Olympiad Notes: Water | Science Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Water |

|
| Sources of Water |

|
| Water Cycle |

|
| Importance of Water Cycle |

|
| Flood |

|
| Drought |

|
| Rainwater Harvesting |

|
Water
- Water is a vital element that is necessary for the survival of all living organisms on our planet. It plays a crucial role in sustaining life and supporting various biological processes.
- Freshwater, also known as potable water, is the type of water that is safe for consumption. It undergoes processes such as purification and treatment to remove impurities and make it suitable for drinking.
- When we consider Earth's surface, approximately 71% is covered by water. However, only a small portion of that water, about 3%, is fresh water. The remaining 97% consists of saltwater found in oceans and seas.

Sources of Water
There are different sources of water that contribute to the availability of this vital resource.
- Rainwater is one such source, which is formed when water vapour in the atmosphere condenses and falls back to the ground as precipitation.
- Groundwater refers to the water present beneath the Earth's surface, stored in spaces within rocks and soil.
- Surface water includes bodies of water like rivers, streams, and creeks. Lakes and ponds are stationary bodies of freshwater, while seawater refers to the saltwater found in oceans and seas.
These various sources of water collectively contribute to the water cycle, which is the continuous movement and circulation of water on Earth.
Water Cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, describes the continuous movement of water between different water bodies such as oceans, rivers, ponds, lakes, and the atmosphere.
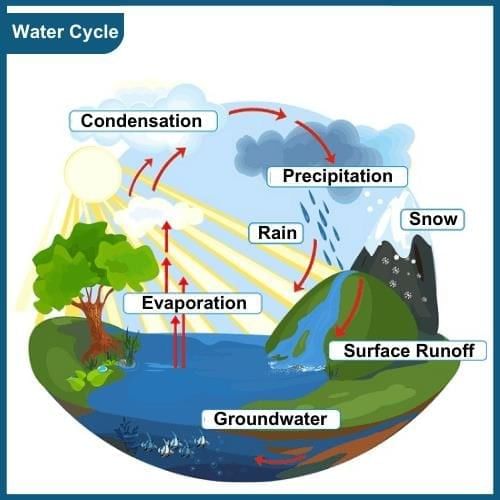
It is a vital natural process that sustains the availability of water on Earth. The water cycle can be summarized as follows:
- Evaporation: This is the process by which water is converted into water vapour. The heat from the sun causes water on the Earth's surface, such as in rivers, lakes, and oceans, to change from a liquid state to a gaseous state, forming water vapour.
- Condensation: As water vapour rises into the atmosphere, it cools down and undergoes condensation. This process involves the conversion of water vapour back into its liquid form. Condensation occurs when the air temperature decreases, causing the water vapour to transform into tiny water droplets or ice crystals. These droplets then gather to form clouds.
- Precipitation: When the condensation process continues and the water droplets or ice crystals in the clouds become too heavy to remain suspended, they fall back to the Earth's surface in the form of precipitation. Precipitation can take various forms, including rain, snow, sleet, or hail, depending on the atmospheric conditions.
- Collection: After precipitation, water can follow different paths. It can be absorbed into the ground, becoming groundwater, which replenishes underground aquifers and feeds wells and springs. Water can also flow over the land surface as surface runoff, finding its way into rivers, streams, and eventually into larger bodies of water like lakes and oceans.
- Transpiration: In addition to the processes mentioned above, plants also play a role in the water cycle through transpiration. Transpiration is the process by which water is released from plants' leaves and stems as water vapour. This water vapour then enters the atmosphere and becomes part of the water cycle.
Importance of Water Cycle
- The water cycle is a continuous process that ensures the distribution, purification, and recycling of Earth's water resources.
- It is essential for maintaining the balance of ecosystems, providing water for human consumption, supporting agriculture, and driving weather patterns.
- Understanding the water cycle helps us appreciate the interconnectedness of water and its significance for life on Earth.
Flood
- A flood occurs when there is an overflow of water in rivers, lakes, and ponds due to excessive rainfall.
- This excess water surpasses the capacity of these water bodies, leading to the flooding of surrounding areas.
 Flood
Flood
Effects of Floods
Floods can have various effects, including:
- Crop Loss: Floodwaters can destroy or wash away crops, leading to significant financial losses for farmers. This can result in food shortages and impact the availability and affordability of essential food items.
- Shortage of Food and Drinking Water: Floods can disrupt transportation routes, making it difficult to distribute food supplies to affected areas. Additionally, contaminated water sources due to flood waters can lead to a shortage of safe drinking water, posing health risks to the affected population.
- Waterlogging and Disease Outbreaks: Floods can cause waterlogging, where the excess water accumulates in low-lying areas and remains stagnant. This stagnant water becomes a breeding ground for mosquitoes and other disease-carrying insects, increasing the risk of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever.
- Soil Erosion: The force of flowing floodwaters can erode the topsoil, carrying away valuable nutrients and affecting the fertility of the land. Soil erosion can have long-term consequences on agricultural productivity and the overall health of the ecosystem.
- Damage to Infrastructure and Property: Floodwaters can damage buildings, roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. This leads to financial losses and can disrupt transportation and communication networks, hindering relief and rescue efforts.
Floods are natural disasters that can have devastating impacts on communities and ecosystems. Effective flood management, including early warning systems, proper land-use planning, and infrastructure development, can help minimise the adverse effects of floods and protect vulnerable areas.
Drought
Drought is a prolonged period of time in which a region experiences significantly low rainfall, resulting in a scarcity of water resources.
Droughts can have severe consequences for both the environment and human populations. Drought
Drought
Effects of Drought
Here are some key points about drought and its effects:
- Lack of Rainfall: Droughts occur when there is a prolonged absence of rainfall in a region. The absence of rain leads to reduced soil moisture and a decline in the water levels of rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
- Evaporation and Transpiration: Without sufficient rainfall, the soil loses water through evaporation, which occurs when water on the soil surface transforms into vapour due to heat. Plants also lose water through transpiration, where water evaporates from their leaves. These processes further deplete water resources.
- Impact on Agriculture: Insufficient water availability hampers crop growth and reduces agricultural productivity. Crop failures can lead to food shortages, rising food prices, and an increased risk of famine.
- Water Scarcity: Droughts create a scarcity of water for domestic, industrial, and commercial purposes. Limited water supplies can result in water rationing, affecting daily activities, hygiene, and sanitation.
- Environmental Impact: The lack of water affects the survival of plants, animals, and aquatic life. Increased stress on ecosystems can disrupt biodiversity and ecological balance.
Efforts to reduce the effects of drought include water conservation measures, such as efficient irrigation techniques, water recycling, and implementing drought-resistant agricultural practices.
Rainwater Harvesting
- Rainwater harvesting is the practice of collecting and storing rainwater for future use.
- It involves capturing rainwater from rooftops, land surfaces, or other catchment areas and directing it into storage tanks, cisterns, or underground reservoirs.
- This collected rainwater can then be used for various purposes.
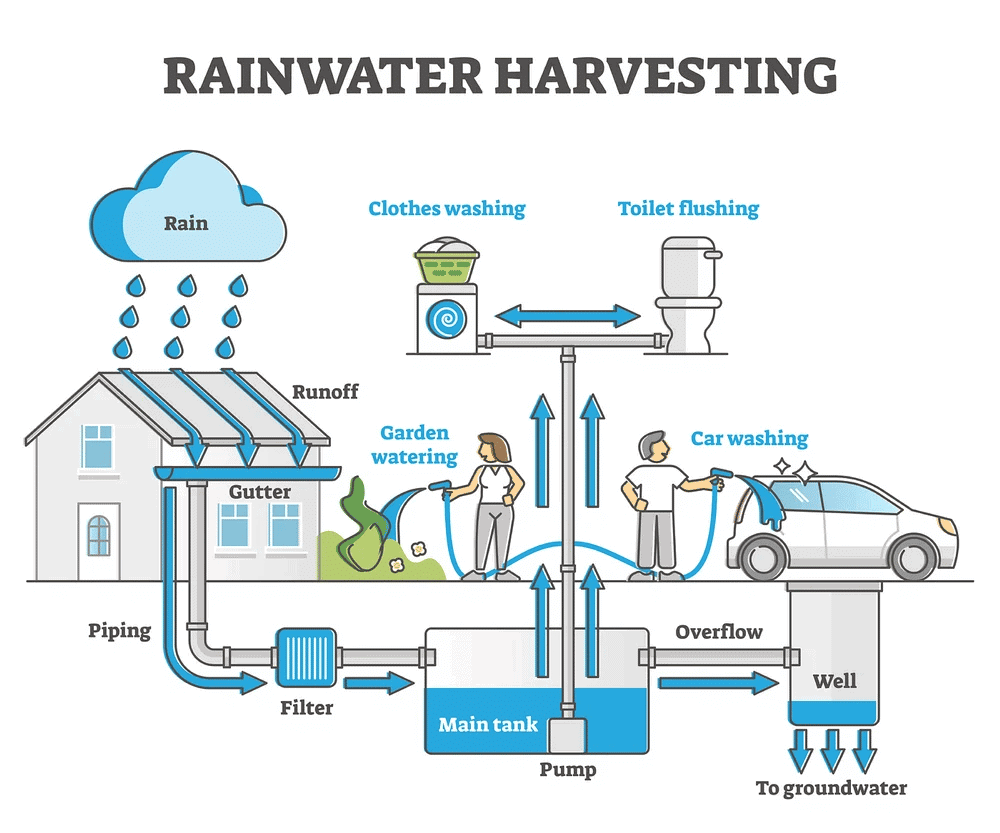
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Here are some key points about rainwater harvesting and its benefits:
- Water Conservation: Rainwater harvesting is an effective way to conserve water. By capturing rainwater, it reduces the reliance on freshwater sources, such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater, for non-potable uses like irrigation, washing vehicles, and flushing toilets. This helps to preserve precious freshwater resources for essential purposes like drinking and cooking.
- Increased Water Availability: Rainwater harvesting increases the availability of water, especially in regions facing water scarcity. It provides an additional water source during dry periods or in areas where access to freshwater is limited.
- Educational and Community Benefits: Rainwater harvesting can promote awareness and education about water conservation and sustainable practices.
|
70 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Water - Science Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What are the main sources of water available on Earth? |  |
| 2. How does the water cycle work and what are its stages? |  |
| 3. Why is the water cycle important for the environment and life on Earth? |  |
| 4. What are the main causes and effects of floods and droughts? |  |
| 5. What is rainwater harvesting and why is it important? |  |



















