Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Q1. What is electricity?
Ans: Electricity is a phenomenon known for its effect like chemical effect, Heating effect and magnetic effect.
Q2. What is the cause of electricity?
Ans: The flow of charge is the main cause of electricity.
Q3. What is charge?
Ans: The fundamental properties of matter caused by gain or loss of electrons.SI unit of charge is Coulomb or C.
Q4. Why is electroplating done?
Ans: To protect materials from corrosion, improve appearance, and enhance properties.
Q5. Define an electrode.
Ans: It is a conductor that carries current into non-metals or poor conductors.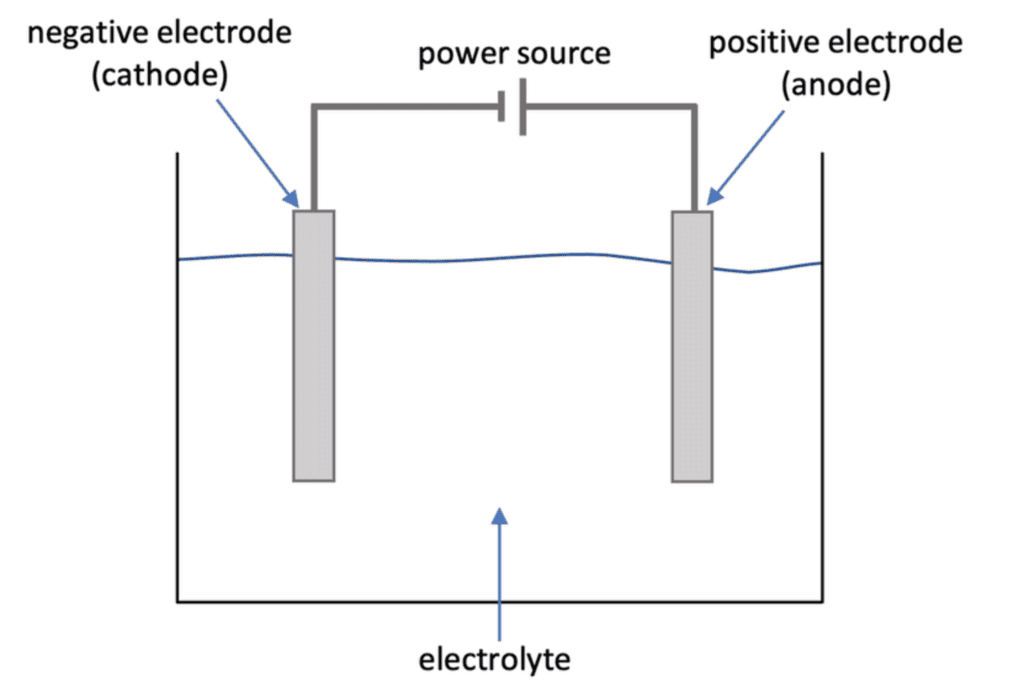
Q6. Name two metals commonly used for electroplating.
Ans: Chromium and zinc are commonly used.
Q7. Name two good conductors of electricity.
Ans: Copper and aluminium are good conductors.
Q8. What do you mean by chemical effect of current?
Ans: The phenomenon of causing chemical change by passing electric current through a conduction solution is called chemical effect of current. For example: Electrolysis and Electroplating
Q9. What do you mean by heating effect of current?
Ans: Whenever current flows through a conductor it causes heating of material. This effect of current is known as heating effect of current.
Q10. What do you mean by magnetic effect of current?
Ans: Whenever current flows through a conductor it behaves like a magnet. This effect of current is known as magnetic effect of current.
Q11. What is LED?
Ans: LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. It emits light when a small electric current passes through it.
Q12. What precaution you should take to add LED in a circuit?
Ans: The longer lead is always connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the shorter lead is connected to the negative terminal of the battery.
Q13. What are good conductors?
Ans. The materials which allow electric current to pass through them are called good conductors of the electricity.
Q14. Give two examples of good conductors of electricity.
Ans. Copper, iron.
Q15. Why is it dangerous to touch an electrical appliance with wet hands?
Ans. Wet hands act as good conductors. So we feel electric shocks when we touch electric appliance with wet hands.
Q16. What are insulators (poor conductors) of electricity?
Ans. The materials which do not allow electric current to pass through them are called poor conductors.
Q17. Give two examples of poor conductors of electricity.
Ans. Dry wood, rubber.
Q18. What is electric current?
Ans. The flow of charges (electricity) is called electric current.
Q19. Do liquids conduct electricity?
Ans. Yes, liquids conduct electricity.
Q20. How can you check current?
Ans. We check current by using tester.
Q21. Give any liquid conductor.
Ans. Tap water.
Q22. Can distilled water conduct electricity?
Ans. No, distilled water cannot conduct electricity.
Q23. How can we test that liquids conduct electricity?
Ans. We use tester to check that the liquids conduct electricity.
Q24. Name some substances which make the liquids good conductor of electricity.
Ans. Acids, Bases and Salts.
Q25. Name two liquid substances other than water which conduct electricity.
Ans. (i) Lemon Juice (ii) Vinegar.
Q26. Sometimes even though the liquid is conducting, the bulb may not glow. Give reason.
Ans. Sometimes the bulb does not glow because the current through it is too weak to make the bulb glow.
Q27. Which effect of current causes the bulb to glow?
Ans. Heating effect of current causes the bulb to glow.
Q28. Name the part of bulb which glows.
Ans. Filament.
Q29. What are insulators?
Ans. They are substances that do not allow electric current to pass through them.
Q30. Why is chromium plating popular?
Ans. It gives a shiny, corrosion-resistant, and scratch-resistant surface.
Q31. What are the three effects of electric current?
Ans. There are three effects of electric current—heating, magnetic and the chemical effect.
Q32. What is magnetic effect of electric current?
Ans. The electric current also produces the magnetic effect by which a current carrying wire behaves like a magnet.
Q33 What happens when a compass needle is brought near a wire in which current is flowing?
Ans. The needle deflects.
Q34. How can we check magnetic effects of current?
Ans. By using magnetic compass.
Q35. Does distilled water conduct electricity?
Ans. No, distilled water does not conduct electricity.
Q36. How can we make distilled water a good conductor of electricity?
Ans. By adding some salt in distilled water.
Q37. What is distilled water?
Ans. The water which is free of salts is called distilled water.
Q38. Name a salt which makes distilled water a good conductor of electricity.
Ans. Common salt.
Q39. Why are tin cans used for storing food?
Ans. Tin is less reactive than iron, preventing food from spoiling.
Q40. Name the gases which release when current is passed through water.
Ans. Hydrogen and oxygen.
Q41. Name the gas deposited on negative electrode.
Ans. Hydrogen.
Q42. Name the gas deposited on a positively charged electrode.
Ans. Oxygen.
Q43. Name the process that shows the chemical effect of electricity.
Ans. Electroplating.
Q44. Define electroplating.
Ans. The coating of a layer of desired metal on other metallic surface by passing electric current is called electroplating.
Q45. Is air a conductor or an insulator?
Ans. Insulator.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Chemical Effects of Electric Current
| 1. What is the chemical effect of electric current? |  |
| 2. What is an electrolyte? |  |
| 3. What is electroplating? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between an anode and a cathode? |  |
| 5. What is the application of chemical effects of electric current in our daily life? |  |

















