SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Cheat Sheet: Early Medieval India and the World
Cheat Sheet: Early Medieval India and the World | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
Timeline
- Period: 6th–13th century CE.
- Begins after Post-Gupta/Post-Harsha period, ends with Delhi Sultanate (~1206 CE).
- Characterized by: fragmented kingdoms, regional powers, trade expansion, religious & cultural developments.
Major Regional Kingdoms of India
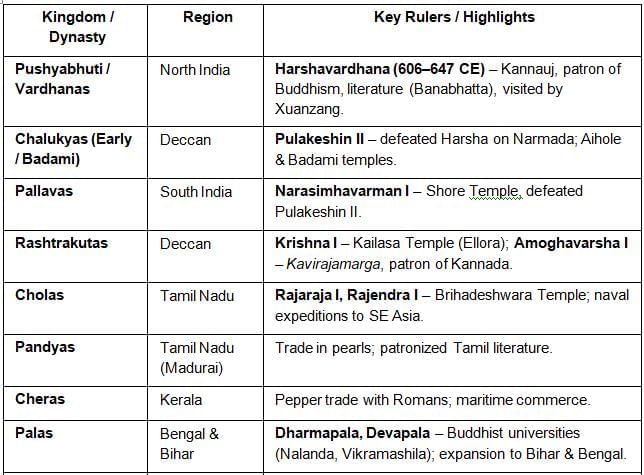
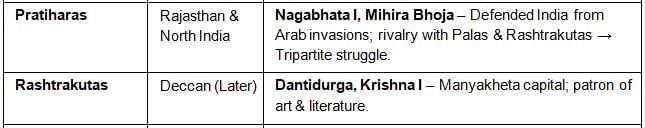
World Interactions
- Arab Invasions: Sindh – Muhammad bin Qasim (712 CE).
- Trade:
- India → SE Asia (spices, textiles) via Cholas’ naval expeditions.
- India ↔ West Asia & Mediterranean → Gujarat ports, South India ports.
- Roman coins, Chinese silk, Arabian trade evidence.
- Religion & Culture:
- Spread of Bhakti & Shaivism/Vaishnavism.
- Buddhism declined in North India; flourished under Palas.
- Temples as economic & cultural centers (South India & Deccan).
- Key Features of Early Medieval India
- Political Fragmentation: Multiple regional powers → no central authority.
- Tripartite Struggle: Palas (Bengal) ↔ Pratiharas (Rajasthan) ↔ Rashtrakutas (Deccan).
- Economy: Agriculture-based; thriving trade; land grants (brahmadeya, agrahara).
- Society: Caste system consolidated; guilds, artisans, merchants gained importance.
- Culture & Architecture:
(i) Dravidian style (Cholas, Pallavas).
(ii) Rock-cut temples (Badami, Aihole, Ellora).
(iii) Buddhist universities → Nalanda, Vikramashila.
(iv) Tamil Sangam culture → Pandyas & Cholas.
The document Cheat Sheet: Early Medieval India and the World | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
448 videos|1497 docs|288 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Early Medieval India and the World - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What were the major regional kingdoms of early medieval India? |  |
Ans. The major regional kingdoms of early medieval India included the Chola, Chera, Pandya, Rashtrakuta, and the Palas. Each of these kingdoms played a significant role in shaping the political, cultural, and economic landscape of India during this period, contributing to advancements in art, architecture, and trade.
| 2. How did the interactions between India and the world influence early medieval Indian society? |  |
Ans. Interactions between India and the world during the early medieval period led to the exchange of ideas, culture, and technology. Trade routes facilitated the movement of goods such as spices, textiles, and precious stones, while also promoting the spread of religions like Buddhism and Hinduism beyond Indian borders. These interactions enriched Indian society and contributed to its diversity.
| 3. What were the key features of the Chola dynasty's rule in early medieval India? |  |
Ans. The Chola dynasty is known for its significant contributions to art, architecture, and naval power during early medieval India. Their administration was marked by efficient governance, the promotion of Tamil culture, and the construction of grand temples like the Brihadeeswarar Temple. The Cholas also established a strong navy that facilitated trade and military expeditions across Southeast Asia.
| 4. What role did trade play in the economy of early medieval Indian kingdoms? |  |
Ans. Trade was a crucial aspect of the economy in early medieval Indian kingdoms. It facilitated wealth accumulation and cultural exchange. Indian merchants engaged in trade with regions such as the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and China, exporting goods like spices, textiles, and precious stones. This trade not only boosted the local economies but also led to the establishment of trade networks and ports.
| 5. How did the political landscape of early medieval India change during this period? |  |
Ans. The political landscape of early medieval India was characterized by the rise and fall of regional kingdoms, often influenced by military conquests and alliances. The decentralization of power led to the emergence of local rulers, which resulted in a fragmented political structure. However, this fragmentation also allowed for cultural diversity and regional identities to flourish, shaping the future of Indian polity.
Related Searches
















