Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures NCERT Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Probe and Ponder (Page No. 116)
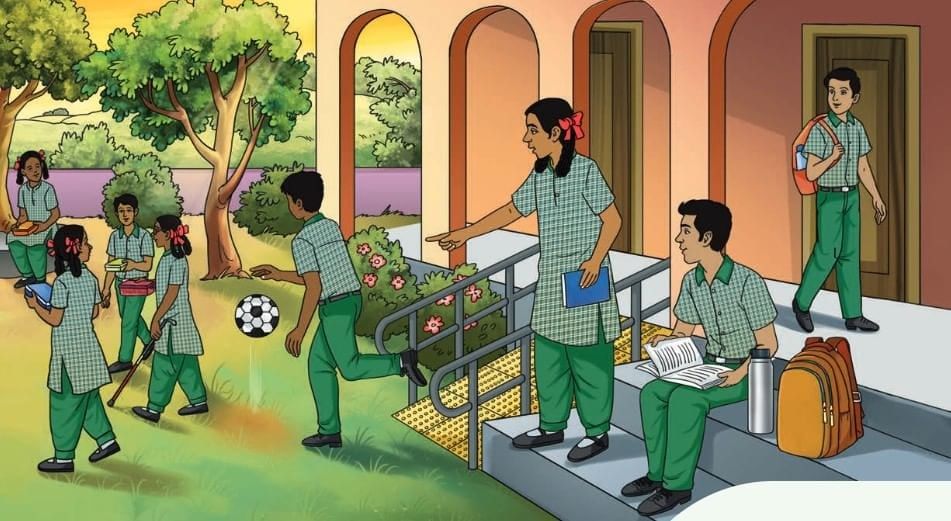

Q1: Which of the entities in the picture below consists of matter, and which of them do not?
Ans: Entities that consist of matter are school buildings, students, trees, metal railings, footballs, school bags, books, water bottles, lunch boxes, and the clothes of students, etc.
Entities that do not consist of matter are light, sound, heat etc.
Q2: How can elements be combined to form a compound?
Ans: A compound is a unique substance that forms when two or more elements combine chemically. Compounds form as a result of chemical reactions. The elements in compounds are held together by chemical bonds.
Q3: How could the discovery of a compound that absorbs carbon dioxide from the air contribute to solving environmental challenges?
Ans: A compound that effectively absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air could significantly help mitigate climate change and other environmental challenges. Removing CO2, a major greenhouse gas, from the atmosphere could reduce global warming, ocean acidification, and other harmful effects associated with excess atmospheric CO2.
Keep the curiosity alive (Page No. 131)
Q1: Consider the following reaction where two substances, A and B, combine to form a product C:
A + B → C
Assume that A and B cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Based on this information, which of the following statements is correct?
(i) A, B, and C are all compounds, and only C has a fixed composition.
(ii) C is a compound, and A and B have a fixed composition.
(iii) A and B are compounds, and C has a fixed composition.
(iv) A and B are elements, C is a compound, and has a fixed composition.
Ans: (iv) A and B are elements, C is a compound, and has a fixed composition.
The question states that A and B cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions. This means A and B are elements, because elements are pure substances made of only one kind of atom and cannot be broken down chemically. When A and B combine chemically to form C, the result is a compound. A compound is formed when two or more elements combine in a fixed ratio through a chemical reaction. Therefore, A and B are elements, and C is a compound with a fixed composition.
Q2: Assertion: Air is a mixture.
Reason: A mixture is formed when two or more substances are mixed, without undergoing any chemical change.
(i) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(ii) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(iii) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(iv) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (i) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
Air is indeed a mixture because it is composed of various gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide, which are mixed without any chemical reaction between them. The properties of these individual gases are retained within the air.
Q3: Water, a compound, has different properties compared to those of the elements oxygen and hydrogen from which it is formed. Justify this statement.
Ans: Water has properties that are completely different from those of hydrogen and oxygen. Water is a liquid, while both hydrogen and oxygen are gases at room temperature. This difference arises because the properties of a compound depend on its molecular structure.
Q4: In which of the following cases are all the examples correctly matched? Give reasons in support of your answers.
(i) Elements – water, nitrogen, iron, air.
(ii) Uniform mixtures – minerals, seawater, bronze, air.
(iii) Pure substances – carbon dioxide, iron, oxygen, sugar.
(iv) Non-uniform mixtures – air, sand, brass, muddy water.
Ans: (iii) Pure substances – Iron, oxygen, and sugar are all pure substances. (Correctly matched).
A pure substance is composed of only one type of particle. Iron and oxygen are elements, while carbon dioxide and sugar are compounds. All four are pure substances.
Q5: Iron reacts with moist air to form iron oxide, and magnesium burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide. Classify all the substances involved in the above reactions as elements, compounds, or mixtures, with justification.
Ans: Iron reacts with moist air to form iron oxide
Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (O2) + Water (H2O) → Iron Oxide (Fe2O3)
Magnesium burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Classification of Substances:
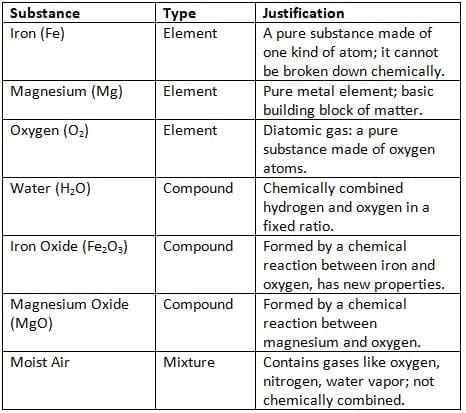
Q6: Classify the following as elements, compounds, or mixtures in the Table.
Carbon dioxide, sand, seawater, magnesium oxide, muddy water, aluminum, gold, oxygen, rust, iron sulfide, glucose, air, water, fruit juice, nitrogen, sodium chloride, sulfur, hydrogen, and baking soda.
Identify pure substances amongst these and list them below.

Ans:
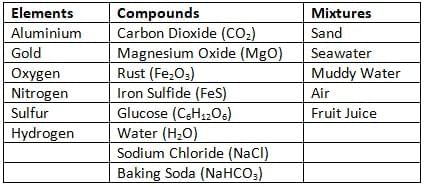
Pure Substances: Aluminium, gold, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, magnesium oxide, iron sulfide, glucose, water, sodium chloride, baking soda.
Q7: What new substance is formed when a mixture of iron filings and sulfur powder is heated, and how is it different from the original mixture? Also, write the word equation for the reaction.
Ans: When iron filings and sulfur powder are heated, they react to form a new substance called Iron sulfide. (FeS), also known as iron sulfide. This is a chemical change, and the resulting compound has different properties from the original iron and sulfur.
The word equation for the reaction is: Iron + Sulfur → Iron sulfide
Original Mixture: Iron filings and sulfur powder are physically mixed. They retain their individual properties, and the mixture can be separated by physical means like using a magnet to attract the iron.
Iron sulfide (FeS): Heating the mixture causes a chemical reaction. Iron and sulfur combine to form a new substance, Iron sulfide. This is a compound, meaning the atoms are chemically bonded.
Difference in Properties: Iron sulfide has its unique properties that are distinct from those of iron and sulfur. For example, it is a black solid, whereas iron is typically gray, and sulfur is yellow. It is also not attracted to magnets like iron.
Word equation: The word equation for the reaction is Iron + Sulfur → Iron sulfide
Q8: Is it possible for a substance to be classified as both an element and a compound? Explain why or why not.
Ans: No, a substance cannot be classified as both an element and a compound. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, while compounds are formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together. The defining characteristic of a compound is that it is composed of multiple elements, whereas an element is a single type of atom. Therefore, a substance cannot be both a single type of atom and a combination of different types of atoms simultaneously.
Q9: How would our daily lives be changed if water were not a compound but a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen?
Ans: Water’s role in life and nature depends on it being a compound with stable properties. If it were a mixture, it would be dangerous and unusable, making life as we know it impossible.
Impact on Daily Life:
- No safe drinking water → Life would not be possible.
- No water for agriculture → Crops would not grow.
- No water for cleaning or cooking → Daily tasks would be unsafe.
- No aquatic life → Fish and underwater plants would die.
- Increased fire hazards → Hydrogen and oxygen together are explosive.
Q10: Analyse the figure. Identify Gas A. Also, write the word equation of the chemical reaction.
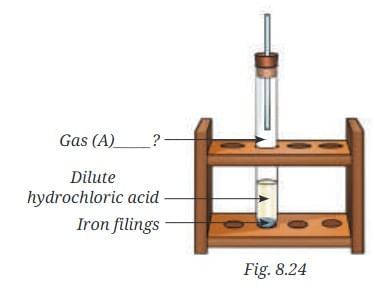
Ans: By analysing the figure, it is found that there will be a chemical reaction inside the test tube between dilute HCl and Fe.
2HCl + Fe → FeCl2 + H2 ↑
So the reaction forms Iron Chloride (FeCl2) and the gas above will be Hydrogen (H2).
Hydrochloric Acid + Iron filings → Iron Chloride + Hydrogen (g)
Thus, Gas A = Hydrogen
Q11: Write the names of any two compounds made only from non-metals, and also mention two uses of each of them.
Ans:
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Made of: Carbon and Oxygen (both non-metals)
Uses:
- Used in fire extinguishers to put out flames.
- Used by plants during photosynthesis to make food.
2. Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Made of: Sulfur and Oxygen (both non-metals)
Uses:
- Used as a preservative in dried fruits and wines.
- Used in the manufacture of sulfuric acid, an important industrial chemical.
Q12: How can gold be classified as both a mineral and a metal?
Ans: A mineral is a naturally occurring substance with a definite chemical composition.
Gold is found in nature in its native form, often embedded in rocks or alluvial deposits. It is extracted through mining, making it a metallic mineral. Minerals like gold are formed by natural geological processes.
Gold as a Metal
After extraction, gold is refined and used as a metal. It is a pure element (symbol: Au) with typical metallic properties:
- Lustrous (shiny)
- Malleable (can be shaped)
- Ductile (can be drawn into wires)
- Good conductor of electricity
- Used in jewelry, electronics, and currency.
Discover, design, and debate (Page No. 133)
Q1: Design and create comic strips from real-life examples to differentiate between elements, compounds, and mixtures with diagrams and illustrate their properties and uses.
Ans: A comic strip can show these three examples:
- Element: A gold ring — made of only one metal, gold (Au).
- Compound: Water — made of hydrogen and oxygen joined chemically; always has the same properties.
- Mixture: Fruit salad — different fruits mixed together, each keeping its own taste.
Properties and Uses:
- Elements have only one type of atom (used in wires, jewellery).
- Compounds have fixed composition and new properties (used as water, salt, medicines).
- Mixtures can be separated easily (used in food items, alloys like brass).
Q2: Search for discoveries of some elements (such as phosphorus, sodium), compounds (such as penicillin) and mixtures (such as brass, bronze, stainless steel). Present your findings in the class.
Ans: (Answer may vary)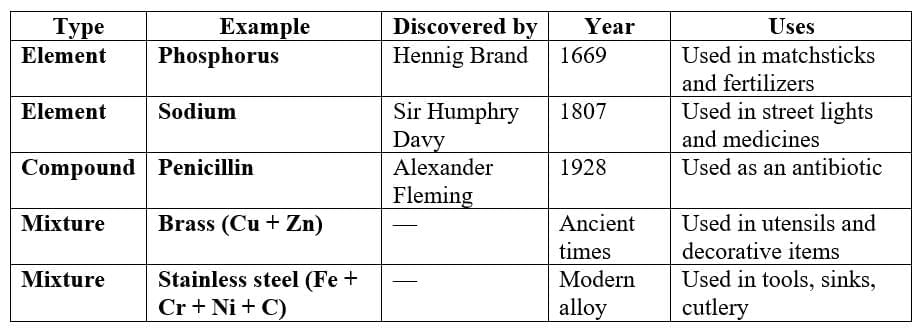
Q3: Let us search: Read labels on items like detergents or snacks, and try to list the mixtures and compounds they contain.
Ans: (Answer may vary)
Examples:
- Detergent: Mixture of surfactants, perfume, color, and sodium carbonate (compound).
- Toothpaste: Mixture of calcium carbonate (compound), fluoride compounds, and flavoring agents.
- Chips Packet: Mixture of potatoes, salt (sodium chloride – compound), and oil.
- Soft Drink: Mixture of water, sugar (compound), carbon dioxide gas, and flavoring substances.
Q4: Work in groups: Each group will pretend to be in the role of either an element, a compound, or a mixture. Debate which category among them is the most important.
Ans:
Team 1 – Elements:
We, the Elements, are the basic building blocks of all matter.
Without us, nothing in the world can exist.
Oxygen helps living beings breathe, iron is used in construction and in our blood, and gold is used to make ornaments.
We are pure substances made of only one kind of atom.
Compounds and mixtures are formed only because of us.
Therefore, elements are the most important.
Team 2 – Compounds:
We, the Compounds, are formed when elements combine chemically in fixed ratios.
We have properties different from the elements that form us.
Water, which gives life to all living beings, and salt, which adds taste to food, are compounds.
Compounds are useful in medicines, fuels, and food.
Without compounds, life would not be possible.
Hence, compounds are the most important.
Team 3 – Mixtures:
We, the Mixtures, are found everywhere around us.
The air we breathe, the food we eat, and the soil that grows crops are all mixtures.
Our components can be easily separated, and each part keeps its own properties.
Alloys like steel and bronze, and drinks like lemonade, are mixtures.
They make daily life possible and comfortable.
Therefore, mixtures are the most important.
Conclusion:
All three – Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures – are equally important.
Elements combine to form compounds, and compounds mix to form mixtures.
Together, they make up everything around us and are all necessary for life and the environment.
|
59 videos|235 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures NCERT Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the difference between elements, compounds, and mixtures? |  |
| 2. Can you give examples of common elements, compounds, and mixtures? |  |
| 3. How can we separate the components of a mixture? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of compounds that distinguish them from mixtures? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding the nature of matter important in science? |  |
















