NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Cell Structure and Functions
Exercises
Q1. Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
(a) Unicellular organisms have a one-celled body. ( )
(b) Muscle cells are branched. ( )
(c) The basic living unit of an organism is an organ. ( )
(d) Amoeba has an irregular shape. ( )
Ans:
(a) True.
- Organism made up of one cell is called unicellular or unicellular organism.
(b) True.
- Muscle tissue is of three types- Striated muscle, Cardiac muscle, Smooth muscle. Muscle cells usually branched cells.
(c) False.
- The basic structural and functional unit of life is the cell, whereas organs are made up of multiple cells.
(d) True.
- Amoeba is known for its changing shape and lacks a fixed form.
Q2. Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
Ans:
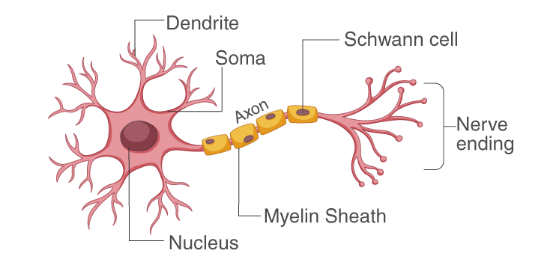 Human Nerve Cell
Human Nerve Cell
Q3. Write short notes on the following:
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus of a cell
Ans:
(a) Cytoplasm
- The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various other components or organelles like Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, Ribosomes, etc. are present in the cytoplasm.
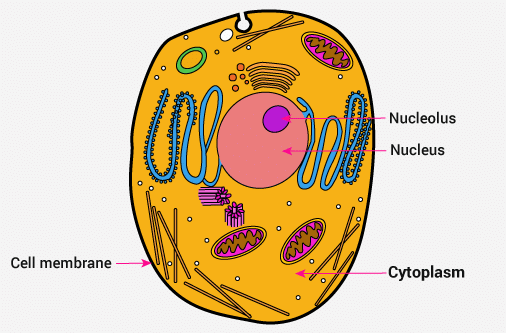
- Cytoplasm helps the exchange and storage of substances among cell organelles.
- Most of the metabolic activities occur inside the cytoplasm.
(b) Nucleus of a Cell
- The nucleus is an important component of the living cell. It is mostly spherical and located in the center of the cell.
 Plant and Animal Cell
Plant and Animal Cell - It is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane.
- In addition, the nucleus contains thread-like structures called chromosomes. These carry genes and help in the inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
- The nucleus, in addition to its role in inheritance, acts as the control centre of the activities of the cell.
Q4. Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Ans: Cell organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm, which is the gel-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. The cytoplasm contains various components, or organelles, including:
- Mitochondria
- Golgi bodies
- Ribosomes
These organelles play essential roles in the cell's functions.
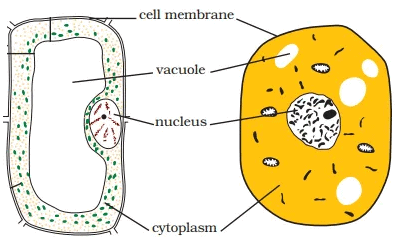
Q5. Make sketches of animal and plant cells. State three differences between them.
Ans: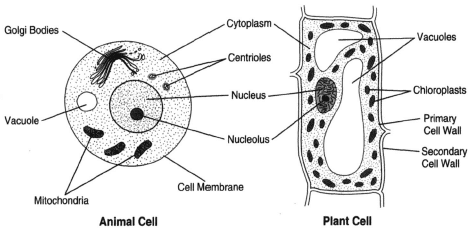
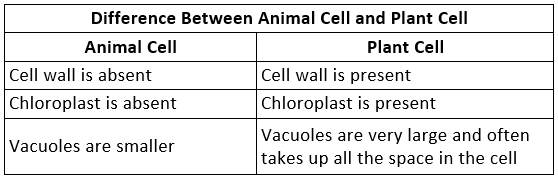
Q6. State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Ans: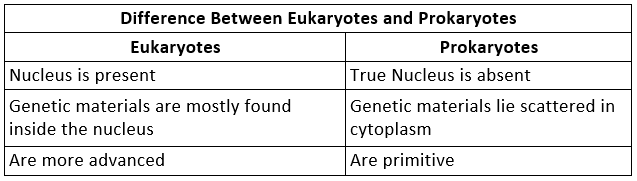
Q7. Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their function.
Ans.
- Chromosomes are found inside the nucleus of a typical cell.
- Chromosomes contain genes that are carriers of genetic information.
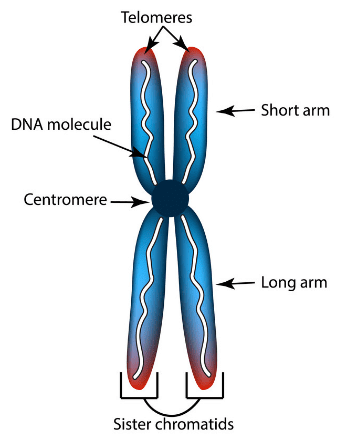 Chromosome
Chromosome
- Chromosomes govern distinct features of an organism.
- Chromosomes take part in cell division.
Q8. ‘Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms’. Explain.
Ans: Cells are the smallest units from which a living organism is made. A cell contains all the necessary structures required to carry out various biological processes. A group of cells forms a tissue, which further combines to create organs, ultimately resulting in a complete organism. Therefore, cells are referred to as the basic structural units of living organisms.
Q9. Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
Ans: Chloroplasts are a specific type of plastid that contain chlorophyll, the green pigment essential for photosynthesis. This process allows green plants to produce their own food using sunlight, which is why chloroplasts are present exclusively in plant cells. Chloroplasts play a crucial role in converting light energy into chemical energy, stored as glucose. Since this ability is vital for the survival of green plants, chloroplasts are not found in animal cells.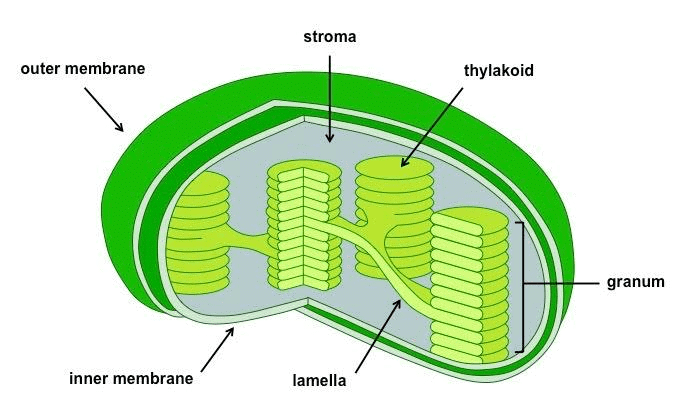 Structure of Chloroplast
Structure of Chloroplast
Q10. Complete the crossword with the help of clues given below:
Across-
1. This is necessary for photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the cell.
8. Units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down-
1. Green plastids.
2. Formed by a collection of tissues.
4. It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding medium.
5. Empty structure in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells.
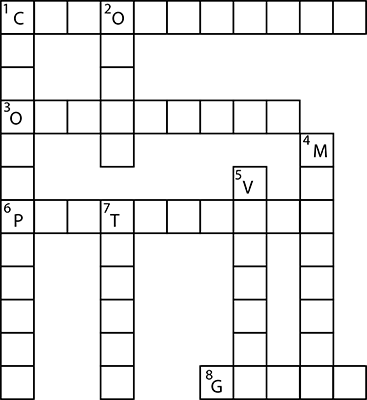 Ans:
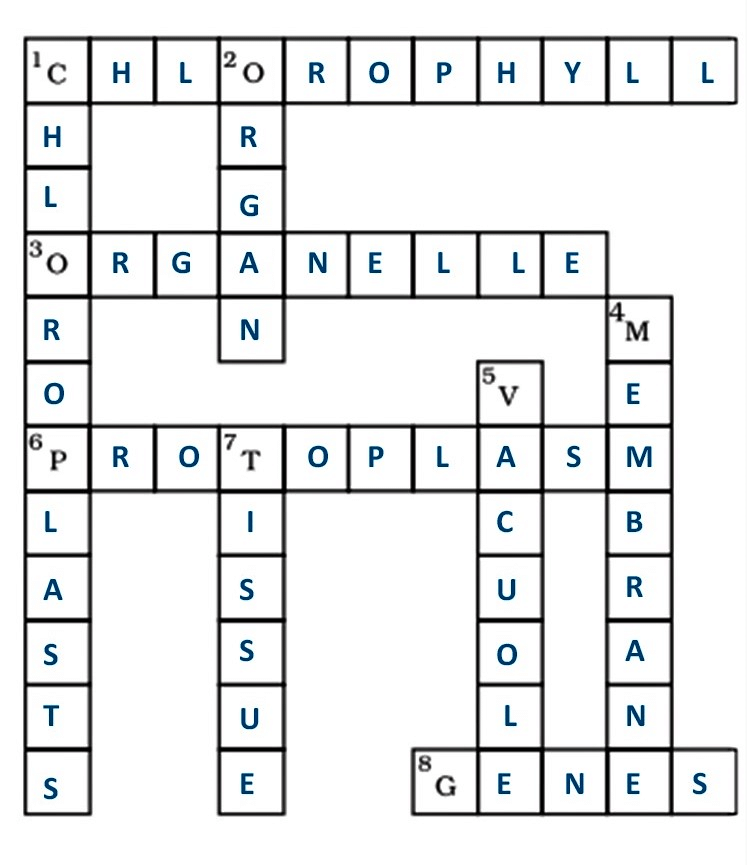
Ans:
Across:
1. Chlorophyll
3. Organelle
6. Protoplasm
8. Genes
Down:
1. Chloroplast
2. Organ
4. Membrane
5. Vacuole
7. Tissue
|
114 videos|534 docs|217 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Cell Structure and Functions
| 1. What is the cell theory? |  |
| 2. What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? |  |
| 3. What is the function of the cell membrane? |  |
| 4. What is the role of ribosomes in cells? |  |
| 5. What is the function of mitochondria in cells? |  |

















