Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 4 | Sample Papers For Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions
This question paper consists of 31 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1-7 are multiple-choice questions and each carries 1 mark. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8-16 are very short-answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 17-26 are short-answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 27-31 are long-answer questions and each carries 5 marks.
Section - A
Q1. Which of the following is used to kill harmful microorganisms in water? (1 mark)
(a) Chlorine
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Carbon dioxide
Ans: (a)
Chlorine is commonly added to water supplies to kill harmful microorganisms and make water safe for drinking.
Q2. Which of these is NOT a physical change? (1 mark)
(a) Melting of ice
(b) Dissolving sugar in water
(c) Rusting of iron
(d) Breaking of glass
Ans: (c)
Rusting of iron is a chemical change because a new substance (iron oxide) is formed, unlike physical changes where no new substance is formed.
Q3. Which organelle is known as the “powerhouse of the cell”? (1 mark)
(a) Chloroplast
(b) Nucleus
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Ribosome
Ans: (c)
Mitochondria are called the “powerhouse of the cell” because they release energy by breaking down glucose during respiration.
Q4. Which of the following travels fastest? (1 mark)
(a) Light in air
(b) Sound in air
(c) Sound in water
(d) Sound in steel
Ans: (a)
Light travels fastest in air at a speed of about 3 × 108 m/s, which is much faster than sound in any medium.
Q5. Which of the following is a fossil fuel? (1 mark)
(a) Biogas
(b) Petrol
(c) Solar energy
(d) Wind energy
Ans: (b)
Petrol is a fossil fuel formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals buried under the earth for millions of years.
Q6. Which one is an example of a physical adaptation? (1 mark)
(a) Long neck of a giraffe
(b) Hunting in groups by lions
(c) Birds migrating
(d) Learning to ride a bicycle
Ans: (a)
The long neck of a giraffe is a physical adaptation that helps it reach leaves on tall trees for survival.
Q7. Which device converts chemical energy into electrical energy? (1 mark)
(a) Bulb
(b) Battery
(c) Generator
(d) Fan
Ans: (b)
A battery converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy, which is then used to power devices.
Section - B
Q8. What is potable water? Name one method to make water potable. (2 mark)
Ans: Potable water is water that is safe for human consumption.
One method: Boiling water kills harmful microorganisms and makes it potable.
Q9. Write two differences between arteries and veins. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood towards the heart.
- Arteries have thick, elastic walls, whereas veins have thin walls with valves to prevent backflow.
Q10. Why do we apply paint on iron articles? (2 mark)
Ans: Paint prevents iron articles from coming in contact with moisture and oxygen, thus protecting them from rusting.
Q11. What is a galaxy? Name one. (2 mark)
Ans: A galaxy is a huge system of stars, dust, and gases bound together by gravity.
Example: The Milky Way Galaxy.
Q12. Write two uses of concave mirrors. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Used by dentists to view enlarged images of teeth.
- Used as reflectors in headlights and torches.
Q13. State two harmful effects of plastics on the environment. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Plastics are non-biodegradable and cause soil and water pollution.
- Animals may swallow plastic, leading to injury or death.
Q14. Why does a needle sink in water but a ship floats? (2 mark)
Ans: A needle sinks because it has high density and displaces less water.
A ship floats because its hollow structure displaces more water, reducing its overall density below that of water.
Q15. Name two communicable diseases and their mode of transmission. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Tuberculosis – spreads through air by coughing or sneezing.
- Cholera – spreads through contaminated food and water.
Q16. What is meant by balance in nature? (2 mark)
Ans: Balance in nature refers to the stable relationship between living organisms and their environment, where natural processes maintain equilibrium (e.g., oxygen and carbon dioxide balance, predator-prey relationship).
Section - C
Q17. Explain crystallisation with an example. (3 mark)
Ans: Crystallisation is the process of obtaining pure crystals of a substance from its solution.
Example: Crystals of copper sulphate can be obtained by evaporating its saturated solution and then cooling it.
Q18. Why are solar cookers painted black from inside and covered with a glass plate? (3 mark)
Ans:
- Black surface absorbs more heat, increasing the efficiency of the cooker.
- The glass plate allows sunlight to enter but traps the heat inside (greenhouse effect).
Q19. Write differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
- Aerobic respiration releases more energy, whereas anaerobic releases less energy.
- End products: Aerobic → Carbon dioxide + water; Anaerobic → Alcohol/lactic acid + carbon dioxide.
Q20. Explain the role of platelets in blood clotting. (3 mark)
Ans: Platelets help in blood clotting by releasing clotting factors at the site of injury.
This prevents excessive bleeding and forms a protective layer (scab) over the wound.
Q21. Define renewable and non-renewable resources with two examples each. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Renewable resources: Resources that can be replenished naturally.
Examples: Solar energy, wind energy.- Non-renewable resources: Resources that are limited and exhaustible.
Examples: Coal, petroleum.
Q22. Explain adaptations in aquatic animals with examples. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Aquatic animals have gills for breathing underwater (e.g., fish).
- Streamlined body reduces resistance while swimming (e.g., dolphins).
- Fins and flippers help in movement.
Q23. How is lightning produced? Mention two safety measures during a thunderstorm. (3 mark)
Ans: Lightning is produced due to the movement of water droplets and air currents in clouds, which causes separation of electric charges. Discharge of charges between clouds or with the ground produces lightning.
Safety measures:
- Stay indoors and avoid open fields.
- Do not stand under trees or near electric poles.
Q24. What is deforestation? Write three effects of deforestation. (3 mark)
Ans: Deforestation is the cutting down of trees on a large scale.
Effects:
- Loss of biodiversity and wildlife habitat.
- Increase in soil erosion and floods.
- Increase in carbon dioxide, leading to global warming.
Q25. Explain how coal and petroleum are formed. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Coal: Formed from the remains of plants buried under the earth millions of years ago. Heat and pressure converted them into coal.
- Petroleum: Formed from dead plants and animals buried under sea beds. Heat, pressure, and absence of air converted them into petroleum and natural gas.
Q26. Write three methods of water conservation. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Rainwater harvesting – collecting and storing rainwater.
- Reuse of water – recycling water for gardening or cleaning.
- Avoiding wastage – closing taps when not in use and repairing leaks.
Section - D
Q27. (a) Define sericulture. (5 mark)
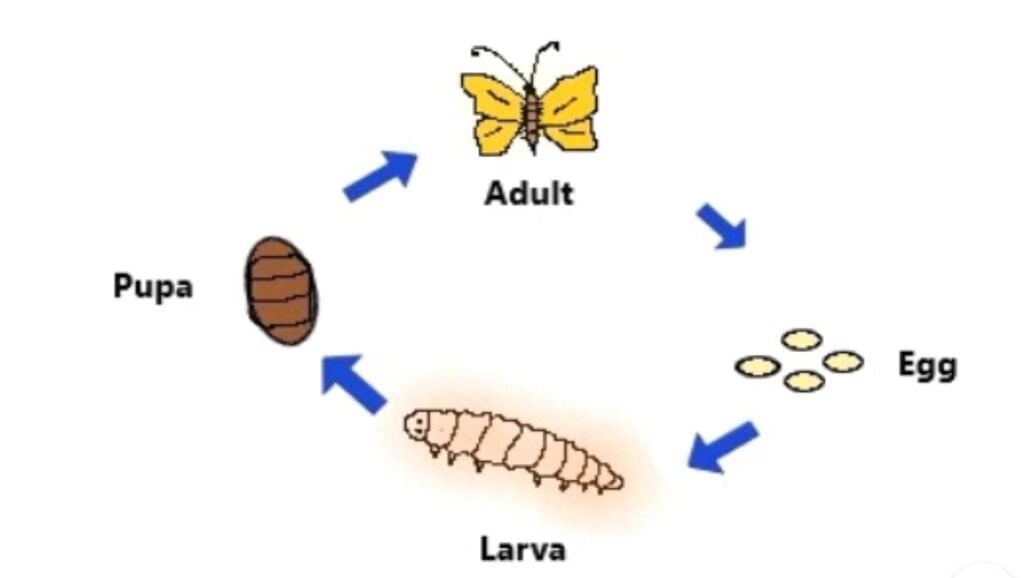
(b) Explain the life cycle of a silkworm with a diagram.
(c) State two uses of silk.
Ans: (a) Sericulture: The rearing of silkworms for the production of silk is called sericulture.
(b) Life cycle of a silkworm:
- The female silk moth lays eggs.
- The eggs hatch into larvae (caterpillars), called silkworms.
- The larvae feed on mulberry leaves and grow.
- The silkworm spins a cocoon made of silk fibres around itself.
- From the cocoon, the adult moth emerges.
(c) Uses of silk:
- Making clothes and garments.
- Used in making upholstery, carpets, and decorative items.
Q28. (a) What is sound pollution? (5 mark)
(b) Mention three causes and three harmful effects of sound pollution.
(c) Suggest two preventive measures.
Ans: (a) Sound pollution: The presence of excessive or unpleasant sound in the environment that causes discomfort to living beings.
(b) Causes:Honking of vehicles.
- Loudspeakers and music systems.
- Industrial machines.
Harmful effects:
- Hearing problems or deafness.
- Lack of sleep and stress.
- Disturbance in wildlife.
(c) Preventive measures:
- Planting more trees to absorb sound.
- Using silencers and controlling noise levels of vehicles and machines.
Q29. (a) What are fossils? (5 mark)
(b) How are they formed?
(c) Mention two uses of fossils for scientists.
Ans:
(a) Fossils: The preserved remains or impressions of ancient plants and animals found in rocks.
(b) Formation: Fossils are formed when plants or animals die, get buried under mud, sand, or sediments. Over time, pressure and chemical processes preserve their shapes in rocks.
(c) Uses of fossils:
- Help scientists understand the evolution of life.
- Provide evidence about the past climate and geological conditions of the Earth.
Q30. (a) Define photosynthesis. (5 mark)
(b) Write its word equation.
(c) Explain how stomata help in photosynthesis.
Ans: (a) Photosynthesis: The process by which green plants prepare food using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
(b) Word equation: Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen (in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll)
(c) Role of stomata: Stomata are small pores present on the leaves that allow the exchange of gases. They help in taking in carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis and releasing oxygen.
Q31. (a) What is force? (5 mark)
(b) Explain effects of force with examples.
(c) State differences between balanced and unbalanced forces.
Ans:
(a) Force: A push or pull acting on an object is called force.
(b) Effects of force (with examples):
- Force can change the state of motion of an object (e.g., kicking a football).
- Force can change the shape of an object (e.g., pressing a rubber ball).
- Force can change the direction of a moving object (e.g., hitting a cricket ball with a bat).
(c) Balanced vs. Unbalanced forces:
- Balanced forces: Two equal and opposite forces acting on an object. They do not change the object’s state of motion (e.g., tug of war when both teams pull equally).
- Unbalanced forces: When unequal forces act on an object, causing a change in motion (e.g., pushing a stationary car to make it move).
FAQs on Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 4 - Sample Papers For Class 8
| 1. What is the marking scheme for Class 8 Science exams? |  |
| 2. How should students prepare for the Class 8 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can be expected in Section D of the exam? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to study all sections in the Class 8 Science syllabus? |  |
| 5. How can students effectively manage their time during the Class 8 Science exam? |  |