Unit Test (Solutions): Temperature and its Measurement | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Attempt all questions.
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 7 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 8 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 13 to 15 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 16 carries 4 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following is used to measure human body temperature? (1 Mark)
(i) Laboratory thermometer
(ii) Digital clinical thermometer
(iii) Room thermometer
(iv) Barometer
Ans: (ii) Digital clinical thermometer
A digital clinical thermometer is specially designed to measure human body temperature quickly and accurately.
Q2: The normal temperature of a healthy human body is __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: 37.0 °C
This is stated as the average normal body temperature in the text.
Q3: A hotter body has a __________ temperature than a colder body. (1 Mark)
(i) Lower
(ii) Higher
(iii) Equal
(iv) Unmeasurable
Ans: (ii) Higher
Temperature is a reliable measure of hotness or coldness, where the difference indicates relative hotness between bodies.
Q4: The device used to measure temperature is called a __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: thermometer
A thermometer is introduced as the tool for measuring temperature reliably.
Q5: What liquid is generally used in a laboratory thermometer? (1 Mark)
(i) Water
(ii) Mercury or alcohol
(iii) Oil
(iv) Milk
Ans: (ii) Mercury or alcohol
The text mentions that laboratory thermometers use alcohol (colored red) or mercury.
Q6: Name the temperature scale that is the SI standard unit for temperature. (1 Mark)
Ans: Kelvin scale
Q7: Who is known as the ‘Weather Woman of India’? (1 Mark)
Ans: Anna Mani
Anna Mani is highlighted for her contributions to weather measurement instruments.
Q8: Why can’t we always rely on our sense of touch to decide if an object is hot or cold? (2 Marks)
Ans: Sense of touch can be misleading because it depends on the temperature our skin was exposed to earlier. For example, after dipping one hand in warm water and the other in cold water, the same tap water may feel cool to one hand and warm to the other.
Q9: State two precautions to be taken while using a laboratory thermometer. (2 Marks)
Ans:
(i) Handle with care to avoid breaking it.
(ii) Do not hold it by the bulb and keep it vertical while taking readings.
Q10: How does a laboratory thermometer indicate temperature changes? (2 Marks)
Ans: A laboratory thermometer indicates temperature changes by the rise or fall of a liquid column (alcohol or mercury) in a narrow glass tube. The level of the liquid coinciding with the Celsius scale mark shows the temperature reading.
Q11: Why are digital thermometers preferred over mercury thermometers? (2 Marks)
Ans: Digital thermometers are preferred because mercury is extremely toxic and difficult to dispose of if the thermometer breaks. Digital thermometers pose no such risk, are easier to read with their display, and use heat sensors for safe measurement.
Q12: Describe the steps to measure your body temperature using a digital clinical thermometer. (3 Marks)
Ans: To measure body temperature:
(i) Wash your hands and the thermometer tip with soap and water.
(ii) Reset the thermometer by pressing the reset button, place it under the tongue, and close your mouth, waiting for a beeping sound.
(iii) Remove it, read the temperature on the digital display, record it, clean the tip, and dry it. This ensures accurate and hygienic measurement.
Q13: Explain why the temperature of boiling water remains constant during boiling. (3 Marks)
Ans: The temperature of boiling water remains constant during boiling because the heat energy supplied is used to change the water from liquid to vapor (steam) rather than increasing the temperature. This phase change takes place at a fixed temperature, so even though heat is continuously given, the thermometer reading does not rise. The temperature remains steady until the entire quantity of water is converted into vapour.
Q14: Discuss the role of air temperature in weather forecasting, mentioning one key contributor. (3 Marks)
Ans: Air temperature is an important weather parameter monitored at weather stations worldwide, providing data alongside other factors for accurate weather forecasts. It helps predict daily variations, such as rising temperatures in summer and falling in winter. Anna Mani, known as the ‘Weather Woman of India,’ contributed by inventing weather instruments, reducing India’s reliance on foreign tools and aiding global weather prediction efforts.
Q15: A laboratory thermometer has 50 divisions between 0 °C and 100 °C. What does each division of this thermometer measure? (3 Marks)
Ans:
Given:
Temperature difference between 0 °C and 100 °C = 100 °C
Number of divisions = 50
Each division measures:
= Total temperature difference ÷ Number of divisions
= 100 °C ÷ 50
= 2 °C per division
So, each division of the thermometer measures 2 °C.
Q16: Compare the features and uses of a clinical thermometer and a laboratory thermometer, including one limitation each. (4 Marks)
Ans:
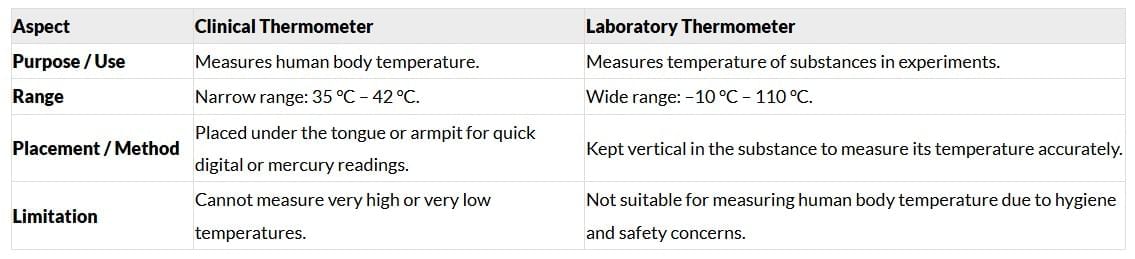
|
86 videos|288 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Temperature and its Measurement - Science for Class 6
| 1. What is temperature, and how is it measured? |  |
| 2. What are the different scales used to measure temperature? |  |
| 3. How can I convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit? |  |
| 4. What is absolute zero, and why is it significant? |  |
| 5. Why is temperature measurement important in daily life? |  |





















