Unit Test(Solutions): Family and Community | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M: 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: What is the primary type of family described as having several generations living together? (1 Mark)
Ans: Joint family.
Q2: What principle is important in Indian culture regarding family duties? (1 Mark)
Ans: Dharma
Q3: Fill in the blank: Family members support each other through love, care, and ______. (1 Mark)
Ans: Cooperation
Q4: Name one way children can help in a family. (1 Mark)
Ans: By helping with household tasks or taking care of younger siblings
Q5: What does ‘interdependence’ mean in the context of families and communities? (1 Mark)
Ans: Relying on each other for support and sharing responsibilities
Q6: Explain the difference between a joint family and a nuclear family with examples. (2 Marks)
Ans: 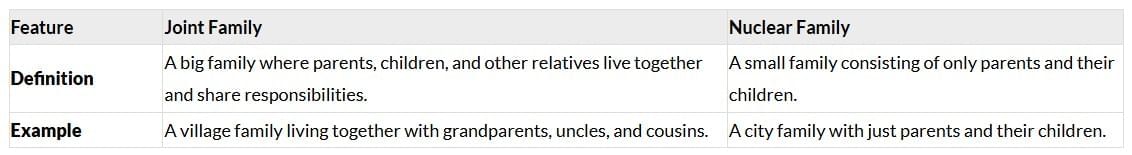
Q7: List and briefly explain two values that children learn in the family as a 'school'. (2 Marks)
Ans: Ahimsa (non-violence) - learning to avoid harm to others; Dana (giving) - learning to share and help family members. (Any two from ahimsa, dana, seva, tyaga.)
Q8: How do communities ensure secure access to shared resources like water or forests? (2 Marks)
Ans: Communities agree on practices or rules for using shared resources, such as water harvesting or grazing lands, requiring individuals to perform duties for smooth functioning.
Q9: How do family members support each other? Provide an example. (3 Marks)
Ans: Family members support each other through love, care, and cooperation. Parents guide and provide for children, while children help at home or care for elders. For example, during festivals or special occasions, family members may share resources like food or clothing to support each other, showing selflessness and strengthening family bonds.
Q10: Explain how communities in urban areas differ from rural communities with an example. (3 Marks)
Ans: Urban communities, like Residents’ Welfare Associations, focus on rules for cleanliness, waste management, and shared spaces, with members participating in decision-making. Rural communities depend on shared resources and collective work, such as farming and water management, often guided by traditions. Both types promote cooperation, but their activities and priorities differ according to their environment and needs.
Q11: What are the various types of communities? Give one example for each. (3 Marks)
Ans: Types include:
Jāti or subdivision – a smaller group within a larger social structure, e.g., a specific caste group.
Religion or region – groups of people who share the same religion or live in the same area, e.g., Mumbai’s Parsi community or Chennai’s Sikh community.
Interest or work – people connected through a common profession, hobby, or activity, e.g., Kerala’s scientific community or a school’s art community.
Additionally, communities can exist in schools, such as classes, sports teams, the National Service Scheme, or the National Cadet Corps. These examples show that communities can be based on social, cultural, professional, or recreational connections, reflecting the diverse ways people come together.
Q12: Discuss the interdependent nature of communities with examples from the chapter. (5 Marks)
Ans: Communities are interdependent because individuals and groups rely on each other for support, resources, and cooperation. In rural areas, communities often come together to share agricultural practices such as land preparation, sowing, and harvesting, and they manage shared natural resources like water, grazing lands, and forest produce. For example, the Bhil community in Madhya Pradesh followed the halma tradition, planting thousands of trees, digging trenches, and creating water harvesting structures to help each other during water crises, without expecting any payment. In urban areas, communities also depend on one another. During the Chennai floods of 2015, various private and religious groups cooked and distributed food to people affected by the disaster. Residents’ Welfare Associations in cities make rules about cleanliness, waste management, and care of shared spaces, and they depend on traders for supplies and municipal workers for waste disposal. These examples show that communities, whether rural or urban, function smoothly only when individuals, families, and groups collaborate, share responsibilities, and support each other, highlighting their interdependent nature.
Q13: Explain how new types of communities have emerged in urban areas and how they function. (5 Marks)
Ans: In urban areas, new types of communities, such as Residents’ Welfare Associations (RWAs), have developed to manage common needs and maintain order within their neighborhoods. These communities create their own rules and regulations related to waste management, cleanliness of shared spaces, maintenance of parks, taking care of pets, and organizing community events. All residents participate in decision-making and follow these rules to ensure the smooth functioning of the community. Urban communities are also interdependent; for example, RWAs rely on local traders for daily supplies and municipal workers to manage garbage and public services. Such collaboration and mutual support help urban communities solve problems together and maintain a safe, organized, and supportive environment for everyone.
|
46 videos|317 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test(Solutions): Family and Community - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What is the significance of family in the community? |  |
| 2. How do communities support families? |  |
| 3. What roles do children play in their families and communities? |  |
| 4. How can families contribute to community development? |  |
| 5. What are some common challenges families face in a community setting? |  |
















