24. Why is it important to conserve biodiversity? Give one example of a conservation effort in India. (3 mark)
Ans: Conserving biodiversity maintains ecosystems, ensuring food, clean water, and air for all life, and supports industries like agriculture and medicine. Loss of species disrupts ecosystems, affecting balance. For example, Project Tiger in India protects tigers by preserving habitats in national parks like Jim Corbett, maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the survival of this endangered species alongside other flora and fauna.
Q25. Describe how electroplating is used in daily life with an example. (3 mark)
Ans: Electroplating coats a metal object with another metal using electricity to enhance durability or appearance. A thin layer of precious metal is deposited on a cheaper metal surface. For example, silver electroplating on steel utensils gives them a shiny, corrosion-resistant finish, making them attractive and long-lasting for daily use in households while being cost-effective.
Q26. How does the use of renewable energy sources benefit the environment? (3 mark)
Ans: Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power reduce pollution by producing clean energy without releasing harmful gases like carbon dioxide. They conserve finite resources like coal and decrease greenhouse gas emissions, combating climate change. For example, solar panels generate electricity without burning fossil fuels, reducing air pollution and helping preserve the environment for future generations.
Section - D
Q27. (a) What is organic farming? (5 mark)
(b) Explain two methods used in organic farming with examples.
(c) Why is it important for sustainable agriculture?
Ans:
(a) Organic farming is a method of farming that avoids the use of chemical fertilisers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). It uses natural substances and eco-friendly practices to maintain soil fertility and control pests.
(b) Two methods used in organic farming:
- Composting – Organic waste like vegetable peels, cow dung, and dry leaves are decomposed into compost, which acts as a natural fertiliser.
Example: Vermicomposting using earthworms.- Crop Rotation – Different crops are grown in the same field in sequence to maintain soil fertility and reduce pests.
Example: Growing pulses after cereals to increase nitrogen in the soil.(c) Importance for sustainable agriculture:
- Maintains soil fertility
- Reduces pollution and chemical hazards
- Produces healthier food
- Conserves biodiversity
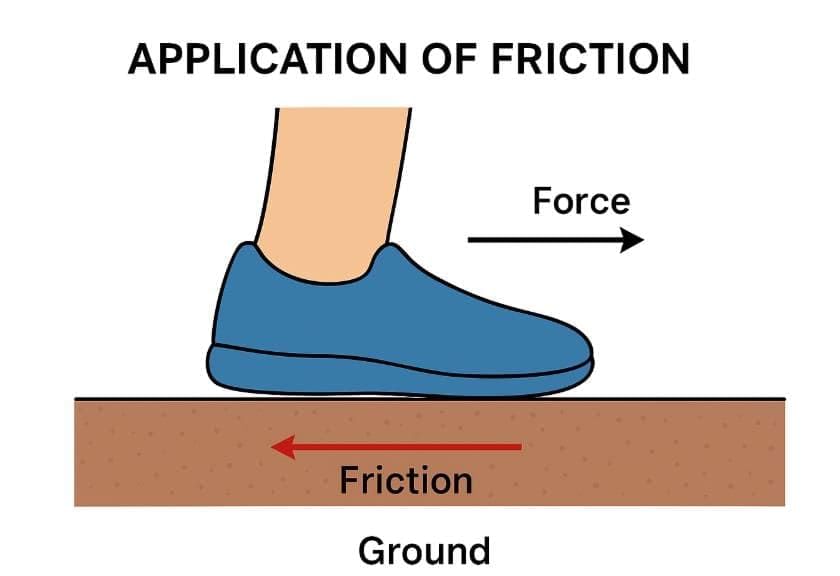
Q28.(a) What is friction? (5 mark)
(b) Differentiate between static and sliding friction with examples.
(c) Draw a diagram showing an application of friction in daily life.
Ans: (a) Friction is the opposing force that comes into play when two surfaces in contact try to move or slide over each other.
(b) Difference between Static and Sliding Friction:
(c) Diagram (application of friction):
Example – Friction between shoe sole and ground while walking.
Q29. (a) What is the greenhouse effect? (5 mark)
(b) Explain two causes of the greenhouse effect with examples.
(c) How can we reduce its impact?
Ans: (a) The greenhouse effect is the warming of Earth’s atmosphere caused by greenhouse gases (like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour) that trap heat radiated from the Earth’s surface.
(b) Two causes of the greenhouse effect:
- Burning of fossil fuels – Vehicles, industries, and power plants release large amounts of CO2.
- Deforestation – Fewer trees reduce CO2 absorption, leading to its accumulation in the atmosphere.
(c) Ways to reduce its impact:
- Planting more trees (afforestation)
- Using renewable energy sources (solar, wind)
- Reducing waste and recycling
- Promoting public transport to cut vehicle emissions
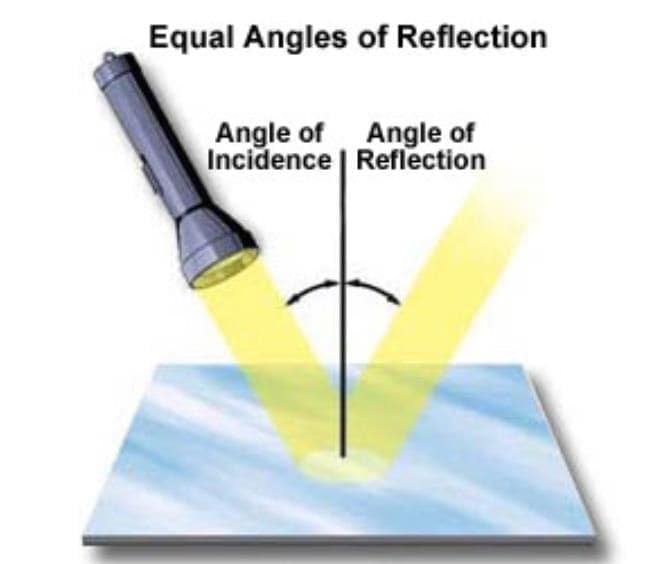
Q30. (a) What is the reflection of light? (5 mark)
(b) Explain the laws of reflection with a diagram.
(c) Give one real-life application of reflection.
Ans: (a) Reflection of light is the bouncing back of light rays when they strike a smooth surface like a mirror.
(b) Laws of Reflection:
- The angle of incidence = The angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
(c) Application of reflection:
- Mirrors used in homes
- Periscopes in submarines
- Reflectors on vehicles
Q31. (a) What are microorganisms? (5 mark)
(b) Name two beneficial and two harmful microorganisms with their effects.
(c) How can we prevent the harmful effects of microorganisms?
Ans: (a) Microorganisms are tiny living organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye and are visible only under a microscope. Examples: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, viruses, algae.
(b) Examples:Beneficial microorganisms:
- Lactobacillus (bacteria) – Converts milk into curd.
- Yeast (fungus) – Used in baking bread and the fermentation of alcohol.
Harmful microorganisms:
- Plasmodium (protozoa) – Causes malaria.
- Salmonella (bacteria) – Causes food poisoning.
(c) Prevention of harmful effects:
- Proper food preservation (refrigeration, pickling, canning)
- Maintaining hygiene and sanitation
- Vaccination against diseases
- Using disinfectants and safe drinking water
FAQs on Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions- 1 - Sample Papers For Class 8
| 1. What is the structure and marking scheme of the Class 8 Science sample paper? |  |
| 2. How can students effectively prepare for the Class 8 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can students expect in the Class 8 Science exam? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to understand the marking scheme of the exam? |  |
| 5. What resources can students use to study for the Class 8 Science exam? |  |