Textbook Solutions: Natural Language Processing | Artificial Intelligence for Class 10 PDF Download
Test Yourself
Q1: What is the primary challenge faced by computers in understanding human languages?
A) Complexity of human languages
B) Lack of computational power
C) Incompatibility with numerical data
D) Limited vocabulary
Ans: A) Complexity of human languages
Explanation: Human languages are highly ambiguous, context-dependent, and involve syntax, semantics, and pragmatics, making it difficult for computers to fully understand them.
Q2: How do voice assistants utilize NLP?
A) To analyze visual data
B) To process numerical data
C) To understand natural language
D) To execute tasks based on computer code
Ans: C) To understand natural language
Explanation: Voice assistants use NLP to interpret spoken or written language, allowing them to understand user queries and respond appropriately.
Q3: Which of the following is NOT a step in Text Normalisation?
A) Tokenization
B) Lemmatization
C) Punctuation removal
D) Document summarization
Ans: D) Document summarization
Explanation: Text normalization involves steps like tokenization, lemmatization, and removing punctuation to clean and standardize text. Document summarization is a separate NLP task.
Q4: In the context of text processing, what is the purpose of tokenisation?
A) To convert text into numerical data
B) To segment sentences into smaller units
C) To translate text into multiple languages
D) To summarize documents for analysis
Ans: B) To segment sentences into smaller units
Explanation: Tokenization splits text into smaller components such as words or sentences, making it easier to process and analyze.
Q5: What distinguishes lemmatization from stemming?
A) Lemmatization produces meaningful words after affix removal, while stemming does not.
B) Lemmatization is faster than stemming.
C) Stemming ensures the accuracy of the final word.
D) Stemming generates shorter words compared to lemmatization.
Ans: A) Lemmatization produces meaningful words after affix removal, while stemming does not.
Explanation: Lemmatization converts words to their base or dictionary form, producing meaningful words, whereas stemming simply trims suffixes, which may result in non-words.
Q6: What is the primary purpose of the Bag of Words model in Natural Language Processing?
A) To translate text into multiple languages
B) To extract features from text for machine learning algorithms
C) To summarize documents for analysis
D) To remove punctuation marks from text
Ans: B) To extract features from text for machine learning algorithms
Explanation: Bag of Words represents text as numerical vectors by counting word occurrences, which can then be used as input for ML models.
Q7: In the context of text processing, what are stop words?
A) Words with the frequent occurrence in the corpus
B) Words with negligible value that are often removed during preprocessing
C) Words with the lowest occurrence in the corpus
D) Words with the most value added to the corpus
Ans: B) Words with negligible value that are often removed during preprocessing
Explanation: Stop words are common words like “the,” “is,” “and” that do not contribute significant meaning to text analysis and are usually removed.
Q8: What is the characteristic of rare or valuable words in the described plot?
A) They have the highest occurrence in the corpus
B) They are often considered stop words
C) They occur the least but add the most value to the corpus
D) They are typically removed during preprocessing
Ans: C) They occur the least but add the most value to the corpus
Explanation: Rare words often carry significant meaning and are informative for distinguishing documents.
Q9: What information does the document vector table provide?
A) The frequency of each word across all documents
B) The frequency of each word in a single document
C) The total number of words in the entire corpus
D) The average word length in the entire corpus
Ans: B) The frequency of each word in a single document
Explanation: A document vector represents individual documents as vectors where each entry corresponds to the frequency of a word in that specific document.
Q10: What is the primary purpose of TFIDF in text processing?
A) To identify the presence of stop words in documents
B) To remove punctuation marks from text
C) To identify the value of each word in a document
D) To translate text into multiple languages
Ans: C) To identify the value of each word in a document
Explanation: TFIDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) assigns weights to words based on their importance, reducing the influence of common words while highlighting informative words.
Q11: Assertion: Pragmatic analysis in natural language processing (NLP) involves assessing sentences for their practical applicability in real-world scenarios.
Reasoning: Pragmatic analysis requires understanding the intended meaning behind sentences and considering their practical or logical implications, rather than solely relying on literal word meanings obtained from semantic analysis.
Options:
A) Both Assertion and Reasoning are true, and Reasoning is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
B) Assertion is true, but Reasoning is false.
C) Both Assertion and Reasoning are true, but Reasoning is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
D) Assertion is false, but Reasoning is true.
Ans: A) Both Assertion and Reasoning are true, and Reasoning is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Explanation: Pragmatics studies the context and intended meaning of language, ensuring sentences are interpreted according to their real-world implications.
Q12: Assertion: Converting the entire text into lowercase following stop word removal is a crucial preprocessing step in natural language processing.
Reasoning: This process ensures uniformity in word representation, preventing the machine from treating words with different cases as distinct entities, thereby enhancing the accuracy of subsequent text analysis.
Options:
A) Both Assertion and Reasoning are true, and Reasoning is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
B) Assertion is true, but Reasoning is false.
C) Both Assertion and Reasoning are true, but Reasoning is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
D) Assertion is false, but Reasoning is true.
Ans: A) Both Assertion and Reasoning are true, and Reasoning is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Explanation: Lowercasing standardizes text, avoiding duplicate representations of the same word due to case differences, which improves the effectiveness of text processing.
Reflection Time
Q1. Mention a few features of natural languages.
Ans: They are governed by set rules that include syntax, lexicon, and semantics, All natural languages are redundant, i.e., the information can be conveyed in multiple ways. All natural languages change over time.
Q2. What is the significance of NLP?
Ans: Artificial Intelligence nowadays is becoming an integral part of our lives, its applications are very commonly used by the majority of people in their daily lives. Here are some of the applications of Natural Language Processing which are used in the real-life scenario:
- Voice assistants – Voice assistants take our natural speech, process it, and give us an output. These assistants leverage NLP to understand natural language and execute tasks efficiently.
- Auto generated captions – Captions are generated by turning natural speech into text in real-time. It is a valuable feature for enhancing the accessibility of video content.
- Language translation – It incorporates the generation of translation from another language. This involves the conversion of text or speech from one language to another, facilitating cross-linguistic communication and fostering global connectivity.
- Sentiment analysis – Sentiment Analysis is a tool to express an opinion, whether the underlying sentiment is positive, negative, or neutral. Customer sentiment analysis helps in the automatic detection of emotions when customers interact with the products, services, or brand
Q3. What do you mean by lexical analysis in NLP?
Ans: NLP starts with identifying the structure of input words. It is the process of dividing a large chunk of words into structural paragraphs, sentences, and words. Lexicon stands for a collection of the various words and phrases used in a language.
Q4. What do you mean by a chatbot?
Ans: A chatbot is a computer program that’s designed to simulate human conversation through voice commands or text chats or both. It can learn over time how to best interact with humans. It can Ans questions and troubleshoot customer problems, evaluate and qualify prospects, generate sales leads and increase sales on an ecommerce site.
Q5. What does the term “Bag of Words” refer to in Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
Ans: Bag of Words is a Natural Language Processing model which helps in extracting features out of the text which can be helpful in machine learning algorithms. In the bag of words, we get the occurrences of each word and construct the vocabulary for the corpus.
Q6. Describe two practical uses of Natural Language Processing in real-world scenarios.
Ans: The two practical uses of NLP in real world are chatbots and voice assistant.
- Chatbots: A chatbot is a computer program that’s designed to simulate human conversation through voice commands or text chats or both. It can learn over time how to best interact with humans. It can Ans questions and troubleshoot customer problems, evaluate and qualify prospects, generate sales leads and increase sales on an ecommerce site.
- Voice assistant: Voice assistants take our natural speech, process it, and give us an output. These assistants leverage NLP to understand natural language and execute tasks efficiently.
Q7. Explain the process of stemming and lemmatization in text processing, supported by an example.
Ans: Stemming and lemmatization both are alternative processes to each other as the role of both the processes is same – removal of affixes. But the difference between both of them isthat in lemmatization, the word we get after affix removal (also known as lemma) is a meaningful one. Lemmatization makes sure that a lemma is a word with meaning and hence it takes a longer time to execute than stemming. Example,
- Caring -> Lemmatization -> Care
- Caring -> Stemming -> Car
Q8. Describe any four applications of TFIDF.
Ans: TFIDF is commonly used in the Natural Language Processing domain. Some of its applications are:
- Document Classification – Helps in classifying the type and genre of a document.
- Topic Modelling – It helps in predicting the topic for a corpus.
- Information Retrieval System – To extract the important information out of a corpus.
- Stop word filtering – Helps in removing unnecessary words from a text body.
Q9. Samiksha, a student of class X was exploring the Natural Language Processing domain. She got stuck while performing the text normalisation. Help her to normalise the text on the segmented sentences given below:
- Document 1: Akash and Ajay are best friends.
- Document 2: Akash likesto play football but Ajay prefers to play online games.
Ans: Text normalization helps to convert text into a standard format to improve NLP processing, it include lowercasing, removing extra spaces, correcting spellings, stemming and lemmatization.
Step 1: Input text given
- Document 1: Akash and Ajay are best friends.
- Document 2: Akash likesto play football but Ajay prefers to play online games.
Step 2: Convert to lowercase
- Document 1: akash and ajay are best friends.
- Document 2: akash likesto play football but ajay prefers to play online games.
Step 3: Remove Extra space
- Document 1: akash and ajay are best friends.
- Document 2: akash likes to play football but ajay prefers to play online games.
Step 4: Tokenization
- Document 1 Tokens: akash, and, ajay, are, best, friends
- Document 2 Tokens: akash, likes, to, play, football, but, ajay, prefers, to, play, online, games
Step 5: Lemmatization
- Document 1: akash and ajay are best friend.
- Document 2: akash like to play football but ajay prefer to play online game.
Q10. Through a step-by-step process, calculate TFIDF for the given corpus
- Document 1: Johny Johny Yes Papa,
- Document 2: Eating sugar? No Papa
- Document 3: Telling lies? No Papa
- Document 4: Open your mouth, Ha! Ha! Ha!
Ans: To calculate TF-IDF, follow the following steps:
Step 1: Tokenize the Documents
- Document 1: Johny, Johny, Yes, Papa
- Document 2: Eating, sugar, No, Papa
- Document 3: Telling, lies, No, Papa
- Document 4: Open, your, mouth, Ha, Ha, Ha
Step 2: Create a Term Frequency (TF) table
Formula for finding Term Frequency
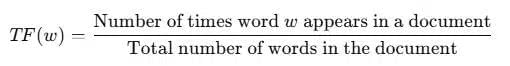
| Term | Document 1 | Document 2 | Document 3 | Document 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johny | 2/4 = 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Yes | 1/4 = 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Papa | 1/4 = 0.25 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 0 |
| Eating | 0 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 0 | 0 |
| sugar | 0 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 0 | 0 |
| No | 0 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 0 |
| Telling | 0 | 0 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 0 |
| lies | 0 | 0 | 1/4 = 0.25 | 0 |
| Open | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1/6 = 0.1667 |
| your | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1/6 = 0.1667 |
| mouth | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1/6 = 0.1667 |
| Ha | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3/6 = 0.5 |
Step 3: Calculate Inverse Document Frequency (IDF)
Formula for Inverse Document Frequency-

| Term | Appears in how many docs? | IDF Calculation | IDF Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Johny | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| Yes | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| Papa | 3 | log(4/3) | 0.287 |
| Eating | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| sugar | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| No | 2 | log(4/2) | 0.693 |
| Telling | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| lies | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| Open | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| your | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| mouth | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
| Ha | 1 | log(4/1) | 1.386 |
Step 4: Calculate TF-IDF Score
Formula for TF-IDF calculation are –
TFIDF(W) = TF(W) * log( IDF(W) )
| Term | Document 1 | Document 2 | Document 3 | Document 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johny | 0.5 x 1.386 = 0.693 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Yes | 0.25 x 1.386 = 0.3465 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Papa | 0.25 x 0.287 = 0.07175 | 0.25 x 0.287 = 0.07175 | 0.25 x 0.287 = 0.07175 | 0 |
| Eating | 0 | 0.25 x 1.386 = 0.3465 | 0 | 0 |
| sugar | 0 | 0.25 x 1.386 = 0.3465 | 0 | 0 |
| No | 0 | 0.25 x 0.693 = 0.17325 | 0.25 x 0.693 = 0.17325 | 0 |
| Telling | 0 | 0 | 0.25 x 1.386 = 0.3465 | 0 |
| lies | 0 | 0 | 0.25 x 1.386 = 0.3465 | 0 |
| Open | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1667 x 1.386 = 0.2310 |
| your | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1667 x 1.386 = 0.2310 |
| mouth | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1667 x 1.386 = 0.2310 |
| Ha | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 x 1.386 = 0.693 |
Q11. Identify any two stop words which should not be removed from the given sentence and why?
Get help and support whether you’re shopping now or need help with a past purchase.
Contact us at abc@pwershel.com or on our website www.pwershel.com
Ans: Stopwords in the given sentence which should not be removed are: @, . (fullstop) ,_(underscore) , 123(numbers) These tokens are generally considered as stopwords, but in the above sentence, these tokens are part of email id. removing these tokens may lead to invalid website address and email ID. So these words should not be removed from the above sentence.
Q12. All of us use smartphones. When we install a new app, it asks us for several permissions to access our phone’s data in different ways. Why do apps collect such data?
Ans:
- To provide customized notifications and recommendations.
- To improve the efficiency and accuracy of the app.
Q13. What will be the results of conversion of the term, ‘happily’ in the process of stemming and lemmatization? Which process takes longer time for execution?
Ans: Stemming Lemmatization happily happi happy Process that takes longer time for execution is lemmatization.
Q14. What do we get from the “bag of words” algorithm?
Ans: Bag of words gives us two things:
- The frequency of these words
- A vocabulary of words for the corpus
Q15. Samiksha, a student of class X was exploring the Natural Language Processing domain. She got stuck while performing the text normalisation. Help her to normalise the text on the segmented sentences given below:
- Document 1: Akash and Ajay are best friends.
- Document 2: Akash likes to play football but Ajay prefers to play online games.
Ans:
- Tokenisation: Akash, and, Ajay, are, best, friends, Akash, likes, to, play, football, but, Ajay, prefers, to, play, online, games
- Removal of stopwords: Akash, Ajay, best, friends, Akash, likes, play, football, Ajay, prefers, play, online, games
- converting text to a common case: akash, ajay, best, friends, akash, likes, play, football, ajay, prefers, play, online, games
- Stemming/Lemmatisation: akash, ajay, best, friend, akash, like, play, football, ajay, prefer, play, online, game
Q16. Identify any 2 stopwords in the given sentence:
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change.The three types of pollution are air pollution, water pollution and land pollution.
Ans: Stopwords in the given sentence are: is, the, of, that, into, are, and
Q17. “Automatic summarization is used in NLP applications”. Is the given statement correct? Justify your Ans with an example.
Ans: Yes, the given statement is correct. Automatic summarization is relevant not only for summarizing the meaning of documents and information, but also to understand the emotional meanings within the information, such as in collecting data from social media. Automatic summarization is especially relevant when used to provide an overview of a news item or blog post, while avoiding redundancy from multiple sources and
maximizing the diversity of content obtained.
Q18. Write any two applications of TFIDF
Ans:
- Document Classification: Helps in classifying the type and genre of a document.
- Topic Modelling: It helps in predicting the topic for a corpus.
- Information Retrieval System: To extract the important information out of a corpus.
- Stop word filtering: Helps in removing the unnecessary words out of a text body.
Q19. Write down the steps to implement bag of words algorithm.
Ans: The steps to implement bag of words algorithm are as follows:
- Text Normalisation: Collect data and pre-process it
- Create Dictionary: Make a list of all the unique words occurring in the corpus. (Vocabulary)
- Create document vectors: For each document in the corpus, find out how many times the word from the unique list of words has occurred.
- Create document vectors for all the documents.
Q20. Explain the term Text Normalisation in Data Processing.
Ans: The first step in Data processing is Text Normalisation. Text Normalisation helps in cleaning up the textual data in such a way that it comes down to a level where its complexity is lower than the actual data. In this we undergo several steps to normalise the text to a lower level. We work on text from multiple documents and the term used for the whole textual data from all the documents altogether is known as corpus.
Q21. Name any 2 applications of Natural Language Processing which are used in the real-life scenario.
Ans: The 4 applications of Natural Language processing are –
- Automatic Summarization: Automatic summarization is relevant not only for summarizing the meaning of documents and information, but also to understand the emotional meanings within the information, such as in collecting data from social media.
- Sentiment Analysis: The goal of sentiment analysis is to identify sentiment among several posts or even in the same post where emotion is not always explicitly expressed.
- Text classification: Text classification makes it possible to assign predefined categories to a document and organize it to help you find the information you need or simplify some activities.
- Virtual Assistants: With the help of speech recognition, these assistants can not only detect our speech but can also make sense out of it.
|
22 videos|68 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solutions: Natural Language Processing - Artificial Intelligence for Class 10
| 1. What is Natural Language Processing and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the key components of Natural Language Processing? |  |
| 3. What are some common applications of Natural Language Processing? |  |
| 4. How does Natural Language Processing handle ambiguity in language? |  |
| 5. What challenges does Natural Language Processing face? |  |















