Heat Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 3
| Table of contents |

|
| Hot and Cold |

|
| Types of Thermometer |

|
| Transfer of Heat |

|
| Kinds of Clothes We Wear in Summer and Winter |

|
| Important Terms: |

|
Hot and Cold
Hot : An object or environment is described as "hot" when it has high temperature, often significantly higher than the surrounding environment or the human body's normal temperature (37ºC or 98.6ºF).
Cold: An object or environment is described as "cold" when it has low temperature, often significantly lower than the surrounding environment or the human body's normal temperature.
Understanding Temperature
Heat is the movement of energy from something hot. We can use our sense of touch to feel how hot or cold something is, but this isn't always accurate. To measure temperature reliably, we use a device called a thermometer.
Scales to measure heat:
- There are three common scales to measure temperature: Degree Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
- Degree Celsius: Written as °C, for example, 20°C is read as twenty degrees Celsius.
- Fahrenheit: Written as °F, for example, 25°F is read as twenty-five degrees Fahrenheit.
- Kelvin: Written as K, for example, 100K is read as one hundred Kelvin.
Thermometers
Thermometer:. clinical thermometer is a long, narrow glass tube with a bulb at one end that contains mercury. You can see a small shiny thread of mercury outside the bulb. If it’s not visible, turn the thermometer slightly until you can see it. The scale used is the Celsius scale, marked by °C.
A clinical thermometer measures temperatures from 35°C to 42°C. Since mercury is toxic and hard to dispose of if the thermometer breaks, digital thermometers that do not use mercury are now available.
Types of Thermometer
Laboratory Thermometer: Laboratory thermometer is used to measure the temperature. The scale of temperature is graduated generally from –10°C to 110°C over the glass tube. Each division of temperature scale is further divided into 10 parts to read fraction of temperature.
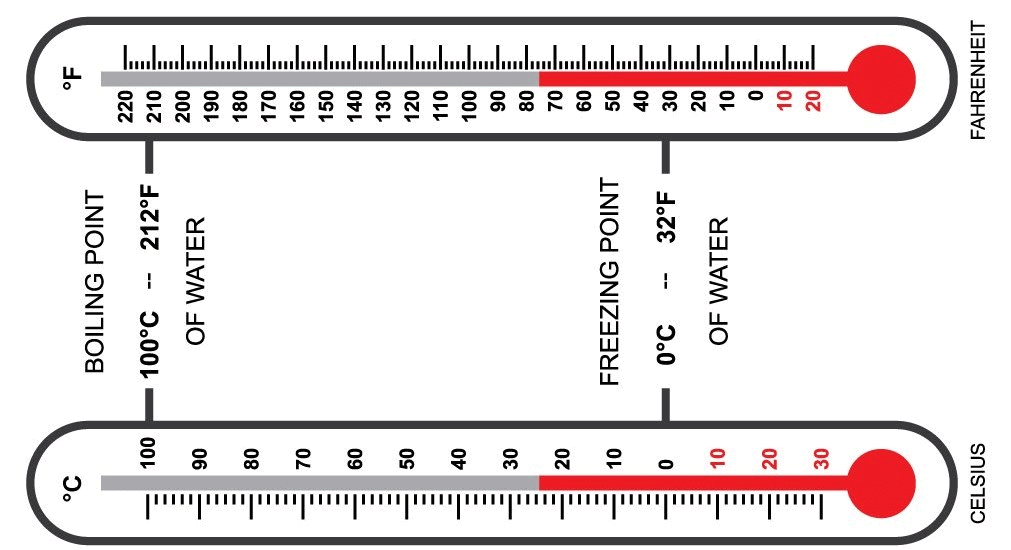 Celsius and Fahrenheit Thermometer
Celsius and Fahrenheit Thermometer
Clinical Thermometer: This thermometer is specifically for measuring body temperature. It usually has a scale from 35°C to 42°C or 94°F to 108°F, which covers the normal range of human body temperature. The average body temperature for a healthy adult is about 37°C (98.6°F), but it may vary slightly for different individuals. There is a kink near the bulb of the clinical thermometer that stops the mercury from falling back automatically. Do not use a clinical thermometer to measure the temperature of anything other than the human body.
Digital Thermometer:. digital thermometer shows the temperature reading on a digital display, similar to a digital watch. This type is considered safer because it does not contain mercury, which is hazardous and difficult to dispose of if a thermometer breaks.
Maximum-Minimum Thermometer: This thermometer is used to record daily temperatures for weather reporting.
Measuring Temperature and Reading a Thermometer
- Hold the thermometer in your hand and look at it closely.
- The thermometer should be cleaned before and after use, preferably with an antiseptic solution.
- Ensure the mercury level is below 35°C before using it.
- Do not grip the thermometer by the bulb.
- Gently rotate the thermometer clockwise and anticlockwise; this will display a shiny silvery thread.
- Read the thermometer at eye level with the mercury line.
- Hold it steady and give it a few taps; this will lower the mercury level below 35°C.
- Place the bulb under your tongue and wait for one minute.
- After one minute, remove the thermometer and check the reading; this shows your body temperature.
- The normal body temperature is around 37°C, but this can vary from person to person.
- Handle the thermometer carefully as it can break if dropped.
- Always state the temperature with its unit, °C.
Use of Laboratory Thermometer
- Fill a beaker or mug with tap water.
- Take a laboratory thermometer and hold it vertically in the water, ensuring that the bulb does not touch the bottom or sides of the beaker and is surrounded by water.
- Watch the mercury in the thermometer. Wait until the mercury stabilises, then read the temperature.
- Next, fill another beaker or mug with hot water. Dip the thermometer in and wait for the mercury to stabilise before noting the temperature.
Difference between Clinical and Laboratory Thermometer
Clinical Thermometer | Laboratory Thermometer |
Clinical thermometer is scaled from 35°C to 42°C or from 94° F to 108°F | Laboratory thermometer is generally scaled from -10°C to 110ºC |
Mercury level does not fall on its own, as there is a kink near the bulb to prevent the fall of mercury level. | Mercury level falls on its own as no kink is present. |
Temperature can be read after removing the thermometer from armpit or mouth. | Temperature is read while keeping the thermometer in the source, such as liquid or anything. |
To lower the mercury level jerks are given. | No need to give jerk to down the mercury level, automatically. |
Clinical thermometer is used to take the body temperature. | Laboratory thermometer is used to take the temperature in laboratory. |
Transfer of Heat
Heat moves in three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. In solids, heat moves through conduction. In liquids and gases, it moves through convection. Radiation can occur without any medium.
Conduction
Transfer of heat from one particle to the adjacent particle is known as conduction of heat. In solids, heat is transferred by the process of conduction. In this process, the transfer of heat takes place through adjacent molecules.
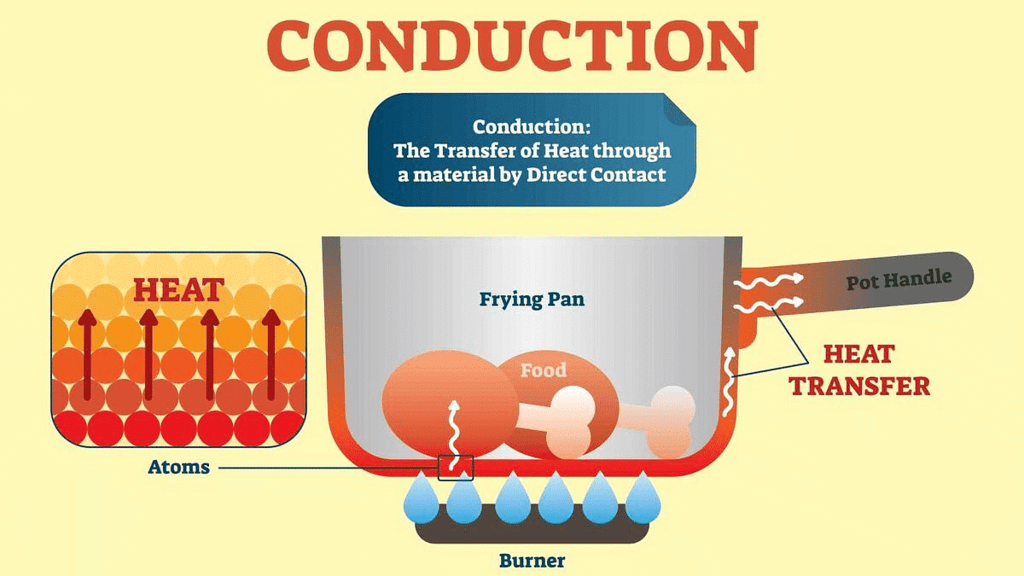
Example: When one end of an iron rod is put over flame then part which is nearer to the flame is heated first and heat is gradually transferred to the other end of the rod. This happens because particles of iron rod which are nearer to the flame receive the heat and transfers this to the adjacent particles.
Subsequently, the adjacent particles transfer the heat to the next adjacent particles. This process continues and heat reaches to the other end of the rod. Thus, heat transfer in solid takes place through conduction.
Conductor and Insulator:
Materials which allow heat to pass through it are called conductor or good conductor of heat, such as iron, copper, aluminium, etc. All metals are good conductors of heat. Since, mercury is a metal and found in liquid state at room temperature, that’s why it is used in thermometer.
Since metals are the good conductor of heat that’s why kitchen utensils are made of metals or alloys of metals (mixture of two or more elements with at least one being a metal).
Materials which do not allow heat to pass through them are called bad conductor or poor conductor of heat. They are also called insulators. Example: rubber, wood, plastic, etc. This is the cause that handles of frying pan or other kitchen utensils are made of plastic.
Convection
The transfer of heat because of movement of the molecules of the medium; via mass transfer; is called convection or convection of heat.
Water and air are bad conductors of heat. But they do become hot, in spite of being bad conductors. Heat transfer in fluids takes place through convection.
Convection in water: When water is heated in a pan, the particles of water which are near the source of heat; get heated first. Because of heating, they become light; and rise in water. The gap which is created because of rise of hot particles is filled cold particles of water from the surrounding area.
Thus a cyclical movement of particles begins and ends up heating the whole water of the pan. The cyclical movement in fluids because of heating is called convection current.
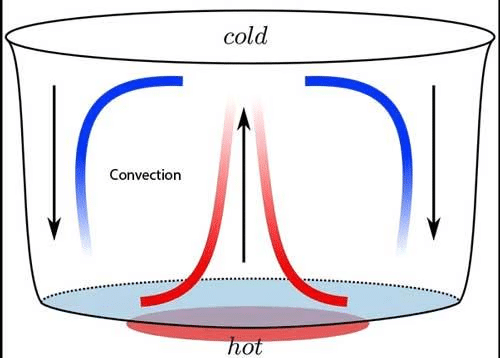
Convection in air: Air gets heated because of convection; the way water gets heated. Air near the source of heat gets heated and rises above. This leaves a gap; which is filled by the colder air from the surrounding. The convection current thus starts in air which results in heating up of air.
When you place your palm above a flame you will feel the hotness of the flame. But when you will place your palm below the flame the area will be colder. This shows how the colder air from below moves up; due to convection current.
Land and Sea Breeze
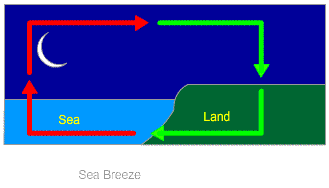
Sea Breeze: In coastal areas, the breeze that moves from sea surface to the land is called sea breeze. This happens because, during daytime, land gets heated more quickly than water. As a result, warm air from land rises up; leaving a gap.
To fill that gap, colder air from the ocean surface rushes towards the land. This phenomenon continues and a continuous flow of cold air keeps coming towards the land. This gives rise to the phenomenon which is called the sea breeze. Because of this, people living in coastal areas prefer to live in a sea facing house.
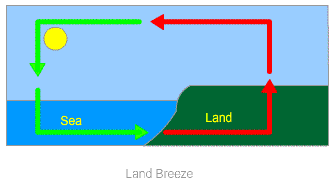
 Land Breeze: In coastal areas, the breeze which moves from land towards the sea is called land breeze. At night, the land cools down more quickly than the ocean surface. This makes the air over the water surface warmer than air over the land surface.
Land Breeze: In coastal areas, the breeze which moves from land towards the sea is called land breeze. At night, the land cools down more quickly than the ocean surface. This makes the air over the water surface warmer than air over the land surface.
Warmer air over the water surface rises in the air and air from the land rushes towards the water surface to fill the gap. This phenomenon continues which creates a flow of air from land to the sea. This phenomenon is called land breeze.
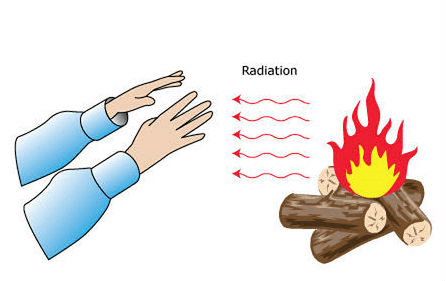
Radiation
All hot objects release heat through radiation. This process occurs regardless of whether there is a medium present. For instance, sunlight reaches the Earth via radiation.
- We feel warmth from a room heater due to radiation.
- A hot utensil placed away from a flame cools down as it gives off heat to the surroundings through radiation.
- Our bodies also emit heat to the environment and absorb heat from it through radiation.
Kinds of Clothes We Wear in Summer and Winter
When heat strikes an object, some of it is absorbed while the rest is reflected. An object's temperature rises due to the absorption of heat.
- A conventional room heater has a reflector that directs heat towards a person nearby.
- Reflection is why we use an umbrella to shield ourselves from the sun's heat in summer.
- Dark surfaces absorb more heat, so we prefer dark-coloured clothes in winter.
- In contrast, light-coloured clothes are better for summer as they reflect most of the heat.
In winter, dark clothes absorb more heat and keep us warm. Light clothes reflect heat and keep us cool in summer. Woollen clothes are ideal for winter because wool is a poor conductor of heat.
- Air trapped between wool fibres prevents heat from escaping our bodies to the cold surroundings.
- This is why we feel warm when wearing wool.
Overall, dark-coloured objects absorb more heat than light-coloured ones.
Woolen Clothes keep us Warm in Winter
Woolen clothes are used in winter season. Wool is a poor conductor of heat. In addition to it; air gets trapped in woolen fiber to further increase the poor conductivity of wool. This prevents the radiation of heat of our body to the surrounding and prevents the cold from surrounding to affect our body. Thus, wearing woolen cloth makes one comfortable in winter season.
Important Terms:
- Temperature:. measure of how hot or cold something is.
- Thermometer:. tool used to measure temperature.
- Degree Celsius:. unit for measuring temperature.
- Clinical Thermometer: This device measures human body temperature, typically from 35°C to 42°C.
- Laboratory Thermometer: Used to measure temperatures in labs, usually from -10°C to 110°C.
- Maximum-Minimum Thermometer:. thermometer that tracks the highest and lowest temperatures in the environment.
- Conduction: The way heat moves through solids.
- Convection: The method of heat transfer in liquids and gases.
- Radiation: The transfer of heat without needing a medium.
- Conductor: Materials that easily allow heat to pass through them.
- Insulator: Materials that do not allow heat to pass through them.
- Land breeze:. breeze that blows from the land to the sea during summer nights.
- Sea breeze:. breeze that flows from the sea to the land during summer days.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Heat Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 3
| 1. What are the different types of thermometers used to measure temperature? |  |
| 2. How does heat transfer occur between objects? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of clothes we wear in summer to keep cool? |  |
| 4. How do hot and cold temperatures affect our bodies? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of understanding heat in everyday life? |  |
















