Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Notes > Digital Electronics > Mind Map: Number System & Representation
Mind Map: Number System & Representation | Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
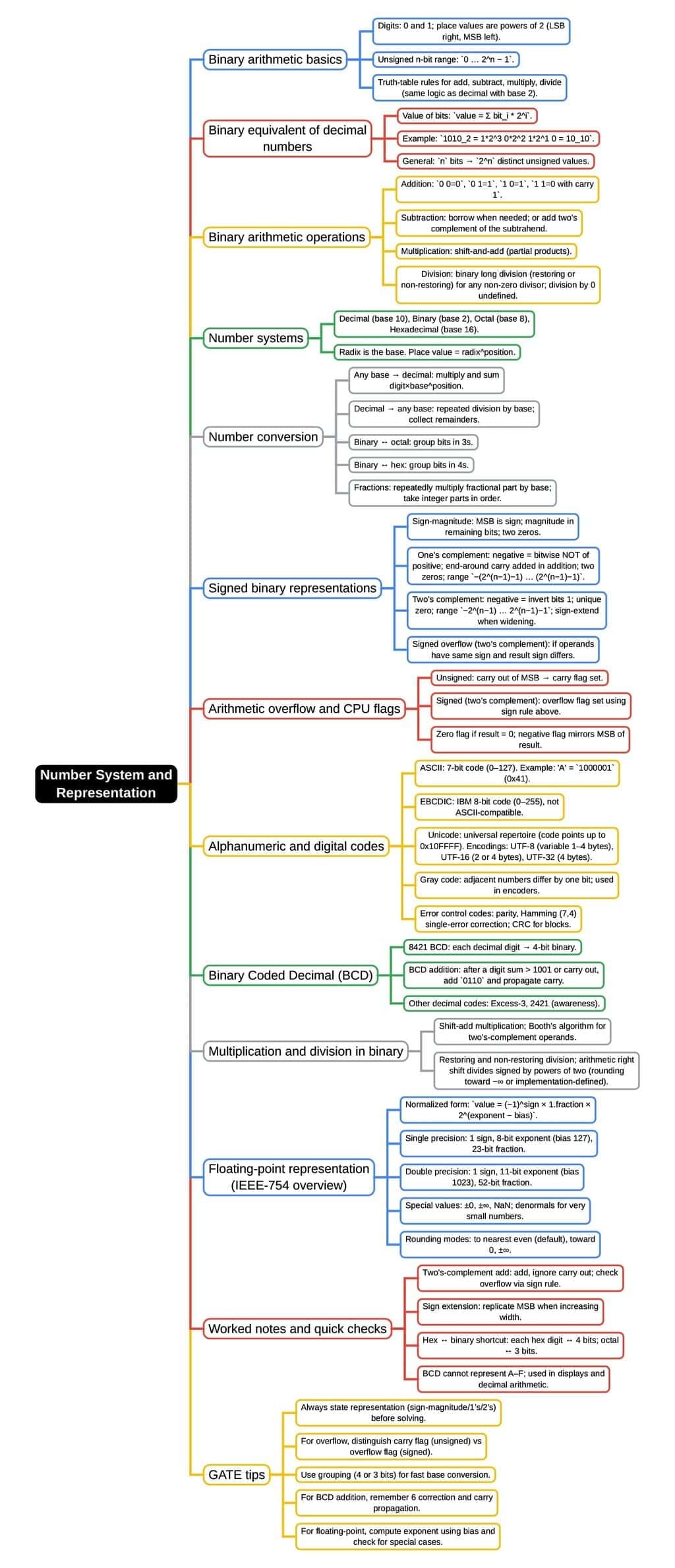
The document Mind Map: Number System & Representation | Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Digital Electronics.
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
113 videos|91 docs|58 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Number System & Representation - Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are the different types of number systems used in electrical engineering? |  |
Ans. In electrical engineering, the most commonly used number systems are the binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal systems. The binary system uses base 2 and consists of only two digits, 0 and 1. The decimal system, which is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers, uses base 10. The octal system is base 8 and uses digits from 0 to 7, while the hexadecimal system is base 16 and includes digits from 0 to 9 and letters A to F, representing values ten to fifteen. Each system has its specific applications in digital electronics and computer systems.
| 2. Why is the binary number system important in electrical engineering? |  |
Ans. The binary number system is crucial in electrical engineering because it directly corresponds to the two states of electrical signals: on and off, or high and low voltage. Digital circuits, including computers and microcontrollers, utilize binary to process and store data. This system simplifies the design of electronic circuits, as components can easily represent binary states through transistors, diodes, and other semiconductor devices, making it foundational for modern electronics and computing.
| 3. How is the conversion between different number systems performed? |  |
Ans. Conversion between number systems can be performed using various methods. For example, to convert a binary number to decimal, you multiply each bit by 2 raised to the power of its position and sum the results. To convert from decimal to binary, repeatedly divide the decimal number by 2 and record the remainders. For octal and hexadecimal conversions, similar principles apply, but the base is adjusted accordingly. These conversions are essential for manipulating and interpreting data across different systems in electrical engineering.
| 4. What role do hexadecimal numbers play in programming and digital systems? |  |
Ans. Hexadecimal numbers play a significant role in programming and digital systems as they provide a more human-readable way to represent binary data. Since one hexadecimal digit corresponds to four binary digits (bits), it simplifies the representation of large binary numbers. Programmers frequently use hexadecimal for tasks such as memory addressing, color coding in graphics, and defining constants in code. This makes it easier to read and understand the values without dealing with lengthy binary sequences.
| 5. How does the concept of signed numbers work in the number systems used in electrical engineering? |  |
Ans. Signed numbers in number systems allow for the representation of both positive and negative values. In binary, signed numbers are typically represented using methods like sign-magnitude, one's complement, or two's complement. The two's complement method is most widely used because it simplifies arithmetic operations. In this system, the most significant bit (MSB) indicates the sign (0 for positive, 1 for negative), while the value is calculated based on the remaining bits. This representation is essential for performing calculations involving both positive and negative numbers in digital systems.
Related Searches















