Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 8
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Reproduction? |

|
| Types of Reproduction |

|
| 2. Sexual Reproduction |

|
| Pollination |

|
| Fertilization |

|
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is a key feature of all living things, allowing them to create new individuals from their parents. In plants, reproduction can take place in different ways, which are grouped into asexual and sexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction, new plants grow from seeds.
Types of Reproduction
1. Asexual Reproduction
This process allows plants to produce offspring without seeds, involving methods like vegetative propagation (using plant parts such as roots, stems, leaves, and buds) or When a single parent is involved in the process, it is called asexual reproduction.Following means of asexual reproduction are used by plants:
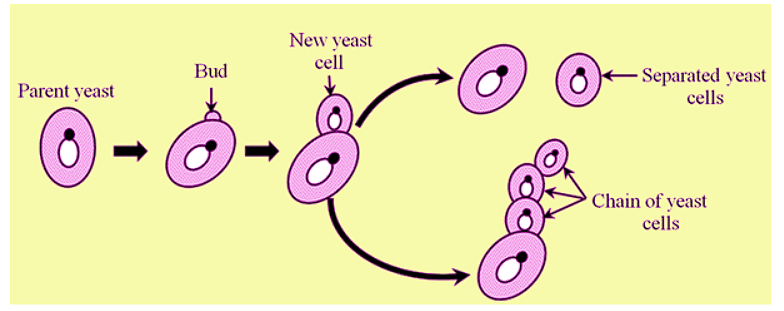
(a) Budding: This method is used by unicellular plants; like yeast. Yeast is a fungus and fungi are also known as non-green plants. The yeast cell produces a bud which gets its own nucleus. The bud develops to certain size and detaches from the mother cell to produce the new yeast.
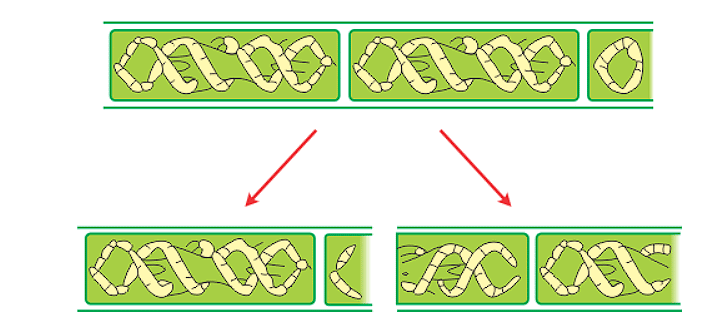
(b)Fragmentation: In some simple plants, the plant body is divided into smaller fragments. Each fragment then develops into a new plant. Example: Spirogyra.
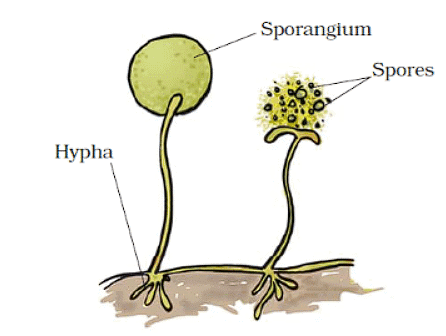
(c) Spore Formation: Special spore-bearing organs are present in some plants; especially in fungi and algae. These are called sporangiophores. The sporangiophore bears spores. The spores germinate to develop a new plant.
(d) Vegetative Propagation: When a new plant is developed by a vegetative part; such as root, stem or leaf; it is known as vegetative propagation. For example: when the tuber of potato is cut into several pieces and each piece bears an ‘eye’; each piece produces a new plant. The stems of moneyplant, rose, mango, etc. can produce new plants when they are inserted in soil. The leaf of bryophyllum produces new plants through its notches.
2. Sexual Reproduction
When two parents are involved in the process, it is known as sexual reproduction. Two types of gametes are produced: male and female. The joining of male and female gametes is called fertilisation. The fertilised egg is known as a zygote, which later develops into an embryo. The mature ovary is referred to as the fruit, while the ovule becomes a seed that contains the developing embryo.
A flower can contain either male or female reproductive parts, which is termed unisexual.
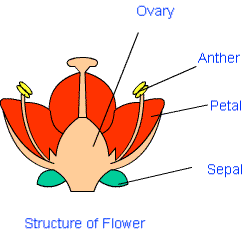
Flower: Flower is a special organ of flowering plants (angiosperms) which works as the reproductive system. A flower is composed of four distinct whorls.
(1) The outermost whorl is called calyx. It is composed of green leaf-like structures; called sepals.
(2) The second whorl is called corolla. It is composed of colourful structures; called petals. Petals are colourful so that insects and other animals can be attracted towards them. This is necessary for pollination.
(3) Androecium: The third whorl is called androecium. It is composed of stamens. Stamen has two main parts. The tube-like portion is called filament. The capsule like structure at the top is called anther. The anther produces pollen grains; which are the male gametes.
(4) Gynoecium: The whorl at the center is called gynoecium. It has a swollen base; called ovary and a tube-like structure; called style. The top of the tube is somewhat flattened and is called stigma. Ovary produces the eggs or female gametes.
Pollination
The movement of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma is referred to as pollination. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. This process occurs in plants with assistance from wind, water, and insects.
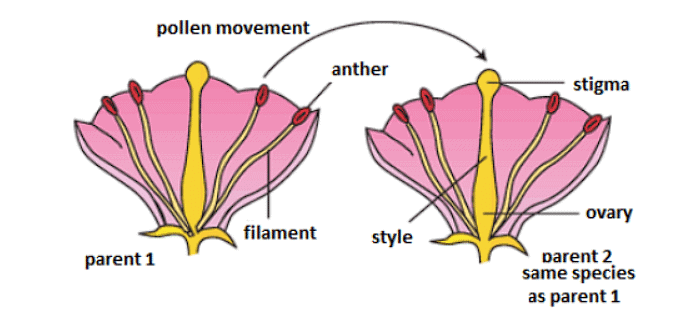
Self Pollination: When anthers of the same flower are transferred to the stigma; it is called self pollination.
Cross Pollination: When anthers from a different flower are transferred to the stigma; it is called cross pollination. The flowers can be on the same plant or on different plants. Cross pollination is the norm in most of the plants. Plants need help from various agents of pollination to carry out cross pollination. Wind, insects, birds and other animals play the role of agent of pollination.
Fertilization
The fusion of the male gamete and the female gamete is called fertilization. When pollen settles on top of the stigma, it germinates to produce a pollen tube. The pollen tube enters the ovary through the style. Male nuclei are transferred to the ovary, through the pollen tube
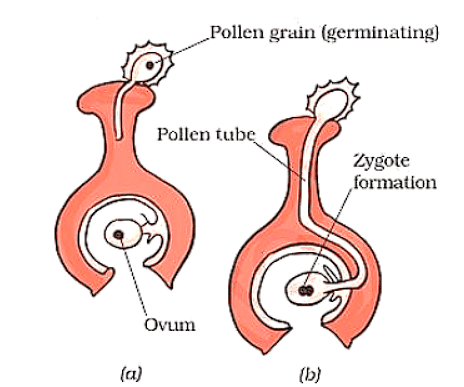 FertilizationThe cell formed, just after fertilization, is called zygote. Zygote develops into embryo. Each embryo develops into a seed. The seed is an embryo which is enclosed in a protective coat. The ovary gets transformed into fruit.
FertilizationThe cell formed, just after fertilization, is called zygote. Zygote develops into embryo. Each embryo develops into a seed. The seed is an embryo which is enclosed in a protective coat. The ovary gets transformed into fruit.
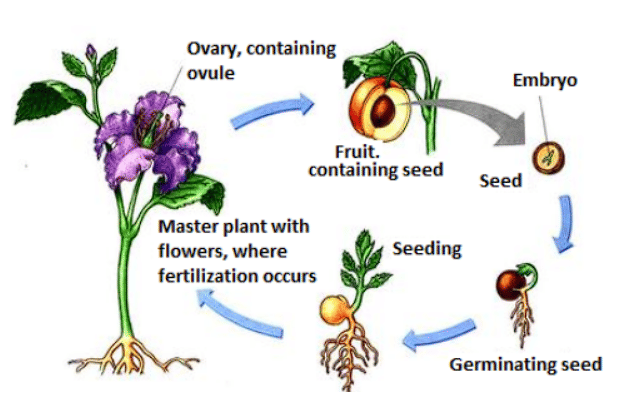
Fruits and Seed Formation
After fertilization, the ovary transforms into a fruit, and the other parts of the flower fall off. The fruit is the mature ovary. The ovules develop into seeds. The seed contains an embryo protected by a seed coat. Some fruits are soft and juicy, like mangoes and oranges, while others are hard, like almonds.
Seed Disprersal
Have you ever wondered why seeds need to spread out? Imagine if all the seeds from a plant fell and grew in the same spot. There would be intense competition among the plants for sunlight, water, minerals, and space. This competition would hinder the healthy growth of the plants.
1. Dispersal by Wind: Seeds of some plants are light-weight and some hair-like or wing-like structures are present on them. Such seeds float on air and are thus dispersed by wind. Example: Dandelion, maple, drumstick, etc.
2. Dispersal by Water: Dispersal by water takes place in some aquatic plants and in some which grow near a water body. Seeds of water lily float and thus dispersed by water. The coconut seed has a tough fibrous covering which has plenty of air inside. This helps the coconut seeds in floating on water.
3. Dispersal by Animals: Some seeds have spine like structures on them. They get stuck to the fur of animals and thus get spread to different places. Examples; Beggar tick, Xanthium, Urena, etc. Some seeds are swallowed by birds and animals along with fruits. These seeds get dispersed with bird or animal droppings.
4. Dispersal by Bursting: Some fruits burst open when they mature. The force of bursting is enough to spread the seeds. Examples; Ladyfinger, castor, balsam, etc.
5. Dispersal by Humans: Human beings also help in dispersal of seeds, especially during farming.
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 8
| 1. What is the difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction in plants? |  |
| 2. How does pollination occur in plants? |  |
| 3. What is fertilization in plants and how does it happen? |  |
| 4. Why is genetic variation important in plant reproduction? |  |
| 5. How do plants ensure successful reproduction through pollination and fertilization? |  |
















