SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > Finance and Economics > Mind Map: Non-Competitive Markets
Mind Map: Non-Competitive Markets | Finance and Economics - SSC CGL PDF Download
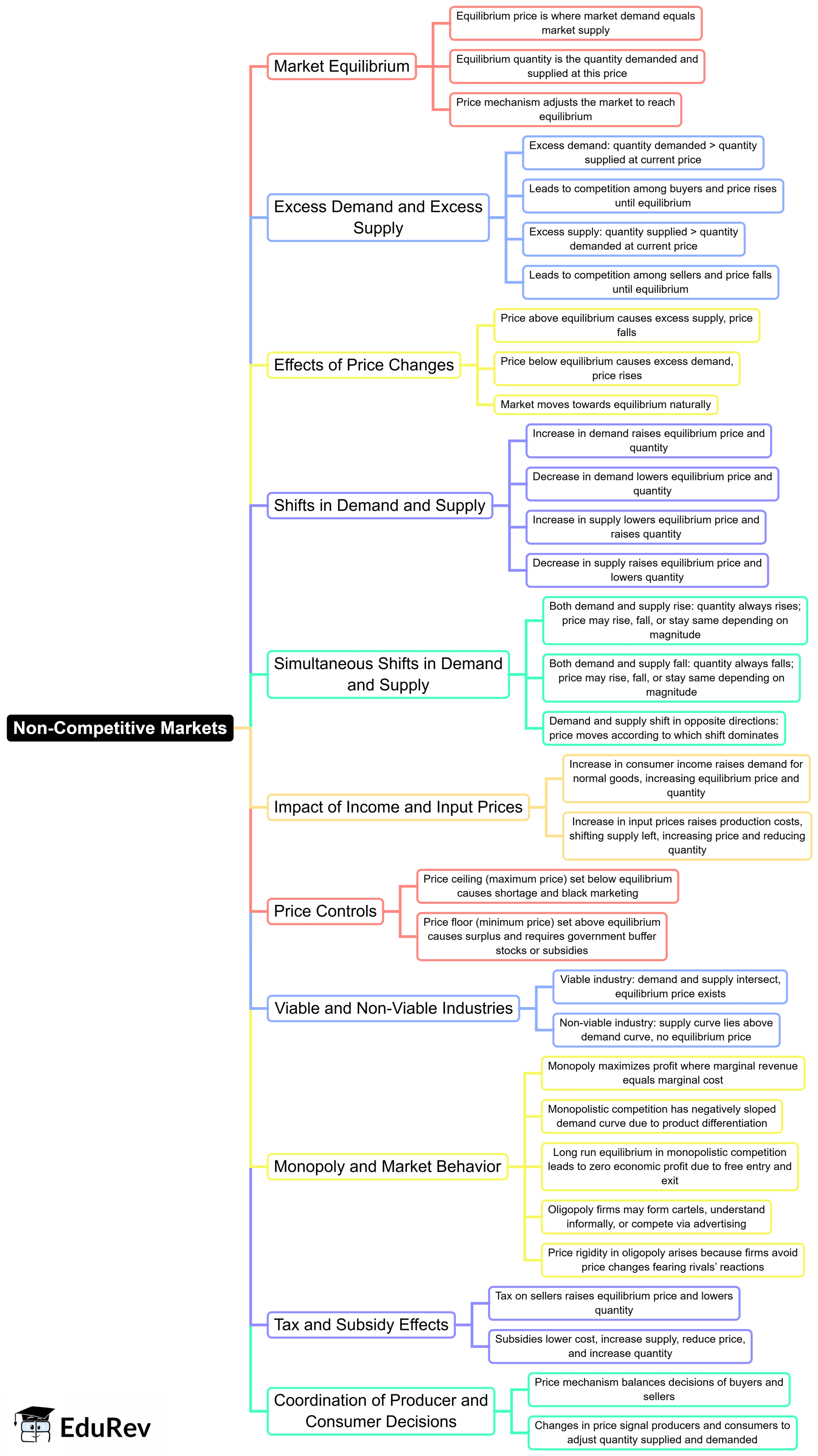
The document Mind Map: Non-Competitive Markets | Finance and Economics - SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course Finance and Economics.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
207 videos|138 docs|66 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Non-Competitive Markets - Finance and Economics - SSC CGL
| 1. What are non-competitive markets and how do they differ from competitive markets? |  |
Ans. Non-competitive markets, also known as imperfect markets, are characterized by a lack of competition among sellers. Unlike competitive markets where numerous firms offer similar products, non-competitive markets often have few sellers or even a single seller (monopoly), leading to price-setting power. This results in higher prices and lower output compared to competitive markets, where prices are determined by supply and demand dynamics.
| 2. What are common examples of non-competitive markets? |  |
Ans. Common examples of non-competitive markets include monopolies, where a single company controls the entire market for a product, such as utility companies. Oligopolies, where a few firms dominate the market (like automobile manufacturers), and monopolistic competition, where many firms sell similar but not identical products (like restaurants), are also considered non-competitive.
| 3. How do price controls affect non-competitive markets? |  |
Ans. Price controls, such as price ceilings or floors, can significantly impact non-competitive markets. In a monopoly, a price ceiling can prevent the seller from charging excessively high prices, potentially leading to shortages if the price is set below the market equilibrium. Conversely, price floors can lead to surpluses if set above the equilibrium price, as firms may produce more than consumers are willing to buy.
| 4. What role does government regulation play in non-competitive markets? |  |
Ans. Government regulation plays a crucial role in non-competitive markets by ensuring fair practices and protecting consumers. Regulations may include antitrust laws to prevent monopolies, price controls to protect consumers from excessive prices, and quality standards to ensure products are safe and effective. These regulations aim to promote competition and prevent market abuses.
| 5. How do non-competitive markets impact consumer choice and welfare? |  |
Ans. Non-competitive markets generally lead to reduced consumer choice and welfare. With fewer firms or a single dominant firm, consumers may have limited options for products and services. This lack of competition can result in higher prices and lower quality, ultimately harming consumer welfare. In contrast, competitive markets typically offer more choices and better prices for consumers.
Related Searches




















