Unit Test (Solution): Materials Around Us | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Attempt all questions.
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 7 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 8 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 13 to 15 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 16 carries 4 marks.
Q1: Which of the following statement is correct? (1 Mark)
(i) Wood is translucent while glass is opaque
(ii) Aluminium foil has lustre while an eraser does not
(iii) Sugar does not dissolve in water whereas sawdust does
(iv) An apple is not matter because it occupies no space
Ans: (ii) Aluminium foil has lustre while an eraser does not
- Wood is opaque, not translucent, and glass is transparent, not opaque.
- Aluminium foil is shiny (lustrous), but an eraser is dull, so this is correct.
- Sugar dissolves in water, sawdust does not.
- Apple is matter because it has mass and occupies space.
Q2: The property of a material that makes it shiny is called __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: lustre
Lustrous materials, such as metals, have a shiny appearance when light falls on them.
Q3: Which of the following materials is opaque? (1 Mark)
(i) Glass
(ii) Water
(iii) Wood
(iv) Cellophane paper
Ans: (iii) Wood
Opaque materials, like wood or metal, do not allow light to pass through.
Q4: Materials that dissolve in water are known as __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: soluble
Soluble materials, like sugar or salt, disappear when mixed with water.
Q5: What unit is used to measure the mass of an object? (1 Mark)
(i) Litre
(ii) Kilogram
(iii) Cubic metre
(iv) Millilitre
Ans: (ii) Kilogram
Mass is measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg) in the International System of Units.
Q6: The saying “All that glitters is not gold” refers to which property of materials? (1 Mark)
Ans: lustre
This saying indicates that not all shiny materials are metals; some are polished or coated non-metals.
Q7: What is the space occupied by matter called? (1 Mark)
Ans: volume
Volume measures the space taken by matter, with units like litre (L) or millilitre (mL).
Q8: Name two examples of translucent materials and explain their property. (2 Marks)
Ans: Butter paper and frosted glass are translucent materials. They allow light to pass through but do not let objects be seen clearly, creating a hazy appearance.
Q9: Why are some metals like iron or copper described as lustrous? (2 Marks)
Ans: Metals like iron or copper are lustrous because their surfaces shine when light falls on them, especially on freshly cut surfaces. However, exposure to air and moisture can dull this shine over time.
Q10: Differentiate between soluble and insoluble materials with one example each. (2 Marks)
Ans: 
Q11: What role does mass play in identifying matter? (2 Marks)
Ans: Mass quantifies the amount of matter in an object, measured in grams or kilograms. It helps distinguish heavier objects (more mass) from lighter ones (less mass), as seen with sand versus water.
Q12: Explain why a tumbler made of cloth cannot be used to store water. (2 Marks)
Ans: A tumbler made of cloth cannot store water because cloth lacks the ability to hold liquid without leaking. Materials like glass or plastic are chosen for their water-holding capacity.
Q13: Describe how materials can be grouped based on their hardness and softness, with examples. (3 Marks)
Ans: 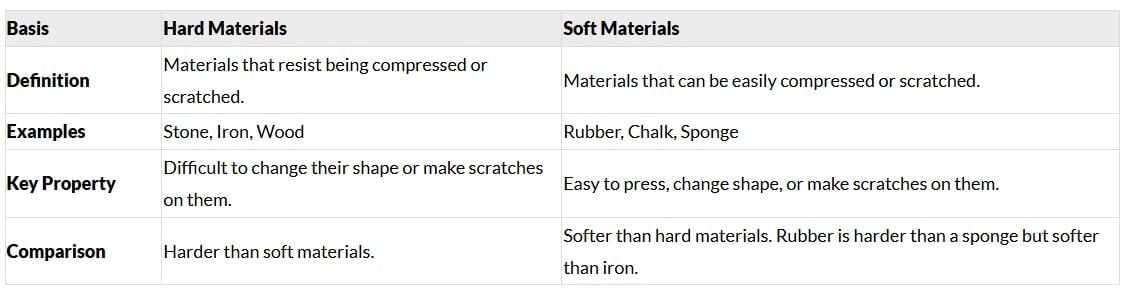
Q14: Explain the significance of classifying materials based on their ability to allow light to pass through. (3 Marks)
Ans:
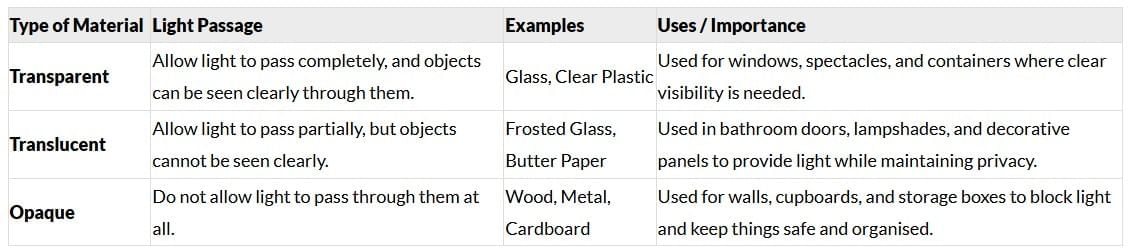
Q15: Discuss how the properties of materials determine their use in daily life, with two examples. (3 Marks)
Ans:
| Property of Material | How it Determines Use | Example 1 | Example 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance (Lustre / Non-Lustre) | Materials with shiny (lustrous) surfaces are used for decoration and making attractive objects, while dull materials are used where looks do not matter much. | Copper or Aluminium – used for utensils because they look shiny and appealing. | Wood – used for furniture even though it is non-lustrous, but can be polished to look attractive. |
| Hardness / Softness | Hard materials are chosen where strength and durability are needed, while soft materials are chosen where flexibility or easy shaping is required. | Iron – used for making tools and machines because it is hard and strong. | Rubber – used for making erasers and tyres because it is soft and flexible. |
Q16: Imagine you have two mysterious materials, X and Y. When you try to press material X, it feels rigid and does not change its shape easily. On the other hand, material Y easily changes its shape when you press it. Now, when you mix both materials in water, only material X dissolves completely, while material Y remains unchanged. What can materials X and Y be? Can you identify whether material X is hard or soft? What about material Y? Justify your answer. (4 Marks)
Ans:
Material X: Since it feels rigid, does not change shape easily, and dissolves in water, it could be salt or sugar.
Material Y: Since it changes shape easily and does not dissolve in water, it could be clay or rubber.
| Material | Observation | Property | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| X | Rigid, hard to press, dissolves completely in water | Hard and soluble | Material X is hard and soluble (like salt/sugar). |
| Y | Changes shape easily, does not dissolve in water | Soft and insoluble | Material Y is soft and insoluble (like clay/rubber). |
Justification:
Hard materials resist change in shape, which is why X is hard.
Soft materials are easily pressed or shaped, which is why Y is soft.
Solubility test shows X is soluble and Y is insoluble, helping us identify their nature.
|
70 videos|367 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solution): Materials Around Us - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of materials classified in our surroundings? |  |
| 2. How do we determine the properties of materials? |  |
| 3. Why is it important to study the materials around us? |  |
| 4. What role do materials play in daily life? |  |
| 5. How can we recycle materials, and why is it important? |  |





















