Basic Mountain-Building (Fold, Block, Volcanic Mountains) | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
Introduction to Mountain-Building (Orogeny)
Mountain-building, or orogeny, is the geological process that forms mountains through tectonic forces, volcanic activity, or faulting. It is a key topic in Physical Geography under the SSC CGL syllabus, specifically within Geomorphology. Understanding the mechanisms, classifications, examples, and geographical significance is crucial, as questions often test factual knowledge, processes, and examples, especially in the Indian context. The primary driver of mountain-building is plate tectonics, involving the movement and interaction of lithospheric plates leading to compression, tension, or volcanic eruptions.
Types of Mountains
Mountains are classified based on their formation processes into three main types: Fold Mountains, Block (Fault-Block) Mountains, and Volcanic Mountains. Below is a detailed breakdown of each type, including formation, characteristics, examples, and key points for SSC CGL preparation.
1. Fold Mountains
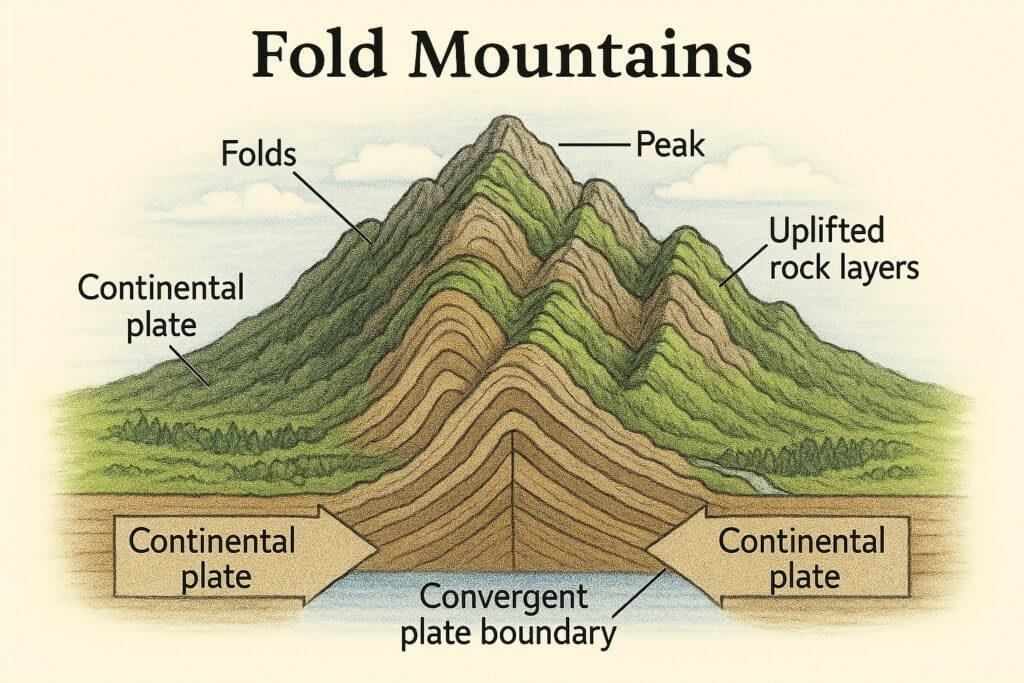 Formation Process:
Formation Process:
- Formed due to compressional forces from the collision of tectonic plates (convergent boundaries).
- Sedimentary rocks in the Earth's crust buckle and fold, creating anticlines (upfolds) and synclines (downfolds).
- Typically results from continental-continental (e.g., Indian and Eurasian plates forming the Himalayas) or oceanic-continental plate collisions.
- The process is slow, taking millions of years, and is associated with orogenic belts and seismic activity.
Characteristics:
- Young Fold Mountains: High, rugged, with sharp peaks (e.g., Himalayas, Alps).
- Old Fold Mountains: Eroded, rounded hills (e.g., Aravalli, Appalachians).
- Found in long, linear ranges with complex geological structures.
- Associated with earthquakes and fold-thrust belts.
Examples:
- World: Himalayas (Asia), Alps (Europe), Andes (South America), Rockies (North America).
- India: Himalayas (young, formed 25–70 million years ago), Aravalli (old, Precambrian).
2. Block (Fault-Block) Mountains
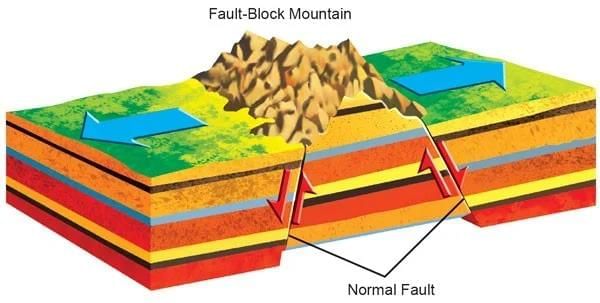 Formation Process:
Formation Process:
- Result from tensional forces causing faulting and fracturing of the Earth's crust, often at divergent boundaries or regions of crustal stretching.
- Uplifted blocks are called horsts (forming mountains), while down-dropped blocks are grabens (forming valleys or rift valleys).
- Faulting occurs along normal faults (due to tension) or occasionally reverse faults (compression).
Characteristics:
- Steep escarpments on one side, gentler slopes on the other.
- Often rectangular in shape, less extensive than fold mountains.
- Associated with rift systems and seismic activity.
Examples:
- World: Vosges (France), Black Forest (Germany), Sierra Nevada (USA).
- India: Vindhya Range (debated as block or eroded fold), Satpura Range (partly block).
- Related Landforms: Great Rift Valley (Africa, a graben).
3. Volcanic Mountains
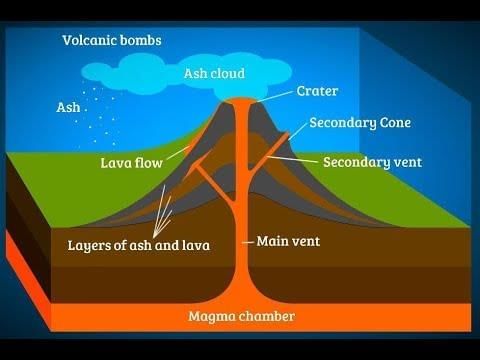 Formation Process:
Formation Process:
- Formed by the accumulation of lava, ash, and pyroclastic materials from volcanic eruptions.
- Occur at hotspots, subduction zones (convergent boundaries), or mid-ocean ridges (divergent boundaries) where magma rises through vents.
- Types of volcanoes:
- Stratovolcanoes: Steep, explosive (e.g., Mount Fuji).
- Shield Volcanoes: Gentle slopes, fluid lava (e.g., Mauna Loa).
- Cinder Cones: Small, steep, single-eruption (e.g., Paricutin, Mexico).
Characteristics:
- Conical shape with craters or calderas at the summit.
- Can be active (e.g., Barren Island), dormant (e.g., Vesuvius), or extinct.
- Often isolated or in volcanic arcs (e.g., Ring of Fire).
Examples:
- World: Mount Fuji (Japan), Mount Kilimanjaro (Africa), Mauna Loa (Hawaii).
- India: Barren Island (Andaman and Nicobar, India’s only active volcano).
Comparison Table for Quick Revision
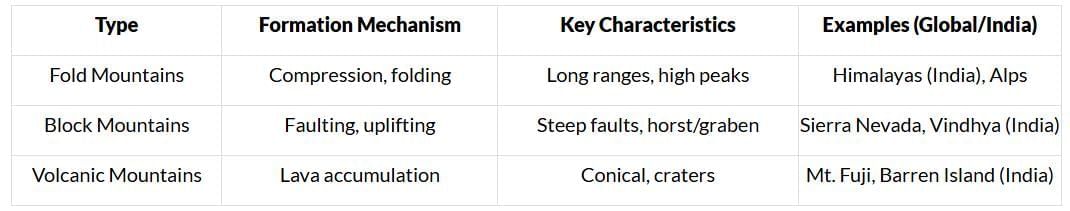
|
482 videos|1427 docs|310 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Mountain-Building (Fold, Block, Volcanic Mountains) - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the main types of mountains and how are they formed? |  |
| 2. What is orogeny and what role does it play in mountain-building? |  |
| 3. How do fold mountains differ from block mountains in terms of formation? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the significance of volcanic mountains in the context of mountain-building? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of famous mountain ranges that were formed through orogeny? |  |
















