Textbook Solutions: Advanced Concept of Modeling in AI | Artificial Intelligence for Class 10 PDF Download
Test Yourself
Q1: In which type of machine learning is the data labeled with the desired output?
a) Supervised Learning
b) Unsupervised Learning
c) Reinforcement Learning
d) Deep Learning
Ans: a) Supervised Learning
Explanation: In supervised learning, the dataset includes both inputs and their corresponding desired outputs. The model learns the mapping from input to output to make predictions. Examples include classification and regression tasks.
Q2: An email spam filter that learns to identify spam emails based on labeled examples is an application of:
a) Supervised Learning
b) Unsupervised Learning
c) Reinforcement Learning
d) Transfer Learning
Ans: a) Supervised Learning
Explanation: Spam filters use labeled emails (spam or not spam) to train the model. The labeled data guides the model in learning patterns that distinguish spam from non-spam emails.
Q3: A machine learning algorithm that groups similar customer purchases into clusters for recommendation systems uses:
a) Supervised Learning
b) Unsupervised Learning
c) Reinforcement Learning
d) Neural Networks
Ans: b) Unsupervised Learning
Explanation: Clustering is an unsupervised technique because it identifies patterns and groups in unlabeled data without prior knowledge of categories.
Q4: An AI agent playing a game and learning from its rewards and penalties is an example of:
a) Supervised Learning
b) Unsupervised Learning
c) Reinforcement Learning
d) Evolutionary Learning
Ans: c) Reinforcement Learning
Explanation: Reinforcement learning trains agents to make decisions by rewarding correct actions and penalizing mistakes, helping the agent learn optimal strategies through trial and error.
Q5: Which of the following statements is NOT true about supervised learning?
a) Requires labeled data for training.
b) Used for classification and regression tasks.
c) Can be less efficient for large datasets.
d) Often used in image recognition applications.
Ans: c) Can be less efficient for large datasets
Explanation: Supervised learning can handle large datasets effectively with modern algorithms, though computational resources may be a factor. Statements a, b, and d are correct.
Q6: In an unsupervised learning scenario, the goal is to:
a) Predict a specific output based on labeled data.
b) Identify patterns and relationships within unlabeled data.
c) Train an AI agent through rewards and penalties.
d) Develop complex neural network architectures.
Ans: b) Identify patterns and relationships within unlabeled data
Explanation: Unsupervised learning focuses on finding hidden structures, patterns, or groupings in data that has no predefined labels.
Q7: Clustering algorithms are commonly used in unsupervised learning for:
a) Spam filtering
b) Image classification
c) Stock price prediction
d) Grouping similar data points
Ans: d) Grouping similar data points
Explanation: Clustering groups similar instances together to find patterns, often used in customer segmentation, recommendation systems, and market analysis.
Q8: Reinforcement learning is particularly useful for scenarios where:
a) Large amounts of labeled data are available.
b) The desired outcome is clear, but the path to achieve it is unknown.
c) The data is structured and easily categorized.
d) The task requires reasoning and logical deduction.
Ans: b) The desired outcome is clear, but the path to achieve it is unknown
Explanation: Reinforcement learning is ideal for tasks like games or robotics where the goal is known, but the agent must explore different actions to find the best strategy.
Q9: Imagine an AI playing a game and learning to win by trial and error. This is an example of:
a) Supervised Learning
b) Unsupervised Learning
c) Reinforcement Learning
d) Natural Language Processing
Ans: c) Reinforcement Learning
Explanation: The AI learns optimal strategies through rewards (winning) and penalties (losing), which is the core of reinforcement learning.
Q10: Artificial neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of:
a) The human brain
b) Quantum computers
c) Complex mathematical models
d) High-speed processors
Ans: a) The human brain
Explanation: Neural networks are designed to mimic the way neurons in the human brain process information, with nodes representing neurons and connections representing synapses.
Q11: The process of adjusting the weights in a neural network to improve performance is called:
a) Activation
b) Learning
c) Optimization
d) Training
Ans: d) Training
Explanation: Training a neural network involves updating weights and biases using optimization algorithms (like gradient descent) to minimize error and improve model performance.
Q12: A neural network with multiple layers of interconnected neurons is called a:
a) Single-layer network
b) Deep Neural Network
c) Linear network
d) Perceptron
Ans: b) Deep Neural Network
Explanation: A deep neural network contains multiple hidden layers between input and output layers, allowing it to learn complex patterns.
Q13: Neural networks are particularly well-suited for tasks involving:
a) Simple calculations and mathematical operations
b) Recognizing patterns in complex data like images and text
c) Performing logical deductions and reasoning tasks
d) Storing and retrieving large amounts of information
Ans: b) Recognizing patterns in complex data like images and text
Explanation: Neural networks excel in pattern recognition tasks, such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
Q14: Training a neural network often requires:
a) A small set of labeled data samples
b) A significant amount of data and computational resources
c) A specific set of programming instructions
d) A human expert to guide the learning process
Ans: b) A significant amount of data and computational resources
Explanation: Neural networks, especially deep networks, require large datasets and high computational power to learn complex patterns and avoid overfitting.
Assertion and Reasoning-based questions
Q1: Assertion: Unsupervised Learning is a type of learning without any guidance.
Reasoning: Unsupervised learning models work on unlabeled datasets, where the data fed into the machine is random and the person training the model may not have any prior information about it.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation for A
(c) A is True but R is False
(d) A is false but R is True
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A
Explanation: Unsupervised learning operates on unlabeled data, and the model identifies patterns or groupings without any guidance about expected output.
Q2: Assertion (A): Information processing in a neural network relies on weights and biases assigned to nodes.
Reasoning (R): These weights and biases determine how strongly a node is influenced by its inputs and its overall contribution to the next layer.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation for A
(c) A is True but R is False
(d) A is false but R is True
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A
Explanation: Weights and biases control how input signals propagate through the network, allowing the network to learn patterns and adjust predictions.
Reflection Time
Q1. Give difference between rule based and learning based AI models.
Ans: The difference between rule based and learning based AI models are –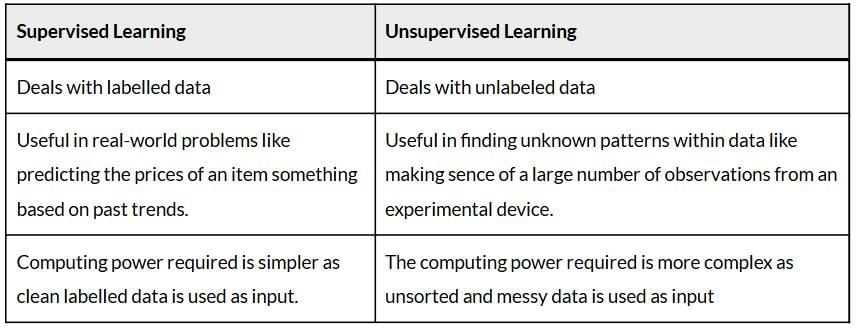
Q2. What is supervised, unsupervised and reinforcement learning? Explain with examples.
Ans:
- Supervised Learning – Supervised learning is a machine learning technique that uses labeled data to train algorithms to predict outcomes. Example of supervised learning is Email spam filtering and Image recognition
- Unsupervised Learning – An unsupervised learning model works on unlabeled dataset. This means that the data which is fed to the machine is random and there is a possibility that the person who is training the model does not have any information regarding it. It helps the user in understanding what the data is about and what are the major features identified by the machine in it. Example of unsupervised learning is medical image and data exploration.
- Reinforcement Learning – This learning approach enables the computer to make a series of decisions that maximize a reward metric for the task without human intervention and without being explicitly programmed to achieve the task. It’s based on a trial-and-error learning process to achieve the goals. Examples of reinforcement learning are question and Ansing, machine translation, and text summarization.
Q3. What is clustering and how is it different from classification?
Ans: Classification uses predefined classes in which objects are assigned. Clustering finds similarities between objects and places them in the same cluster and it differentiates them from objects in other clusters.
Q4. Explain neural networks. Also give functions of three layers of neural networks.
Ans: Neural networks are modelled on the human brain and nervous system. They are able to automatically extract features without input from the programmer.
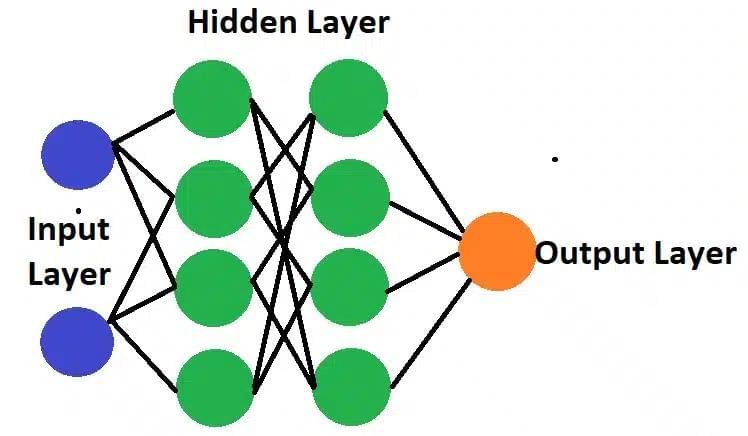
These neurons are known as nodes. An artificial neural network has an input layer, an output layer, and hidden layers. The input layer is responsible for receiving the data from the real world, and all the input data passes through one or multiple hidden layers and transforms the result using the output layer.
Q5. Differentiate between Classification and Regression.
Ans: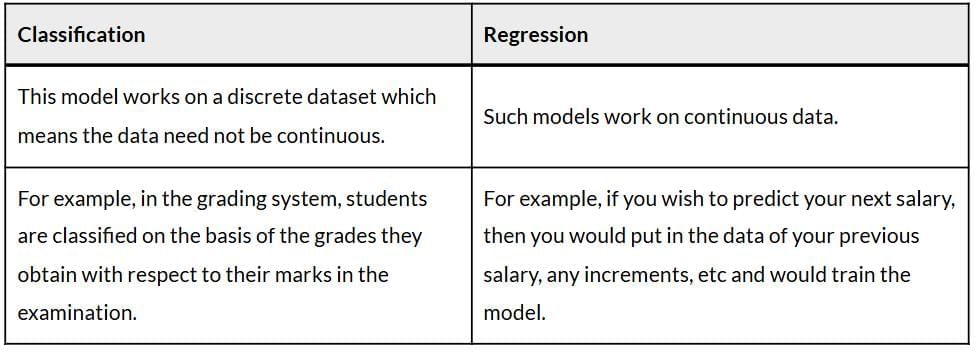
Q6. What is neural network? Give the functioning of its three layers?
Ans: A neural network is an AI model inspired by the human brain that learns patterns from data to make predictions or decisions.
Three layers and their functions:
- Input Layer: Receives raw data and passes it to the network.
- Hidden Layer: Processes data using weights and activation functions to extract patterns.
- Output Layer: Produces the final result or prediction.
Example: In image recognition, input = pixels, hidden = features like edges, output = cat/dog prediction.
|
22 videos|68 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solutions: Advanced Concept of Modeling in AI - Artificial Intelligence for Class 10
| 1. What is the significance of modeling in AI, and how does it aid in problem-solving? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of models commonly used in AI, and what are their applications? |  |
| 3. How does data quality impact the effectiveness of AI models? |  |
| 4. What role does feedback play in refining AI models? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the ethical considerations involved in AI modeling? |  |















