Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Notes > Analog and Digital Electronics > Mind Map: Operational Amplifier
Mind Map: Operational Amplifier | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
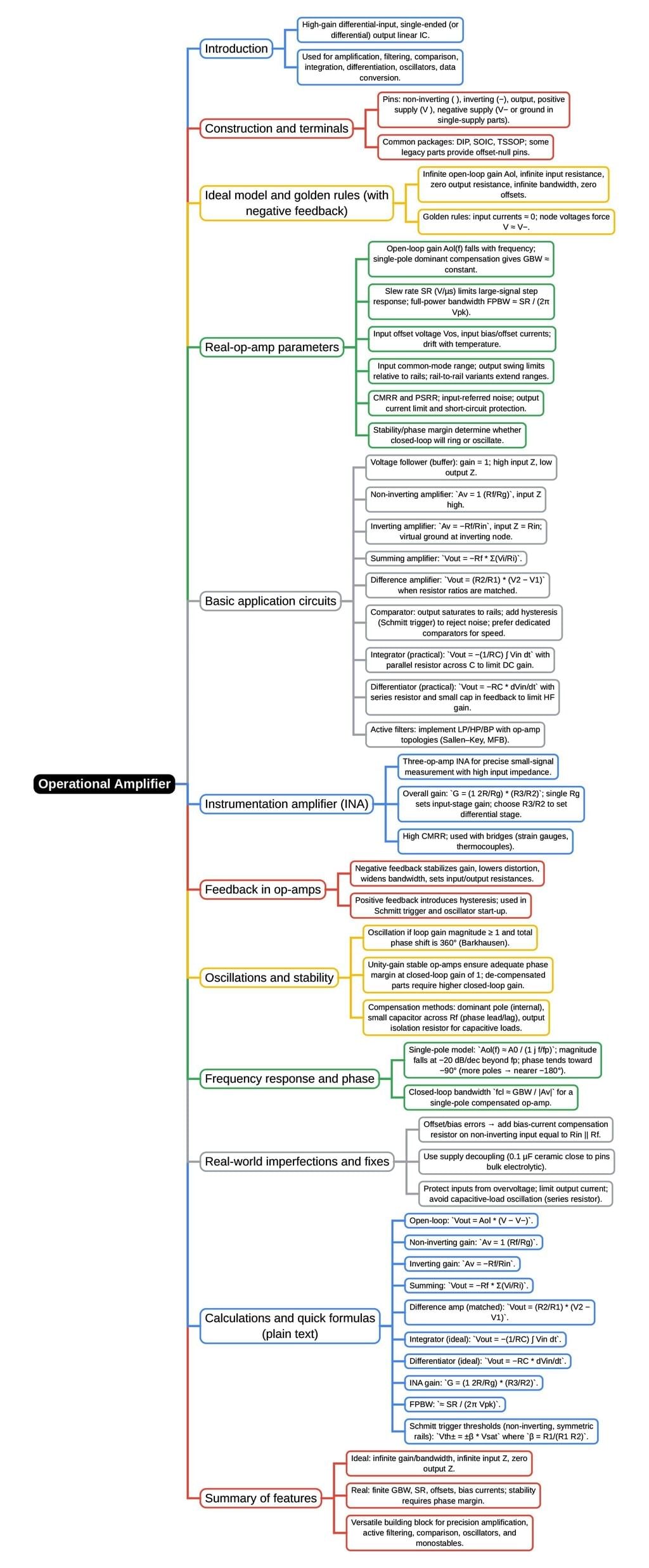
The document Mind Map: Operational Amplifier | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Analog and Digital Electronics.
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
135 videos|181 docs|71 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Operational Amplifier - Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is an operational amplifier and how does it function? |  |
Ans. An operational amplifier (op-amp) is a high-gain voltage amplifier with a differential input and typically a single-ended output. It amplifies the difference in voltage between its two input terminals (inverting and non-inverting). The fundamental operation is based on feedback, where the output voltage is fed back to the inverting input to control the gain and stability of the circuit.
| 2. What are the ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier? |  |
Ans. The ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier include infinite open-loop gain, infinite input impedance, zero output impedance, infinite bandwidth, and zero offset voltage. These characteristics allow the op-amp to amplify signals without distortion and interact minimally with other circuit components.
| 3. What are common applications of operational amplifiers in electrical engineering? |  |
Ans. Operational amplifiers are widely used in various applications, including signal conditioning, filtering, mathematical operations (like addition, subtraction, integration, and differentiation), voltage followers, and as components in analog computing circuits. They are also essential in creating oscillators, comparators, and amplifiers in audio and instrumentation systems.
| 4. Can you explain the difference between inverting and non-inverting amplifier configurations? |  |
Ans. In an inverting amplifier configuration, the input signal is applied to the inverting terminal, resulting in a phase shift of 180 degrees and an output signal that is inverted relative to the input. The gain of an inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of two resistors. In contrast, a non-inverting amplifier applies the input signal to the non-inverting terminal, maintaining the phase of the signal, and the gain is given by 1 plus the ratio of the feedback resistor to the input resistor.
| 5. What is negative feedback in operational amplifiers, and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Negative feedback in operational amplifiers refers to feeding a portion of the output signal back to the inverting input terminal. This technique is crucial for stabilizing the gain, improving linearity, and minimizing distortion. It also enhances bandwidth and reduces sensitivity to component variations, making the overall circuit more reliable and predictable.
Related Searches















