Coconut Farm NCERT Solutions | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 119 |

|
| Page No. 120-121 |

|
| Page No. 122 |

|
| Page No. 123 |

|
| Page No. 124 |

|
| Page No. 125 |

|
| Page No. 126-128 |

|
| Page No. 130-131 |

|
| Page No. 132-133 |

|
| Page No. 134 |

|
| Page No. 135 |

|
Page No. 119
Q: Observe the following array of coconuts. Write two division facts using the given multiplication fact.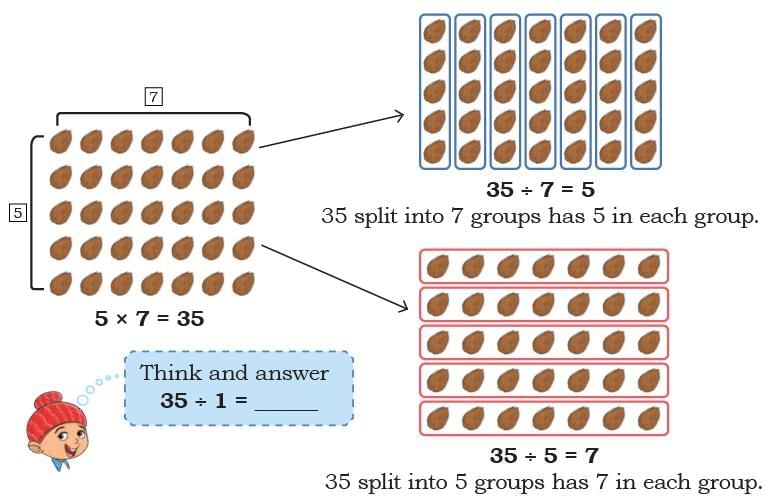 Ans: 35 ÷ 1 = 35
Ans: 35 ÷ 1 = 35
Q: Write the appropriate multiplication fact for the array shown below. Write two division facts that follow from the multiplication fact.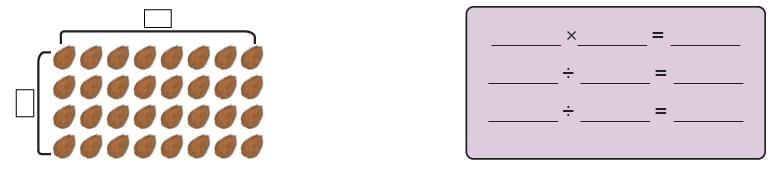 Ans:
Ans: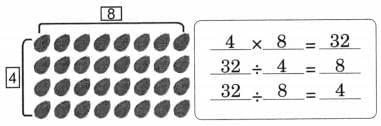
Page No. 120-121
Let us Play
Identify the numbers that can fill the circles such that the numbers in the squares are the products or the quotients of the numbers in the circles.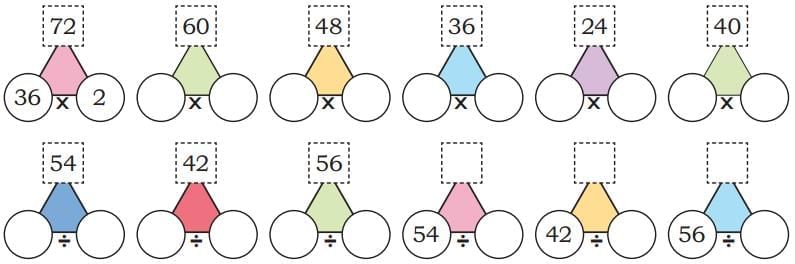 Ans:
Ans: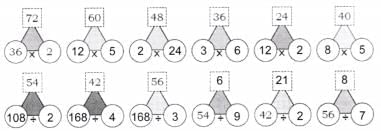 (Answer may vary)
(Answer may vary)
Let Us Do
Q1: Solve the following multiplication problems. Write two division statements in each case. Ans:
Ans: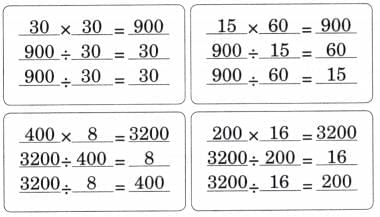
 Ans:
Ans: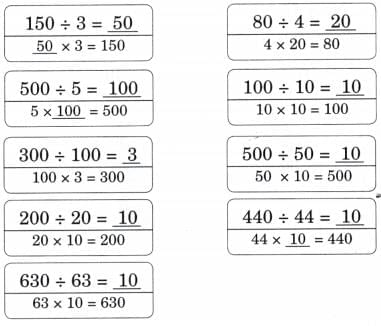
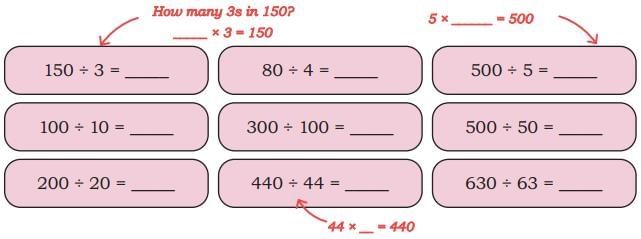
Patterns in Division and Place Value
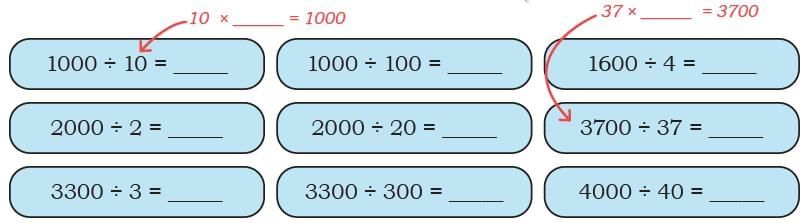
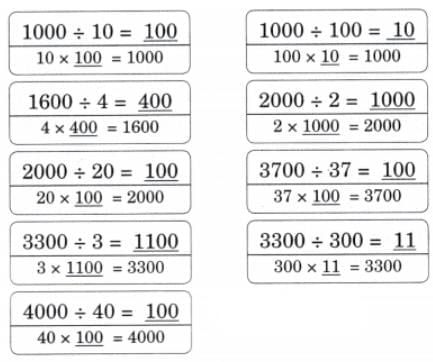
Q: Now fill the place value chart.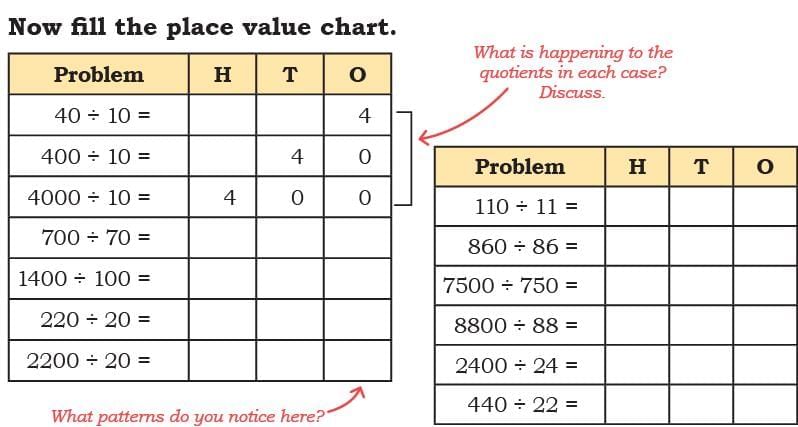 Ans:
Ans: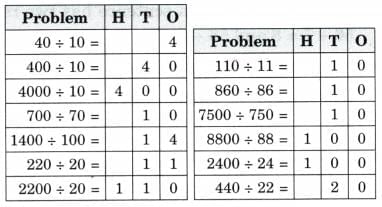 We observed that when dividend is increasing 10 times, the quotient is also increasing 10 times.
We observed that when dividend is increasing 10 times, the quotient is also increasing 10 times.
Page No. 122
Let Us Do
Ans:
Sabina cycles 160 km in 20 days.
To find the number of kilometres she cycles each day, we need to divide 160 by 20
160 ÷ 20 = 8
Therefore, she cycles 8 km each day.
Q2: How many notes of ₹ 100 does Seema need to carry if she wants to buy coconuts worth ₹ 4200?
Ans:
4200 ÷ 100 = 42
Therefore, Seema needs to carry 42 notes of ₹ 100.
Q3: The owner of an electric store has decided to distribute ?5500 equally amongst 5 of his employees as a Diwali gift. What amount will each employee get?
What will happen if he distributes the same amount of money among 10 employees? Will each employee get more or less? How much money would he have to distribute if everyone must get the same amount as earlier?
Ans:
If ₹ 5500 will be divided equally among 5 employees, then each employee will get:
5500 ÷ 5 = moo
If ₹ 5500 will be divided equally among 10 employees, then each employee will get:
5500 ÷ 10 = ₹ 550
Since, ₹ 550 < ₹ 1100, in this case each employee will get less.
To find the required amount to be distributed equally among 10 employees so that each employee can get ₹ 1100, we need to multiply 1100 by 10.
1100 × 10 =11000
Therefore, the required amount is ₹ 11000.
Q4: Place the numbers 1 to 8 in the following boxes so that all the four operations, division, multiplication, addition and subtraction are correct. No number must be repeated.
Is there more than one answer.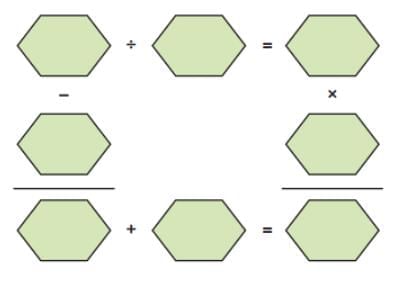 Ans:
Ans:
There are two possible solutions.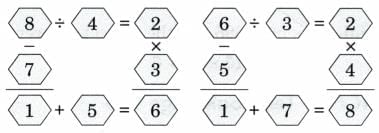
Q5: Fill in the blanks
(a) _____ ÷ 18 = 100.
(b) _____ ÷ 10 = 610.
(c) _____ ÷ 100 = 72.
(d) _____ ÷ 100 = 10.
(e) 870 ÷ _____ = 87.
(f) _____ ÷ 100 = 70.
(g) 200 ÷ _____ = 2.
(h) 130 ÷ _____ = 13.
Ans:
(a) 1800 ÷ 18 = 100.
(b) 6100 ÷ 10 = 610.
(c) 7200 ÷ 100 = 72.
(d) 1000 ÷ 100 = 10.
(e) 870 ÷ 10 = 87.
(f) 7000 ÷ 100 = 70.
(g) 200 ÷ 100 = 2.
(h) 130 ÷ 10 = 13.
Page No. 123
Try It!
Q1: Ans:
Ans: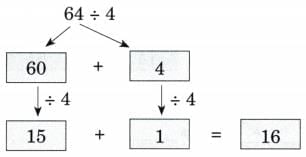
Q2: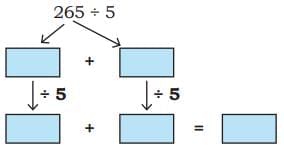 Ans:
Ans: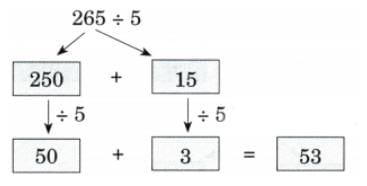
Q3: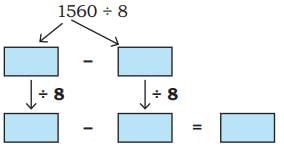 Ans:
Ans: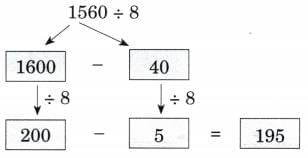
Q4: Ans:
Ans: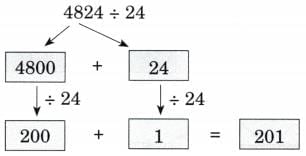
Q5: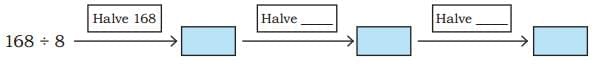 Ans:
Ans:
Q6: Ans:
Ans: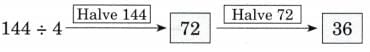
Page No. 124
Let Us Solve
Solve the following problems using strategies used in the previous question.
(a) 256 ÷ 4
Ans: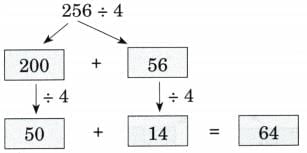
(b) 545 ÷ 5
Ans: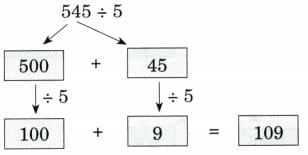
(c) 147 ÷ 7
Ans: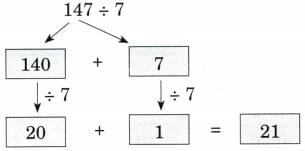
(d) 1212 ÷ 6
Ans: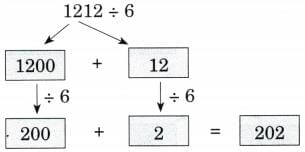
(e) 648 ÷ 12
Ans: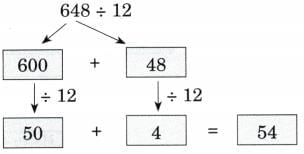
(f) 9648 ÷ 48
Ans: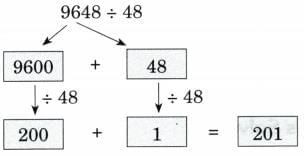
(g) 775 ÷ 25
Ans: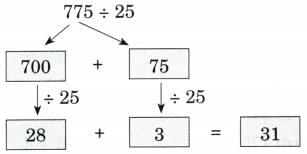
(h) 796 ÷ 4
Ans: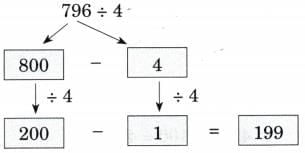
Page No. 125
Let Us Learn to Divide
Q: 726 ÷ 4
Ans:
No, we cannot write 200 instead of 100 as 200 × 4 = 800 > 726
Q: 902 ÷ 16
Ans: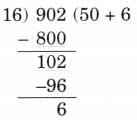
No, we cannot multiply 16 with a larger tens than 50 because
60 × 16 = 960 > 902
Q: Is 726 = 4 × 181? Yes/No.
So, 726 = 4 × 181 + _______.
Ans:
4 × 181 = 724.
So, the correct answer is No.
726 = 4 × 181 + 2
Q: Is 902 = 16 × 56? Yes/No.
So, 902 = 16 × 56 + _____.
Ans:
16 × 56 = 896.
So, the correct answer is No.
902 = 16 × 56 + 6
Page No. 126-128
Let Us Solve
Solve the following word problems
Q1: Rani is planning to host a party. She estimates that 250 guests will attend. She plans to serve one samosa to each guest. Samosas are available in packs of 6 or 8. Which pack should Rani buy? Explain your answer.
Ans:
Rani should choose the packs in such a way that the total number of samosas is not less than 250 but as close as possible to 250.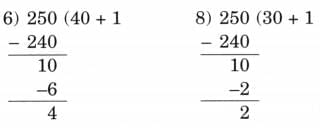
So, 42 packs of samosas will have 252 samosas, and 32 packs of 8 samosas will have 256 samosas.
Here, 252 is closer to 250.
Therefore, Rani should buy samosas in pack of 6.
Q2: 342 students from a school are going on a trip to the Science Park. Each bus can carry a maximum of 41 students. How many buses does the school need to arrange?
Ans:
The number of buses need to be arranged is 342 ÷ 41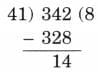
They need 8 buses and 1 more than to accommodate 14 remaining students. Therefore, 9 buses needs to be arranged.
Q3: Sofia has only ₹ 50 and ₹ 20 notes. She needs to pay ₹ 520 using these notes. How many ₹ 50 and ₹ 20 notes does she need to make ₹ 520? Find out the different possible combinations.
Ans:
Let us check some possibilities by using division.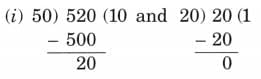
So, 10 × ₹ 50 + 1 × ₹ 20 = ₹ 520
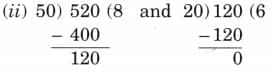
So, 8 × ₹ 50 + 6 × ₹ 20 = ₹ 520

So, 6 × ₹ 50 + 11 × ₹ 20 = ₹ 520
So, Sofia can pay using ten ₹ 50 notes and one ₹ 20 note, eight ₹ 50 notes and six ₹ 20 notes, or six ₹ 50 notes and eleven ₹ 20 notes.
There can be other possible combinations also.
Q4: Three friends decide to split the money spent on their picnic equally. They buy snacks and sweets for ₹ 157, juice and fruits for ₹ 124 and pulav and paratha for ₹ 136. How much should each person pay to share the cost equally?
Ans:
Total money spent = ₹ 157 + ₹ 124 + ₹ 136 = ₹ 417
So, each person needs to pay ₹ 417 ÷ 3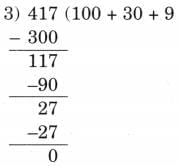
Therefore, each person needs to pay ₹ 139.
Q5: Identify the remainder, if any. Check if N = D × Q + R.
(a) 887 ÷ 3
Ans:
Here, N = 887, D = 3, Q = 295, R = 2
Since, 3 × 295 + 2 = 885 + 2 = 887
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(b) 283 ÷ 8
Ans: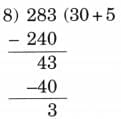
Here, N = 283, D = 8, Q = 35, R = 3
Since, 8 × 35 + 3 = 280 + 3 = 283
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(c) 745 ÷ 5
Ans:
Here, N = 745, D = 5, Q = 149, R = 0
Since, 5 × 149 + 0 = 745 + 0 = 745
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(d) 767 ÷ 26
Ans:
Here, N = 767, D = 26, Q = 29, R = 13
Since, 26 × 29 + 13 = 754 + 13 = 767
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(e) 530 ÷ 41
Ans: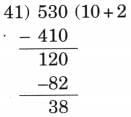
Here, N = 530, D = 41, Q = 12, R = 38
Since, 41 × 12 + 38 = 492 + 38 = 530
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(f) 888 ÷ 67
Ans: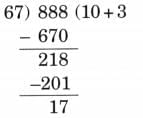
Here, N = 888, D = 67, Q = 13, R = 17
Since, 67 × 13 + 17 = 871 + 17 = 888
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
Kalpavruksha Coconut Oil
Q1: In a particular year, Susie an Sunitha used 4376 coconuts for extracting coconut oil. They can extract 1 l of oil from 8 coconuts. What quantity of oil were they able to extract? They would get 4376 + 8 litres of coconut oil.
How much will they earn if they sell the oil at ₹ 175 for 11?
They will earn ₹ 547 × 175. Find out.
Ans: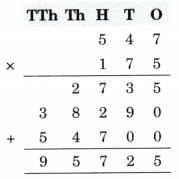
Therefore, they will earn ₹ 95725.
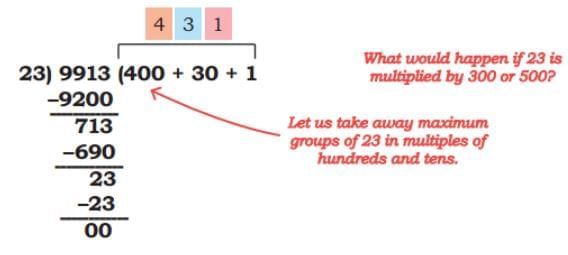
Q2: Coconut husk is used for making coir. Coir is a natural fibre used in gardening, farming, boat making, and making decorative items. Susie and Sunitha’s farm sells coconut husk at ₹23 per kilogram. They earned ₹ 9913 from the sale of husk in May. What quantity of husk did they sell in May?
Ans:
The quantity of husk sold in May is 9913 ÷ 23 kg
Q3: In the hot summer months, tender coconuts are sold for ₹ 35. Ibrahim earns ₹ 8890 in a week. How many tender coconuts did he sell? The number of tender coconuts sold by Ibrahim is 8890 ÷ 35.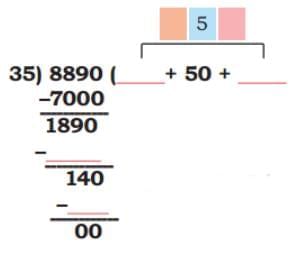 Q: Ibrahim sold ______ tender coconuts.
Q: Ibrahim sold ______ tender coconuts.
Ans: Ibrahim sold 254 tender coconuts.
Ibrahim sold 254 tender coconuts.
Q: Ibrahim had bought the tender coconuts for ₹ 20 each. How much extra money did he earn by selling the coconuts at ₹ 35?
Ans:
The cost of 254 coconuts at ₹ 20 each = 254 × ₹ 20 = ₹ 5080.
He earned ₹ 8890 from the sale.
The extra amount he earned is ₹ 8890 – ₹ 5080 = ₹ 3810.
Page No. 130-131
Let Us Divide
(a) 7,032 ÷ 6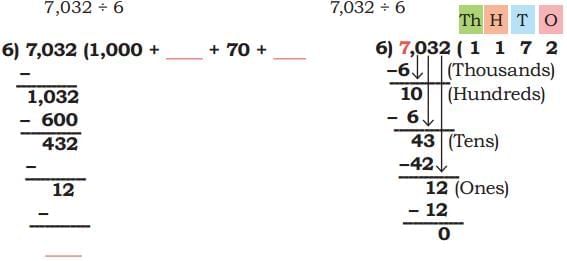 Ans:
Ans:

(b) 3,005 ÷ 5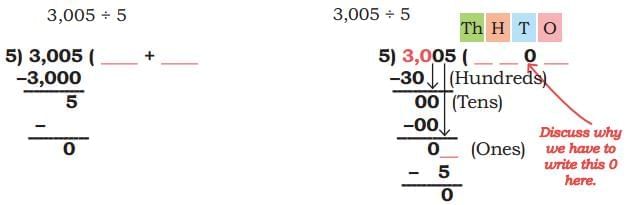 Ans:
Ans: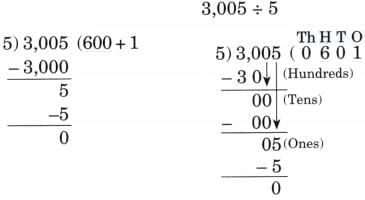 3005 = 3 Thousands + 0 hundreds + 0 tens + 5 ones.
3005 = 3 Thousands + 0 hundreds + 0 tens + 5 ones.
3 Thousands ÷ 5 → not possible without regrouping
Regroup 3 thousands into hundreds.
30 hundreds
30 hundreds ÷ 5 = 6 hundreds
0 tens ÷ 5 = 0 tens
5 ones ÷ 5 = 1 ones
(c) 2,874 ÷ 14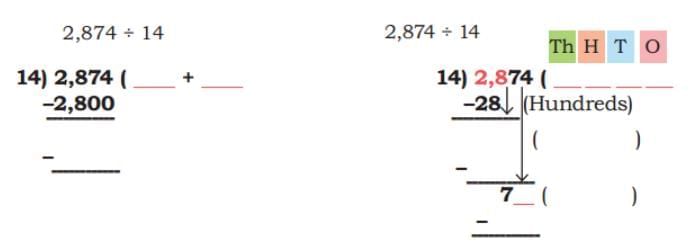 Ans:
Ans:
(d) 9,805 ÷ 32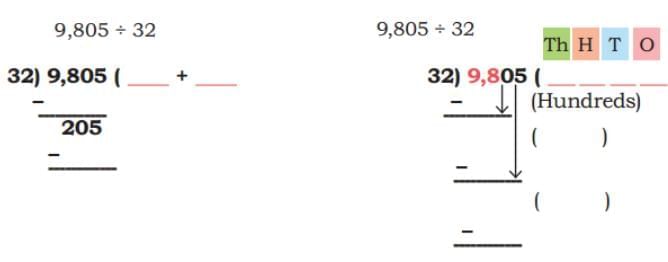 Ans:
Ans:
Let Us Do
Q1: Find the missing numbers such that there is no remainder. Remember, there could be more than one solution.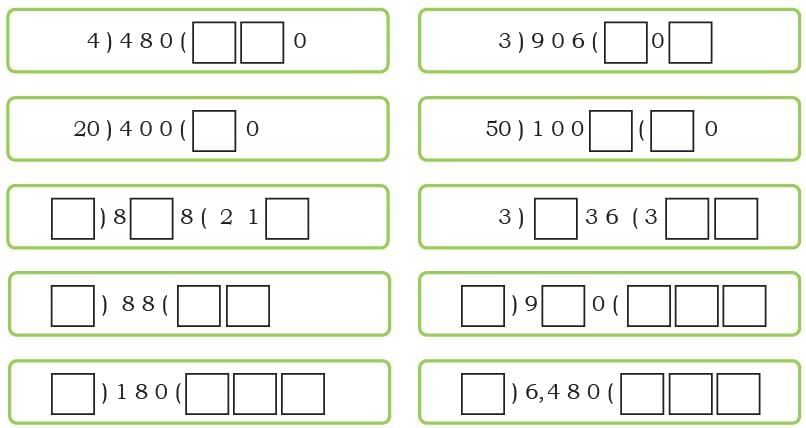
I am a 3-digit number.
- If you divide me by 5, you get 42.
- If you multiply me by 2, you get 420.
What number am I?
Ans:
210.
As, 210 + 5 = 42
210 × 2 = 420
Page No. 132-133
Let Us Solve
Q1: A theatre company can accommodate 45 people during one show.
(a) A total of 475 people bought tickets for a puppet show. How many shows are needed to seat all the people who bought tickets?
(b) There are 2 shows in a day. How many days will be needed to accommodate all the people?
Ans:
(a) The number of shows required for 475 people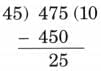
= 475 ÷ 45
Ten shows will accommodate 450 people and one more show will accommodate for the remaining 25 people.
Therefore, 11 shows are needed to seat all the people who bought tickets.
(b) From part (a) number of shows required is 11.
If there are 2 shows in a day, then in 5 days there will be 10 shows, and on 6th day the 11th show will be held.
Thus, 6 days are needed to accommodate all the people.
Q2: Naina bought 5 kg of ice cream as a birthday treat for her 23 friends. 400 g ice cream was left after everyone had an equal share. How much ice cream did each of her friends eat?
Ans:
Total ice cream shared = 500 kg – 400 g
= 5000 g – 400 g = 4600 g
Share of each of her friend = 4600 ÷ 23 = 200
Therefore, each of her friend ate 200 g of ice cream.
Q3: Megha packs 15 packets of ragi-oats biscuits for a 4-day group trip. Each packet contains 8 biscuits. There are 6 people in the group. If distributed evenly, how many biscuits can one person have each day.
Ans:
Total number of biscuits in 15 packets = 15 × 8 = 120
Total number of biscuits distributed per day = 120 + 4 = 30
Number of biscuits one person can have per day = 30 4- 6 = 5
Therefore, each person can have 5 biscuits each day.
Q4: Solve the following and identify the remainder, if any. Check whether N = D × Q + R in each case.
(a) 9,045 ÷ 5
Ans:
Here, N = 9045, D = 5, Q = 1809, R = 0
Since, 9045 = 5 × 1809 + 0
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(b) 1,034 ÷ 4
Ans:
Here, N = 1034, D = 4, Q = 258, R = 2
Since, 1034 = 4 × 258 + 2
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(c) 2,504 ÷ 7
Ans:
Here, N = 2504, D = 7, Q = 357, R = 5
Since, 2504 = 7 × 357 + 5
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(d) 8,900 ÷ 15
Ans:
Here, N = 8900, D = 15, Q = 593, R = 5
Since, 8900 = 15 × 593 + 5
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(e) 9,876 ÷ 32
Ans: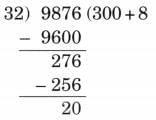
Here, N = 9876, D = 32, Q = 308, R = 20
Since, 9872 = 32 × 308 + 20
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
(f) 7,506 ÷ 24
Ans:
Here, N = 7506, D = 24, Q = 312, R = 18
Since, 7506 = 24 × 312 + 18
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
Q5: Find the solutions for part A. Observe the relations between the quotient, divisor and dividend and use it to answer parts B and C. Ans:
Ans:
From part A, we can observe that: When the divisor is doubled, the quotient becomes half and when divisor is halved, the quotient becomes double. On the other hand, when the dividend is doubled the quotient also becomes double, when the dividend is halved the quotient becomes half.
Q6: A company in Mumbai organises cycle rallies from Mumbai to Panjim, Goa every year. They aim to cover 576 km in 12 days.
(а) How much distance should they cycle every day, to cover the distance evenly?
(b) After reaching Ratnagiri, they rest for 1 day. How much distance should they cycle each day to reach Goa in 4 days? Assume that they cover the distance evenly.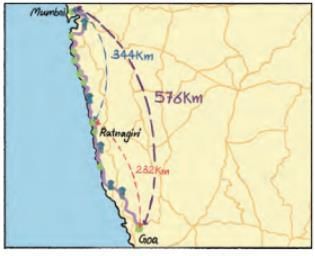 Ans:
Ans:
(a) The distance they should cycle every day = 576 ÷ 12 = 48 km
(b) Distance from Ratnagiri to Goa = 232 km
The distance they should cycle each day to reach Goa in 4 days = 232 ÷ 4 = 58 km.
Q7: Given below are a few problems. You may need some additional information to solve these. Identify the missing information. Write the missing information and find the answer.
(a) A fruit vendor sells 6 baskets of mangoes. Each basket contains 12 mangoes. How much did the vendor earn in total?
(b) A school has 8 classrooms, and each classroom has an equal number of desks. How many desks are there in each classroom?
(c) Rahul buys 5 cricket bats for his team. The total bill is ₹ 3500. How much does one bat cost?
(d) A restaurant serves 125 plates of idlis in a day. The total earnings from selling all the idli plates is ₹ 6250. How many idlis are there in each plate?
Ans:
(a) Missing information: The cost of each mango.
Let each mango costs ₹ 10
The cost of each basket = 12 × 10 = ₹ 120
Therefore, the cost of 6 baskets = 6 × 120
= ₹ 720
Thus, the vendor earn ₹ 720 in total.
(Answer may vary)
(b) Missing information: Total number of desks in the school.
Let the total number of desks in the school is 160.
Therefore, the total number of desks in each classroom = 160 ÷ 8 = 20
(Answer may vary)
(c) No information is missing.
The cost of one bat = 3500 ÷ 5 = ₹ 7„00
(d) Missing information: The cost of one idli. Let the cost of each idli is ₹25 The cost of one plate idli
= 6250 ÷ 125 = ₹ 50
Therefore, the number of idlis in one plate = 50 ÷ 25 = 2
(Answer may vary)
Q8: To make one bookshelf, a carpenter needs the following things 4 long wooden panels 8 short wooden panels 16 small clips 4 large clips 32 screws
The carpenter has a stock of 264 long wooden panels, 306 short wooden panels, 2400 small clips, 120 large clips, and 2800 screws. How many bookshelves can the carpenter make? Discuss your thoughts. Ans:
Ans:
Since 264 ÷ 4 = 66
Therefore, the long wooden panels are sufficient for 66 bookshelves.
306 ÷ 8 = 38 and remainder 2.
So, the short wooden panels are sufficient 38 bookshelves.
2400 ÷ 16 = 150 and remainder 2.
So, the small clips are sufficient for 150 bookshelves
120 ÷ 4 = 30
So, large clips are sufficient for 30 bookshelves 2800 ÷ 32 = 87 and remainder 16.
So, screws are sufficient for 87 bookshelves. Based on the above data the carpenter can make 30 bookshelves.
Page No. 134
Vegetable Market
Q: Munshi Lai has a big farm in Bihar. Every Saturday, he sells the vegetables from his farm at Sundar Sabzi Mandi. Munshi ji maintains a detailed record of the quantity of vegetables he sends to the Mandi and the cost of each vegetable. The following table shows his record book on one Saturday.
His naughty grandson has erased some numbers from his record book. Help Munshi Lai complete the table.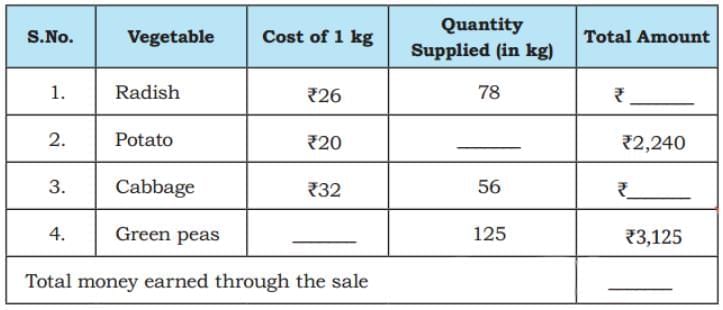 Ans:
Ans: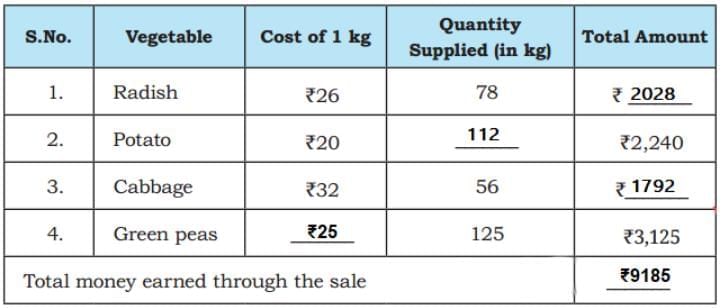
Let Us Solve
Q: Divide the following. Try dividing using place values, whenever you can. Identify the remainder, if any, and check whether N = D × Q + R.
1. 506 ÷ 5
Ans: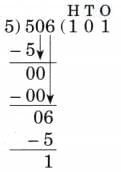
N = 506, D = 5, Q = 101, R = 1
5 × 101 + 1 = 505 + 1 = 506
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
2. 918 ÷ 8
Ans: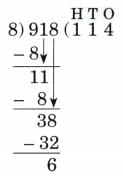
N = 918, D = 8, Q = 114, R = 6
8 × 114 + 6 = 912 + 6 = 918
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
3. 8,126 ÷ 7
Ans: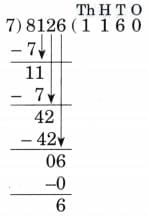
N = 8126, D = 7, Q = 1160, R = 6
7 × 1160 + 6 = 8120 + 6 = 8126
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
4. 9,324 ÷ 4
Ans: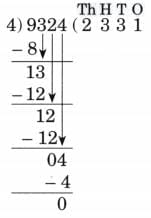
N = 9324, D = 4, Q = 233, R = 0
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
5. 876 ÷ 6
Ans: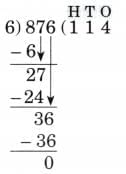
N = 876, D = 6, Q = 146, R = 0
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
6. 7,008 ÷ 3
Ans: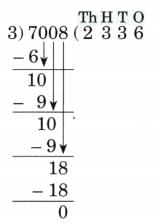
N = 9324, D = 4, Q = 233, R = 0
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
7. 934 ÷ 12
Ans: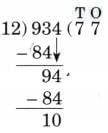
N = 934, D = 12, Q = 77, R = 10
12 × 77 + 10 = 924 + 10 = 934
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
8. 829 ÷ 23
Ans:
N = 829, D = 23, Q = 36, R = 1
23 × 36 + 1 = 828 + 1 = 829
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
9. 705 ÷ 18
Ans: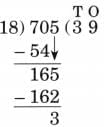
N = 705, D = 18, Q = 39, R = 3
18 × 39 + 3 = 702 + 3 = 705
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
10. 8,704 ÷ 32
Ans:
N = 705, D = 18, Q = 39, R = 3
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
11. 6,790 ÷ 45
Ans: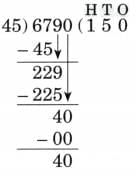
N = 6790, D = 45, Q = 150, R = 40
45 × 150 + 40 = 6750 + 40 = 6790
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
12. 5,074 ÷ 21
Ans: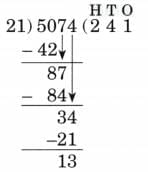
N = 5074, D = 21, Q = 241, R = 13
21 × 241 + 13 = 5074
Therefore, N = D × Q + R
Page No. 135
Mathematical Statements
Q1: Find out whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F). A true sentence is one where both sides of the ‘=’ sign have the same value.
(a) 8 × 9 = 70 + 2
(b) 20 – 6 = 7 × 3
(c) 48 – 3 = 4 × 4
(d) 89 – 9 = 90 + 0
(e) 25 + 10 = 45 – 10
Ans:
(a) 8 × 9 = 72 and 70 + 2 = 72
Therefore, 8 × 9 = 70 + 2 is True.
(b) 20 – 6 = 14 and 7 × 3 = 21
Since 14 and 21 are not equal.
Therefore, 20 – 6 = 7 × 3 is False.
(c) 48 – 3 = 16 and 4 × 4 = 16
Therefore, 48 + 3 = 4 × 4 is True.
(d) 89 – 9 = 80 and 90 + 0 = 90
Since, 80 and 90 are not equal.
Therefore, 89 – 9 = 90 + 0 is False.
(e) 25 + 10 = 35 and 45 – 10 = 35
Therefore, 25 + 10 = 45 – 10 is True.
Q2: Complete the following statements such that they are true.
(a) 7 × 6 = _____ + 17
(b) 87 + 6 = _____ × 31
(c) 63 + _____ = 74 – 4
(d) _____ – 9 = 16 – 2
Ans:
(a) 7 × 6 = 42 and 25 + 17 = 42
Therefore, 7 × 6 = 25 +17
(b) 87 + 6 = 93 and 3 × 31 = 93
Therefore, 87 + 6 = 3 × 31
(c) 74 – 4 = 70 and 63 + 7 = 70
Therefore, 63 + 7 = 74 – 4
(d) 16 – 2 = 8 and 72 – 9 = 8
Therefore, 72 – 9 = 16 – 2
Q3: Think about the following statements and find examples as suggested below.
(a) “When two odd numbers are added, the sum is even.”
Find 5 examples for the above statement. Can you find an example to show that the statement can be false? Always true
(b) “Multiplying a number by 2 can give an odd number.”
Give some example for this statement. Can you find any? -Never true
(c) “Halving a number always leads to an even number.”
Give 3 examples for the statement. Can you find 3 examples when this is not true? -Sometimes true.
Ans:
(a) Examples: 5 + 3 = 8, 9 + 5 = 14, 105 + 7 = 112, 11 + 13 = 24, 15 + 5 = 20, etc.
Since the statement is always true, we cannot find an example that the statement is false.
(b) Multiplying a number by 2 always gives an even number. So, the given statement is never true and hence we cannot find any such example to show that the given statement is true.
(c) Examples when statement is true:
8/2 = 4, 12/2 = 6, 16/2 = 8, 32/2 = 16
Examples when statement is false:
10/2 = 5, 30/2 = 15, 50/2 = 25, 70/2 = 35
Q4: Tick in the appropriate cell for the following statements.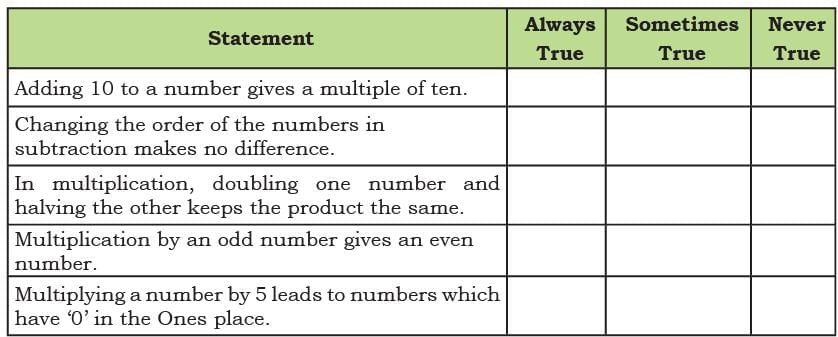 Ans:
Ans: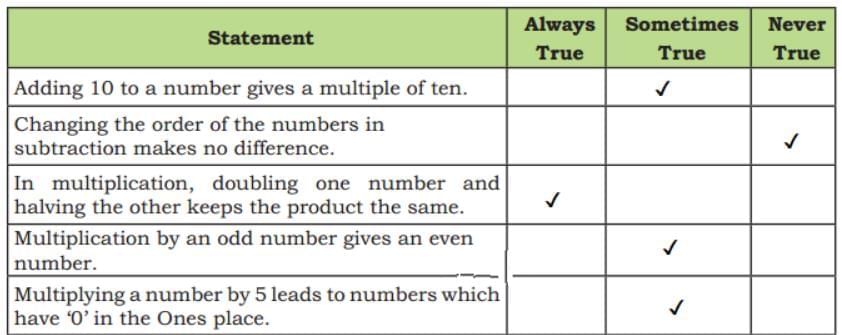
|
35 videos|322 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Coconut Farm NCERT Solutions - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main benefits of coconut farming? |  |
| 2. How does coconut farming contribute to the environment? |  |
| 3. What are the common pests and diseases that affect coconut crops? |  |
| 4. What are the steps involved in coconut harvesting? |  |
| 5. What are the economic prospects of coconut products in the market? |  |




















