Unit Test (Solutions): Grassroots Democracy - Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M: 30
Instructions: Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: What is the oldest municipal institution in India? (1 Mark)
Ans: The Madras Corporation (now Greater Chennai Corporation).
Q2: Which urban local body governs cities with a population above 10 lakhs? (1 Mark)
Ans: Municipal Corporation.
Q3: What is the smallest unit of urban local governance? (1 Mark)
Ans: Ward.
Q4: Which city in India has been awarded the cleanest city title for seven years in a row? (1 Mark)
Ans: Indore.
Q5: What does the term 'decentralised' mean in the context of urban local bodies? (1 Mark)
Ans: It means local communities have a direct say in managing their areas instead of operating under a central authority.
Q6: Name two functions of ward committees in urban areas. (2 Marks)
Ans: Ward committees facilitate activities like conducting health camps and organising campaigns against single-use plastics.
Q7: How does the participation of citizens help urban local bodies perform efficiently? (2 Marks)
Ans: Citizens help by following waste segregation instructions and reporting issues like water leaks promptly, which makes garbage collection easier and prevents water wastage.
Q8: What are the three types of urban local bodies? (2 Marks)
Ans: Municipal Corporation, Municipal Council, and Nagar Panchayat. These bodies are formed based on the population size of the city or town and manage local governance.
Q9: Explain the role of urban local bodies in managing city infrastructure. (3 Marks)
Ans: Urban local bodies are responsible for maintaining infrastructure like roads, managing burial grounds, collecting and disposing of garbage, and ensuring the implementation of government schemes. They also play a role in planning the area's economic and social development, and they respond quickly to local problems like water leaks, blocked drains, or damaged roads to keep the city functioning smoothly.
Q10: Describe the significance of the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai in the history of urban governance. (3 Marks)
Ans: The Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai, originally Bombay Municipal Corporation, was created in 1865 and is one of the oldest municipal bodies in India. It represents an early example of local governance, allowing citizens to participate in managing their city, setting a precedent for urban administration, similar to how the Madras Corporation pioneered municipal taxation and city management in the 18th century.
Q11: How do urban local bodies fund their activities? (3 Marks)
Ans: Urban local bodies fund their activities through collecting local taxes and fines, such as property tax, and by offering paid services like water tanker supply, debris clearance, and auditorium rentals, as seen in the services of the Indore Municipal Corporation. These funds are used to maintain city infrastructure, support welfare schemes, and plan for future development projects.
Q12: Discuss the similarities and differences between the Panchayati Raj system and urban local bodies. (5 Marks)
Ans: Similarities:
 Differences:
Differences: 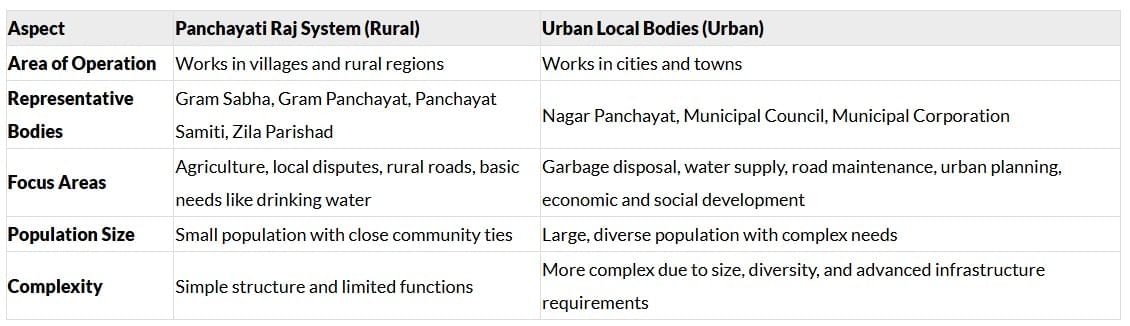
Q13: What actions can responsible citizens take to support their urban local bodies? Provide at least five examples. (5 Marks)
Ans: Responsible citizens can:
- Follow waste segregation instructions to ease garbage collection.
- Report water leaks promptly to prevent wastage.
- Participate in community activities like health camps and awareness campaigns.
- Pay local taxes and fees on time to support funding for development.
- Raise awareness about government schemes to ensure their implementation.
- Promptly report issues like damaged roads, blocked drains, or unsafe electric wires to authorities so they can be fixed quickly.
|
46 videos|241 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Grassroots Democracy - Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What is the role of local government in urban areas? |  |
| 2. How does grassroots democracy function in urban local governments? |  |
| 3. What are the benefits of having a local government in urban areas? |  |
| 4. What challenges do local governments face in urban areas? |  |
| 5. How can citizens participate in their local government? |  |















