Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Notes > Engineering Mechanics > Mind Map: Impulse, Momentum & Collision
Mind Map: Impulse, Momentum & Collision | Engineering Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
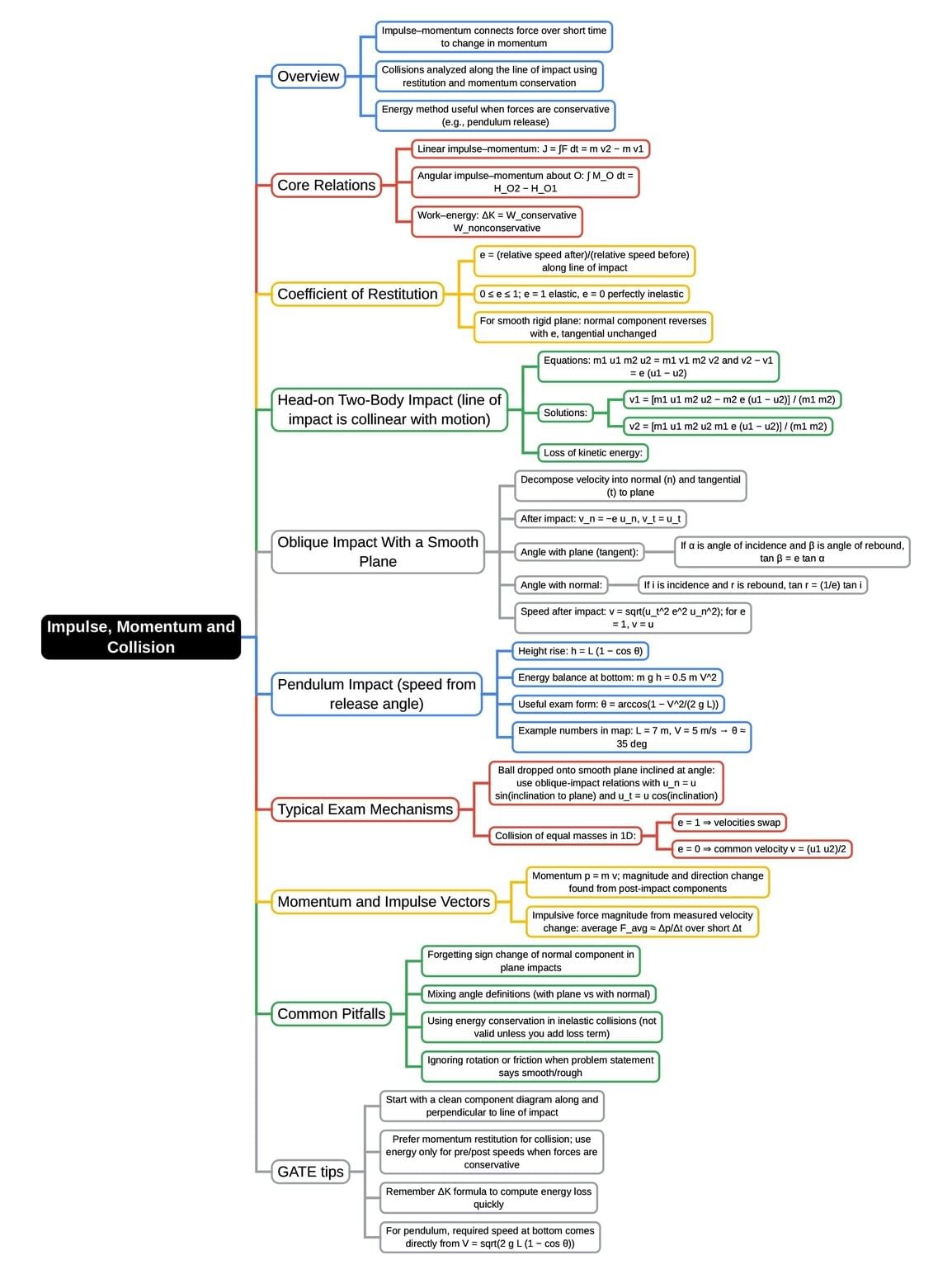
The document Mind Map: Impulse, Momentum & Collision | Engineering Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) is a part of the Civil Engineering (CE) Course Engineering Mechanics.
All you need of Civil Engineering (CE) at this link: Civil Engineering (CE)
|
24 videos|69 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Impulse, Momentum & Collision - Engineering Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the relationship between impulse and momentum in civil engineering? |  |
Ans. In civil engineering, impulse refers to the change in momentum of an object when a force is applied over a period of time. The relationship is defined by the impulse-momentum theorem, which states that the impulse applied to an object is equal to the change in its momentum. Mathematically, this can be expressed as Impulse = Δp = F × Δt, where Δp is the change in momentum, F is the force applied, and Δt is the time duration of the force application.
| 2. How do collisions affect structural design in civil engineering? |  |
Ans. Collisions can significantly impact structural design as they may lead to unexpected loads and stresses on structures. Engineers must consider potential collision scenarios, such as vehicle impacts on bridges or buildings, to ensure that structures can withstand these forces. This often involves implementing safety features, such as crash barriers, and using materials and designs that can absorb and dissipate energy effectively during a collision.
| 3. What are the different types of collisions relevant to civil engineering? |  |
Ans. There are primarily two types of collisions relevant to civil engineering: elastic and inelastic collisions. In elastic collisions, both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved, while in inelastic collisions, momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not. Understanding these types of collisions helps engineers design structures that can either withstand or mitigate the effects of impacts, ensuring safety and durability.
| 4. How is momentum conserved in a collision involving a structure? |  |
Ans. In a collision involving a structure, momentum is conserved in a closed system where no external forces are acting. This means that the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision. Engineers use this principle to analyze the forces that structures may experience during impacts and design them to handle these forces without failing.
| 5. What role do impulse and momentum play in the analysis of dynamic loads on structures? |  |
Ans. Impulse and momentum are crucial in analyzing dynamic loads, such as those from impacts or seismic events. By understanding how impulse affects momentum, engineers can predict how structures will respond to sudden forces. This analysis helps in designing resilient structures that can absorb and dissipate energy from dynamic loads, ensuring they remain safe and functional under various conditions.
Related Searches















