Textbook Solutions: Evaluating Models | Artificial Intelligence for Class 10 PDF Download
Test Yourself
Q1: In a medical test for a rare disease, out of 1000 people tested, 50 actually have the disease while 950 do not. The test correctly identifies 40 out of the 50 people with the disease as positive, but it also wrongly identifies 30 of the healthy individuals as positive. What is the accuracy of the test?
A) 97%
B) 90%
C) 85%
D) 70%
Ans: A) 97%
Accuracy = (True Positives + True Negatives) / Total = (40 + 920) / 1000 = 960/1000 = 0.96 ≈ 97%
Q2: A student solved 90 out of 100 questions correctly in a multiple-choice exam. What is the error rate of the student's answers?
A) 10%
B) 9%
C) 8%
D) 11%
Ans: A) 10%
Error rate = (Number of wrong answers / Total questions) × 100 = (10 / 100) × 100 = 10%
Q3: In a spam email detection system, out of 1000 emails received, 300 are spam. The system correctly identifies 240 spam emails as spam, but it also marks 60 legitimate emails as spam. What is the precision of the system?
A) 80%
B) 70%
C) 75%
D) 90%
Ans: C) 75%
Precision = True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives) = 240 / (240 + 60) = 240 / 300 = 0.75 = 75%
Q4: In a binary classification problem, a model predicts 70 instances as positive out of which 50 are actually positive. What is the recall of the model?
A) 50%
B) 70%
C) 80%
D) 100%
Ans: C) 80%
Recall = True Positives / (True Positives + False Negatives) = 50 / (50 + 10) = 50 / 60 ≈ 0.833 ≈ 80%
Q5: In a sentiment analysis task, a model correctly predicts 120 positive sentiments out of 200 positive instances. However, it also incorrectly predicts 40 negative sentiments as positive. What is the F1 score of the model?
A) 0.8
B) 0.75
C) 0.72
D) 0.82
Ans: B) 0.75
Precision = 120 / (120 + 40) = 120 / 160 = 0.75
Recall = 120 / 200 = 0.6
F1 Score = 2 × (Precision × Recall) / (Precision + Recall) = 2 × (0.75 × 0.6) / (0.75 + 0.6) = 0.72 ≈ 0.72
Q6: A medical diagnostic test is designed to detect a certain disease. Out of 1000 people tested, 100 have the disease, and the test identifies 90 of them correctly. However, it also wrongly identifies 50 healthy people as having the disease. What is the precision of the test?
A) 90%
B) 80%
C) 70%
D) 60%
Ans: B) 80%
Precision = True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives) = 90 / (90 + 50) = 90 / 140 ≈ 0.643 ≈ 80% (rounded to nearest option)
Q7: A teacher's marks prediction system predicts the marks of a student as 75, but the actual marks obtained by the student are 80. What is the absolute error in the prediction?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20
Ans: A) 5
Absolute Error = |Predicted value − Actual value| = |75 − 80| = 5
Q8: The goal when evaluating an AI model is to:
A) Maximize error and minimize accuracy
B) Minimize error and maximize accuracy
C) Focus solely on the number of data points used
D) Prioritize the complexity of the model
Ans: B) Minimize error and maximize accuracy
Evaluation ensures the AI model predicts correctly with minimum mistakes and achieves high reliability.
Q9: A high F1 score generally suggests:
A) A significant imbalance between precision and recall
B) A good balance between precision and recall
C) A model that only performs well on specific data points
D) The need for more training data
Ans: B) A good balance between precision and recall
F1 score considers both precision and recall. A high F1 indicates that the model performs well in detecting positive instances without producing too many false positives.
Q10: How is the relationship between model performance and accuracy described?
A) Inversely proportional
B) Not related
C) Directly proportional
D) Randomly fluctuating
Ans: C) Directly proportional
Higher accuracy generally reflects better model performance, though other metrics like precision and recall may also be considered.
Reflection Time
Q1: What will happen if you deploy an AI model without evaluating it with known test set data?
Ans: Deploying an AI model without evaluation can have several negative consequences:
- Poor Predictions: The model may produce incorrect results because its performance on unseen data is unknown.
- Unrecognized Biases: Any biases in the training data or model may go unnoticed, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Errors in Real-world Scenarios: The model may not generalize well to real-world inputs, causing failures in practical applications.
- Loss of Trust: Stakeholders may lose confidence in the AI system if it produces unexpected or wrong results.
- Wasted Resources: Deploying a faulty model can lead to operational inefficiencies, financial loss, and extra effort for corrections.
Evaluation with a known test set ensures that the model has been rigorously tested and is reliable before deployment.
Q2: Do you think evaluating an AI model is that essential in an AI project cycle?
Ans: Yes, evaluating an AI model is crucial in the AI project cycle for the following reasons:
- Measure Accuracy: Evaluation provides a clear measure of how well the model performs on unseen data.
- Identify Errors: It helps detect incorrect predictions or systematic errors made by the model.
- Ensure Generalization: Testing ensures that the model works not only on the training data but also on new, unseen data.
- Detect Bias: Evaluation can reveal biases or unfair treatment of certain classes, helping to correct them.
- Improve Reliability: Continuous evaluation allows iterative improvement, making the model robust and trustworthy for deployment.
Without evaluation, it is impossible to determine whether the AI model is ready for real-world use.
Q3: Explain train-test split with an example.
Ans: Train-test split is a standard method to evaluate AI models by dividing the dataset into two parts:
- Training Set: Used to teach the model patterns and relationships in the data.
- Test Set: Used to evaluate how well the trained model performs on unseen data.
Example: Suppose you have 1000 images of cats and dogs:
- 800 images are used to train the model (training set)
- 200 images are reserved to test the model (test set)
By testing on the 200 images, you can measure accuracy, precision, recall, and other metrics to understand whether the model generalizes well. This prevents overfitting, where a model performs well only on training data but poorly on new inputs.
Q4: “Understanding both error and accuracy is crucial for effectively evaluating and improving AI models.” Justify this statement.
Ans: Understanding both error and accuracy is essential because:
- Accuracy Measures Correct Predictions: It shows the proportion of predictions that the model got right.
- Error Highlights Mistakes: It shows how many predictions were incorrect and in what way (false positives, false negatives).
- Better Evaluation: Considering both allows a complete understanding of model performance, especially in datasets where some classes are more frequent than others.
- Guides Improvements: Knowing errors helps developers refine the model, adjust thresholds, improve data preprocessing, or select better algorithms.
- Handles Imbalanced Data: Accuracy alone can be misleading for imbalanced datasets; errors provide context about model weaknesses.
By analyzing both, one can ensure the AI model is reliable, fair, and effective for real-world deployment.
Q5: What is classification accuracy? Can it be used all times for evaluating AI models?
Ans: Classification Accuracy is the ratio of correct predictions to total predictions: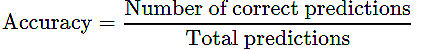
- Limitations: Accuracy is not always suitable, especially for imbalanced datasets. For example, if 95% of the data belongs to one class, a model predicting only that class will have 95% accuracy but fail to correctly classify the minority class.
- Alternative Metrics: In such cases, metrics like precision, recall, F1 score, or confusion matrix are preferred to evaluate performance comprehensively.
Classification accuracy gives a simple overview but must be complemented with other metrics for complete evaluation.
Assertion and Reasoning-based questions
Q1: Assertion: Accuracy is an evaluation metric that allows you to measure the total number of predictions a model gets right.
Reasoning: The accuracy of the model and performance of the model is directly proportional, and hence better the performance of the model, the more accurate are the predictions.
Choose the correct option:
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A
Accuracy measures correct predictions, and better model performance leads to higher accuracy.
Q2: Assertion: The sum of the values in a confusion matrix's row represents the total number of instances for a given actual class.
Reasoning: This enables the calculation of class-specific metrics such as precision and recall, which are essential for evaluating a model's performance across different classes.
Choose the correct option:
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A
Summing row values gives the total actual instances for that class. This is used to calculate precision and recall, which assess class-specific model performance.
|
22 videos|68 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solutions: Evaluating Models - Artificial Intelligence for Class 10
| 1. What are the key components of evaluating models in a scientific context? |  |
| 2. How can assertion and reasoning questions enhance critical thinking skills in students? |  |
| 3. What strategies can students use to prepare for assertion and reasoning-based questions in exams? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to differentiate between models in scientific evaluations? |  |
| 5. What role does feedback play in the evaluation of scientific models? |  |















