NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Soil
Ques1: In addition to the rock particles, the soil contains
(i) air and water
(ii) water and plants
(iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water
(iv) water, air and plants
Ans: (iii) minerals organic matter, air and water
Ques2: The water holding capacity is the highest in
(i) sandy soil
(ii) clayey soil
(iii) loamy soil
(iv) mixture of sand and loam
Ans: (ii) Clayey soil
Ques3: Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
Column A | Column B |
(i) A home for living organisms | (a) Large particles |
(ii) Upper layer of the soil | (b) All kinds of soil |
(iii) Sandy soil | (c) Dark in colour |
(iv) Middle layer of the soil | (d} Small particles and packed tight |
(v) Clayey soil | (e) Lesser amount of humus |
Answer -
Column A | Column B |
(i) A home for living organisms | (b) All kinds of soil |
(is) Upper layer of the soil | (c) Dark in colour |
(iii j Sandy soil | (a) Large particles |
(ivj Middle layer of the soil | (e} Lesser amount of humus |
(v) Clayey soil | (d) Small particles and packed tight |
Ques4: Explain how soil is formed.
Ans: Soil is formed by the process of weathering. The breaking down of rocks because of the action of wind, rain, ice, etc. is called weathering.
Ques5: How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Ans: Clayey soil can retain much water and consequently contains lot of moisture even in summer. That’s why it is most useful for crops like paddy which requires lot of water. Clayey soil is useful for wheat also.
Ques6: List the differences between clayey soil and sandy soil.
Ans:
Difference between Clayey and Sandy Soil | |
Clayey Soil | Sandy Soil |
Particles are of very small size | Particles are of quite large size |
Particles are tightly packed together | Particles are not closely packed |
Not aerated enough | Well aerated |
Can retain water for long time | Cannot hold water |
Water does not drain easily | Water drains easily |
Fertile | Not fertile |
Suitable for many crops | Not suitable for crops |
Ques7: Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers.
Ans:
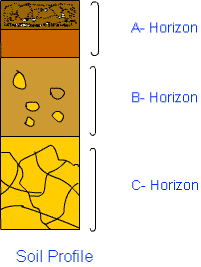
Ques8: Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation. She observed that it took 40 min for 200 mL of water to percolate through the soil sample. Calculate the rate of percolation.
Ans:
Given, Time = 40 minute
VolumeVolume of water = 200 ml
Ques9: Explain how soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented.
Ans: Soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented using following:
Plantation
Better farming method, like crop rotation and mixed farming
Use of manure instead of synthetic fertilization.
Use of natural pesticides.
Avoid dumping non-biodegradable items in soil.
Terrace farming in hilly areas.
Ques10: Solve the following crossword puzzle with the clues given:
Across
2. Plantation prevents it.
5. Use should be banned to avoid soil pollution.
6. Type of soil used for making pottery.
7. Living organism in the soil.
Down
1. In desert soil erosion occurs through.
3. Clay and loam are suitable for cereals like.
4. This type of soil can hold very little water.
5. Collective name for layers of soil.
Ans:
|
113 videos|527 docs|217 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Soil
| 1. What is soil erosion? |  |
| 2. How does soil conservation help in maintaining soil fertility? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of soil? |  |
| 4. How does soil pollution affect human health? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of soil testing? |  |

















