Olympiad Notes: Numerals | Math Olympiad for Class 2 PDF Download
Introduction
Numerals are symbols or numbers used to show quantity. We use numerals for counting, comparing, and calculations.
Olympiad questions include:
- Writing numbers in figures and words
- Understanding place value and face value
- Writing expanded form
- Comparing numbers
- Ordering numbers (ascending/descending)
- Using ordinal numbers
- Reading and writing Roman numerals
Numeral and Number Name
- Numeral: A number written in digits.
Example: 45 - Number Name: A number written in words.
Example: Forty-five - Tip: Use a hyphen between tens and ones: Twenty-one, Thirty-two
Numbers and Number Names
Place Value and Face Value
Place Value: Place value is the value of a digit depending on its position in a number.
Face Value: Face value is the value of the digit itself, ignoring its position.
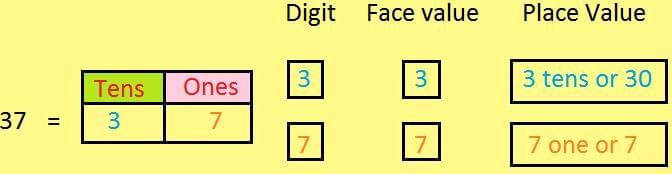
Example: 45
- 4 → Place value = 40, Face value = 4
- 5 → Place value = 5, Face value = 5
Expanded Form
Expanded form is writing a number to show the value of each digit.
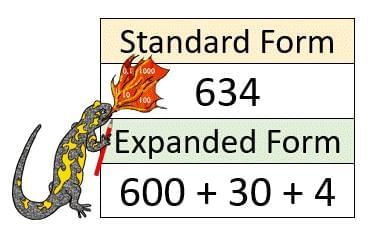
Examples:
- 450 = 400 + 50 + 0
- 36 = 30 + 6
- 50 = 50 + 0
Comparing Numbers
Comparing numbers is finding which number is greater, smaller, or equal.

Rules:
- The number with more digits is greater.
- If the number of digits is the same, compare digits from left to right.
Examples:
- 45 < 67
- 32 > 21
- 80 = 80
Symbols: > (greater), < (less), = (equal)
Ascending and Descending Order
Ascending Order: Arranging numbers from smallest to largest.
Descending Order: Arranging numbers from largest to smallest.
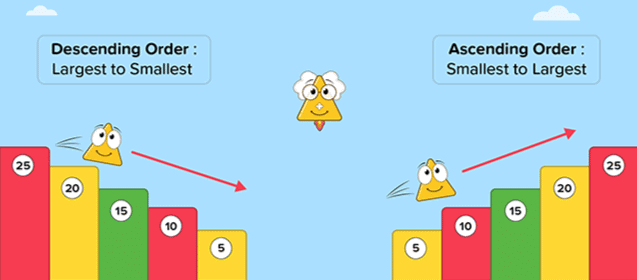
Example:
- Ascending: 12, 24, 36, 48
- Descending: 90, 70, 50, 30
Ordinal Numbers
Ordinal numbers show the position or rank of a person or thing.
Examples:
1st → First,
2nd → Second,
3rd → Third, 4th → Fourth
Sentence: Riya came 2nd in the race.
Roman Numerals
- Roman numerals are numbers written with letters.
- Used in clocks, books, events, and awards.
Roman Numerals 1–20
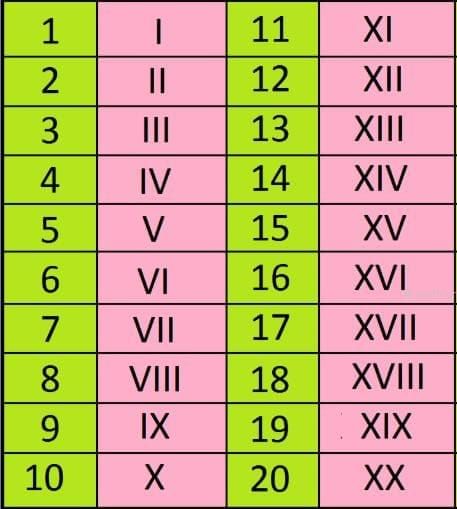
Rules:
Smaller numeral after bigger → add. Example: VI = 5 + 1 = 6
Smaller numeral before bigger → subtract. Example: IV = 5 – 1 = 4
Repeating the same numeral → addition. Example: III = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
Examples in Use:
- Clock: 12 → XII
- Book chapters: Chapter 5 → Chapter V
- Events: Olympics XX → 20th Olympic Games
|
32 videos|79 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Numerals - Math Olympiad for Class 2
| 1. What is the difference between numeral and number name? |  |
| 2. How do you determine the place value and face value of digits in a number? |  |
| 3. What is expanded form and how do you write a number in expanded form? |  |
| 4. How can we compare numbers to determine which is greater or lesser? |  |
| 5. What are ordinal numbers and how are they different from cardinal numbers? |  |















