Case Based Questions: Data Handling and Presentation | Mathematics for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Case Study 1 |

|
| Case Study 2 |

|
| Case Study 3 |

|
| Case Study 4 |

|
Case Study 1
Ankita manages a book stall at a fair. She recorded the genres of books sold on Monday and presented the data in the following table 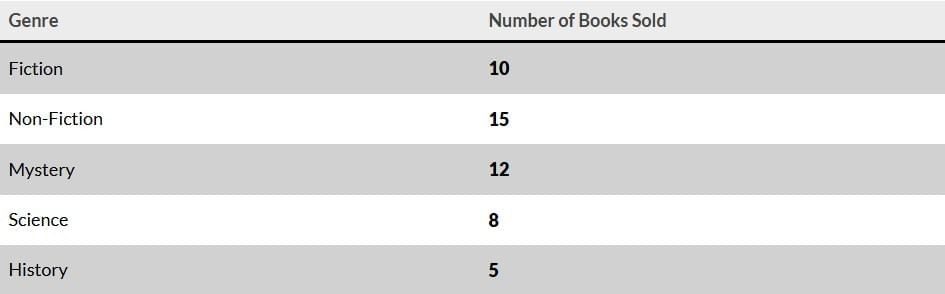 Q.1.What is the total number of books sold on Monday?
Q.1.What is the total number of books sold on Monday?
(a) 45
(b) 50
(c) 55
(d) 60
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 50
10 + 15 + 12 + 8 + 5 = 50
The total number of books sold is 50 after adding all genres.
Q.2. Which genre of books sold the least on Monday?
(a) Fiction
(b) Non-Fiction
(c) History
(d) Science
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) History
History books sold = 5, which is the smallest number in the table.
Q.3. If Ankita sells 5 more mystery books on Tuesday, what will be the total number of mystery books sold?
(a) 12
(b) 15
(c) 17
(d) 20
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 17
12 (Monday) + 5 (Tuesday) = 17
Q.4. The price of one fiction book is ₹150. How much money did Ankita earn by selling all fiction books on Monday?
(a) ₹1,000
(b) ₹1,200
(c) ₹1,500
(d) ₹1,800
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) ₹1,500
10 × 150 = 1500
Multiplying the number of fiction books by the price per book gives ₹1,500.
Q.5. If Ankita wants to present this data in a bar graph, how many bars will the graph contain?
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 5
There are 5 genres, so there will be 5 bars in the graph.
Each genre will be represented by one bar, so there will be five bars in total.
Case Study 2
Shobhit works in a shoe store. He records the shoe sizes and the number of pairs sold every day. On Tuesday, he sold 60 pairs. His record for the day is shown below.
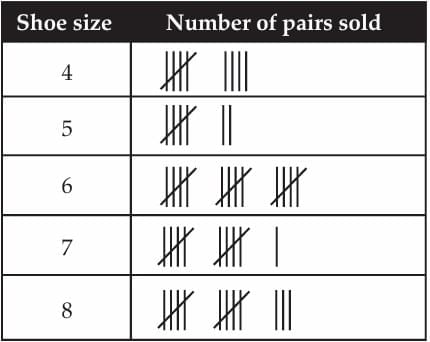
Q.1. How many pairs of size 8 were sold on Tuesday?
(a) 3
(b) 10
(c) 11
(d) 13
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) 13
The tally for size 8 shows two full groups of five (2 × 5 = 10) plus three single tallies, so 10 + 3 = 13.
Q.2. Which shoe size sold the most?
(a) Size 4
(b) Size 6
(c) Size 8
(d) Size 9
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Size 6
Compare the counts: size 6 has 15 pairs, which is greater than size 8 (13), size 7 (11), size 4 (9), and size 5 (7). Therefore size 6 sold the most.
Q.3. Shobit realised that he had not fully recorded the sale for Tuesday. How many sold pairs had he not recorded?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 5 pairs were not recorded.
The problem statement says 60 pairs were sold that day but the tallies add to 55. Missing = 60 − 55 = 5 pairs.
Q.4. The unrecorded data was of shoe size 7. Shobit corrected his record accordingly. Which of the following statements will be true now?
(a) Shoe size 8 sold the least now
(b) Shoe size 7 sold the most now
(c) Shoe size 5 is the new mode of the data
(d) Number of shoe pairs of size 3 can be calculated
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Shoe size 7 sold the most now.
Add the 5 unrecorded pairs to size 7: 11 + 5 = 16 pairs for size 7. After correction the counts become 9 (size 4), 7 (size 5), 15 (size 6), 16 (size 7), 13 (size 8). Size 7 now has the highest count (16), so it is the mode. Option (a) is false because size 5 (7 pairs) is now the least, not size 8. Option (c) is false because size 7, not size 5, is the mode. Option (d) is irrelevant — there is no data for size 3.
Q.5. The price of one shoe pair of size 5 is 800. How much money had Shobhit collected by selling all the shoe pairs of size 5?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: ₹5,600.
Number of size 5 pairs = 7. Revenue = 7 × ₹800 = ₹5,600.
Case Study 3
Read the pictograph given below and answer the following questions:Persons employed in one year
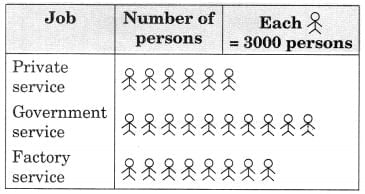 Q.1.What is the number of persons employed in government service?
Q.1.What is the number of persons employed in government service? View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Number of persons employed in government service = 10 x 3000 = 30,000
(b) How many more person were employed in government service than in private service?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 10 x 3000 – 6 x 3,000 = 30,000 – 18,000 = 12,000 persons were employed more in government service than in private service.
(c) In which service, were the maximum number of persons employed?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In government service, the maximum number of persons were employed.
Case Study 4
The given bar graph represents the frequency of a, e, i, o, and u in a piece of English writing.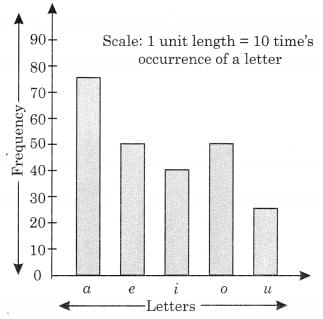 Q.1. Which letter occurred the maximum number of times?
Q.1. Which letter occurred the maximum number of times?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: a letter occurred the maximum number of times.
Q.2. Which letter occurred 40 times?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: i letter occurred 40 times.
Q.3. Which letter occurred less than 30 times?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: u letter occurred less than 30 times.
Q.4. Write down the five letters in the decreasing order of frequencies.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: a, e, o, i, u is the decreasing order of their frequencies
|
48 videos|334 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on Case Based Questions: Data Handling and Presentation - Mathematics for Class 6
| 1. What is data handling in the context of Class 6 studies? |  |
| 2. Why is data presentation important for students? |  |
| 3. What types of data representation are commonly taught in Class 6? |  |
| 4. How can students ensure accuracy when collecting data for their projects? |  |
| 5. What skills do students develop through data handling and presentation activities? |  |















